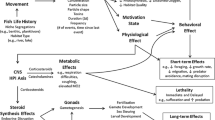
Abstract
Atrazine has been shown to affect freshwater snails from the subcellular to community level. However, most studies have used different snail species, methods, endpoints, and atrazine exposure concentrations, resulting in some conflicting results and limiting our understanding. The goal of this study was to address these concerns by (1) investigating the acute and chronic effects of atrazine on four species of freshwater snails (Biomphalaria glabrata, Helisoma trivolvis, Physa acuta, and Stagnicola elodes) using the same methods, endpoints, and concentrations, and (2) summarizing the current literature pertaining to the effects of atrazine on freshwater snails. We conducted a 48 h acute toxicity test with an atrazine concentration higher than what typically occurs in aquatic environments (1000 µg/L). Additionally, we exposed snails to environmentally relevant atrazine concentrations (0, 0.3, 3, and 30 µg/L) for 28 days and assessed snail survival, growth, and reproduction. We also summarized all known literature pertaining to atrazine effects on freshwater snails. The literature summary suggests snails are often affected by environmentally relevant atrazine concentrations at the subcellular and cellular levels. These effects are typically not transitive to effects on survival, growth, or reproduction at the same concentrations. Our acute exposures corroborate the general trend of no direct effect on snail populations as atrazine did not directly affect the survival of any of the four snail species. Similarly, environmentally relevant concentrations did not significantly affect the survival, growth, or reproduction of any snail species. These results indicate that, in the absence of other possible stressors, the direct effects of environmentally relevant atrazine concentrations may not be realized at the snail population level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso A, Camargo JA (2003) Short-term toxicity of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate to the aquatic snail Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Hydrobiidae, Mollusca). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:1006–1012. doi:10.1007/s00128-003-0082-5
Arthur J, West C, Allen K, Hedtke S (1987) Seasonal toxicity of ammonia to five fish and nine invertebrate species. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 38:324–331. doi:10.1007/BF01606682
Barky FA, Abdelsalam HA, Mahmoud MB, Hamdi SAH (2012) Influence of atrazine and Roundup pesticides on biochemical and molecular aspects of Biomphalaria alexandrina snails. Pestic Biochem Physiol 104:9–18. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2012.05.012
Baturo W, Lagadic L (1996) Benzo[a]pyrene hydroxylase and glutathione S-transferase activities as biomarkers in Lymnaea palustris (Mollusca, Gastropoda) exposed to atrazine and hexachlorobenzene in freshwater mesocosms. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:771–781. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<0771:baphag>2.3.co;2
Baturo W, Lagadic L, Caquet T (1995) Growth, fecundity and glycogen utilization in Lymnaea palustris exposed to atrazine and hexachlorobenzene in freshwater mesocosms. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:503–511. doi:10.1002/etc.5620140320
Baxter LR, Moore DL, Sibley PK, Soloman KR, Hanson ML (2011) Atrazine does not affect algal biomass of snail populations in microcosm communities at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:1689–1696. doi:10.1002/etc.552
Baxter LR, Moore DL, Sibley PK, Solomon KR, Hanson ML (2012) The herbicide atrazine, algae, and snail populations reply. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:974–976. doi:10.1002/etc.1797
Baxter LR, Sibley PK, Solomon KR, Hanson ML (2013) Interactions between atrazine and phosphorus in aquatic systems: effects on phytoplankton and periphyton. Chemosphere 90:1069–1076. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.09.011
Bluzat R, Jonot O, Lespinasse G, Seuge J (1979) Chronic toxicity of acetone in the fresh water snail Lymnea stagnalis. Toxicology 14:179–190. doi:10.1016/0300-483X(79)90063-5
Boerger H (1975) A comparison of the life cycles, reproductive ecologies, and size–weight relationships of Helisoma anceps, H. campanulatum, and H. trivolvis (Gastropoda, Planorbidae). Can J Zool 53:1812–1824. doi:10.1139/z75-215
Bolek MG, Janovy J Jr (2007) Evolutionary avenues for, and constraints on, the transmission of frog lung flukes (Haematoloechus spp.) in dragonfly second intermediate hosts. J Parasitol 93:593–607. doi:10.1645/GE-1011R.1
Brown KM (1979) The adaptive demography of four freshwater pulmonate snails. Evolution 33:417–432. doi:10.2307/2407631
Brown KM (1982) Resource overlap and competition in pond snails: an experimental analysis. Ecology 63:412–422. doi:10.2307/1938959
Burch JB (1989) North American freshwater snails. Malacological Publications, Hamburn
Clampitt PT (1970) The comparative ecology of the snails Physa gyrina and Physa integra (Basommatophora: physidae). Malacologia 10:113–151
Daszak P, Cunningham AA, Hyatt AD (2001) Anthropogenic environmental change and the emergence of infectious diseases in wildlife. Acta Trop 78:103–116. doi:10.1016/s0001-706x(00)00179-0
Dillon RT (2000) The ecology of freshwater molluscs. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gerard C, Poullain V (2005) Variation in the response of the invasive species Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Smith) to natural (cyanobacterial toxin) and anthropogenic (herbicide atrazine) stressors. Environ Pollut 138:28–33. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.02.028
Graymore M, Stagnitti F, Allinson G (2001) Impacts of atrazine in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Int 26:483–495. doi:10.1016/s0160-4120(01)00031-9
Gustafson KD, Bolek MG (2015) Tradeoff between establishing an infection and killing the host: response of snails (Physa acuta) to a gradient of trematode (Halipegus eccentricus) exposures. J Parasitol 101:104–107. doi:10.1645/14-563.1
Gustafson KD, Kensinger BJ, Bolek MG, Luttbeg B (2014) Distinct snail (Physa) morphotypes from different habitats converge in shell shape and size under common garden conditions. Evol Ecol Res 16:77–89
Huber W (1993) Ecotoxicological relevance of atrazine in aquatic systems. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1865–1881. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1993)12[1865:eroaia]2.0.co;2
Hutchinson T, Shillabeer N, Winter M, Pickford D (2006) Acute and chronic effects of carrier solvents in aquatic organisms: a critical review. Aquat Toxicol 76:69–92. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.09.008
Johnson PTJ, Chase JM, Dosch KL, Hartson RB, Gross JA, Larson DJ, Sutherland DR, Carpenter SR (2007) Aquatic eutrophication promotes pathogenic infection in amphibians. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:15781–15786. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707763104
Koprivnikar J, Walker PA (2011) Effects of the herbicide atrazine’s metabolites on host snail mortality and production of trematode cercariae. J Parasitol 97:822–827. doi:10.1645/ge-2814.1
Lévêque C, Pointier J (1976) Study of the growth of Biomphalaria glabrata (Say) and other Planorbidae in Guadalupe (West Indies). Ann Trop Med Parasitol 70:199–204
Mona MH, Gaafar RM, Helal IB, Omran NE, Salama WM (2013) Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of atrazine and glyphosate herbicides on Biomphalaria glabrata snails. J Basic Appl Zool 66:68–75. doi:10.1016/j.jobaz.2013.05.004
Muñoz I, Real M, Guasch H, Navarro E, Sabater S (2001) Effects of atrazine on periphyton under grazing pressure. Aquat Toxicol 55:239–249. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(01)00179-5
Omran NE, Salama WM (2013) The endocrine disrupter effect of atrazine and glyphosate on Biomphalaria alexandrina snails. Toxicol Ind Health. doi:10.1177/0748233713506959
Pointier JP (1999) Invading freshwater gastropods: some conflicting aspects for public health. Malacologia 41:403–411
Rittschof D, McClellan-Green P (2005) Molluscs as multidisciplinary models in environment toxicology. Mar Pollut Bull 50:369–373. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.02.008
Rohr JR, Crumrine PW (2005) Effects of an herbicide and an insecticide on pond community structure and processes. Ecol Appl 15:1135–1147. doi:10.1890/03-5353
Rohr JR, McCoy KA (2010) A qualitative meta-analysis reveals consistent effects of atrazine on freshwater fish and amphibians. Environ Health Perspect 118:20–32. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901164
Rohr JR, Raffel TR, Sessions SK, Hudson PJ (2008a) Understanding the net effects of pesticides on amphibian trematode infections. Ecol Appl 18:1743–1753. doi:10.1890/07-1429.1
Rohr JR, Schotthoefer AM, Raffel TR, Carrick HJ, Halstead N, Hoverman JT, Johnson CM, Johnson LB, Lieske C, Piwoni MD, Schoff PK, Beasley VR (2008b) Agrochemicals increase trematode infections in a declining amphibian species. Nature 455:1235–1239. doi:10.1038/nature07281
Rohr JR, Halstead NT, Raffel TR (2012) The herbicide atrazine, algae, and snail populations. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:973–974. doi:10.1002/etc.1796
Rosés N, Poquet M, Muñoz I (1999) Behavioural and histological effects of atrazine on freshwater molluscs (Physa acuta Drap. and Ancylus fluviatilis Mull. Gastropoda). J Appl Toxicol 19:351–356. doi:10.1002/(sici)1099-1263(199909/10)19:5<351:aid-jat588>3.0.co;2-h
Russo J, Lagadic L (2000) Effects of parasitism and pesticide exposure on characteristics and functions of hemocyte populations in the freshwater snail Lymnaea palustris (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Cell Biol Toxicol 16:15–30. doi:10.1023/A:1007640519746
Russo J, Lagadic L (2004) Effects of environmental concentrations of atrazine on hemocyte density and phagocytic activity in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Environ Pollut 127:303–311. doi:10.1016/s0269-7491(03)00269-0
Russo J, Madec L, Brehélin M (2009) Haemocyte lysosomal fragility facing an environmental reality: a toxicological perspective with atrazine and Lymnaea stagnalis (Gastropoda, Pulmonata) as a test case. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1719–1726. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.05.015
Sandland GJ, Carmosini N (2006) Combined effects of a herbicide (Atrazine) and predation on the life history of a pond snail, Physa gyrina. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2216–2220. doi:10.1897/05-596r.1
Sawasdee B, Köhler H-R (2009) Embryo toxicity of pesticides and heavy metals to the ramshorn snail, Marisa cornuarietis (Prosobranchia). Chemosphere 75:1539–1547. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.085
Shoop WL (1988) Trematode transmission patterns. J Parasitol 74:46–59. doi:10.2307/3282478
Solomon KR, Baker DB, Richards RP, Dixon DR, Klaine SJ, LaPoint TW, Kendall RJ, Weisskopf CP, Giddings JM, Giesy JP, Hall LW, Williams WM (1996) Ecological risk assessment of atrazine in North American surface waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:31–74. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<0031:eraoai>2.3.co;2
Solomon KR, Carr JA, Du Preez LH, Giesy JP, Kendall RJ, Smith EE, Van Der Kraak GJ (2008) Effects of atrazine on fish, amphibians, and aquatic reptiles: a critical review. Crit Rev Toxicol 38:721–772. doi:10.1080/10408440802116496
Streit B, Peter HM (1978) Long-term effects of atrazine to selected freshwater invertebrates. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie Suppl 55:62–77
Strong EE, Gargominy O, Ponder WF, Bouchet P (2008) Global diversity of gastropods (Gastropoda; Mollusca) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595:149–166. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-9012-6
Thorp JH, Covich AP (2009) Ecology and classification of North American freshwater invertebrates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Van Der Kraak GJ, Hosmer AJ, Hanson ML, Kloas W, Solomon KR (2014) Effects of atrazine in fish, amphibians, and reptiles: an analysis based on quantitative weight of evidence. Crit Rev Toxicol 44:1–66. doi:10.3109/10408444.2014.967836
Acknowledgments
We thank Rachel Eguren and Wade Arthur for assistance with acute toxicity tests and snail husbandry. We thank Ben Hanelt (UNM) for providing Biomphalaria glabrata snails for our laboratory cultures and Cedar Point Biological Station for laboratory space during our collections of S. elodes. Finally, we thank two anonymous reviewers for providing helpful comments which greatly improved the manuscript. This Project was partially funded by two Southwestern Association of Parasitologists student research grants, one American Society of Parasitologists student research grant, and a National Academy of Sciences Ford Foundation Dissertation Fellowship awarded to KDG, and by a National Science Foundation grant (DEB-0949951) awarded to MGB.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gustafson, K.D., Belden, J.B. & Bolek, M.G. The effects of the herbicide atrazine on freshwater snails. Ecotoxicology 24, 1183–1197 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1469-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1469-x