Abstract
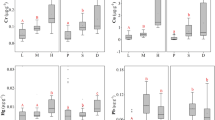
Heavy metal pollution in marine fish has become an important worldwide concern, not only because of the threat to fish in general, but also due to human health risks associated with fish consumption. To investigate the occurrence of heavy metals in marine fish species from the South China Sea, 14 fish species were collected along the coastline of Hainan China during the spring of 2012 and examined for species- and tissue-specific accumulation. The median concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Zn, Pb and As in muscle tissue of the examined fish species were not detectable (ND), 2.02, 0.24, 2.64, 0.025, and 1.13 mg kg−1 wet weight, respectively. Levels of Cu, Zn, Cd and Cr were found to be higher in the liver and gills than in muscle, while Pb was preferentially accumulated in the gills. Differing from other heavy metals, As did not exhibit tissue-specific accumulation. Inter-species differences of heavy metal accumulation were attributed to the different habitat and diet characteristics of marine fish. Human dietary exposure assessment suggested that the amounts of both Cr and As in marine wild fish collected from the sites around Hainan, China were not compliant with the safety standard of less than 79.2 g d−1 for wild marine fish set by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Further research to identify the explicit sources of Cr and As in marine fish from South China Sea should be established.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilandžić N, Đokić M, Sedak M (2011) Metal content determination in four fish species from the Adriatic Sea. Food Chem 124:1005–1010
Burger J, Gaines KF, Shane Boring C, Stephens WL, Snodgrass J, Dixon C, McMahon M, Shukla S, Shukla T, Gochfeld M (2002) Metal levels in fish from the Savannah River: potential hazards to fish and other receptors. Environ Res 89:85–97
Canli M, Atli G (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121:129–136
Celik U, Oehlenschlager J (2007) High contents of cadmium, lead, zinc and copper in popular fishery products sold in Turkish supermarkets. Food Control 18:258–261
Cheung KC, Leung HM, Wong MH (2008) Metal concentrations of common freshwater and marine fish from the Pearl River Delta, South China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:705–715
Copat C, Bella F, Castaing M, Fallico R, Sciacca S, Ferrante M (2012) Heavy metals concentrations in fish from Sicily (Mediterranean Sea) and evaluation of possible health risks to consumers. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:78–83
Costa OTF, Fernandez MN (2002) Chloride cell changes induced by nitrite exposure in an Amazonian fish species. In: Kennedy C, Kolok A, MacKinlay D (eds) Aquatic toxicology: mechanism and consequences. International Congress of Fish Biology, Canada
Dalman O, Demirak A, Balci A (2006) Determination of heavy metals (Cd, Pb) and trace elements (Cu, Zn) in sediments and fish of the Southeastern Aegean Sea (Turkey) by atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 95:157–162
de Mora S, Fowler SW, Wyse E, Azemard S (2004) Distribution of heavy metals in marine bivalves, fish and coastal sediments in the Gulf and Gulf of Oman. Mar Pollut Bull 49:410–424
Ebrahimpour M, Pourkhabbaz A, Baramaki R, Babaei H, Rezaei M (2011) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in freshwater fish species Anzali, Iran. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87:386–392
EC (2006) European Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs, OJ, L364/5
FAO (2012) Part 1: World review of fisheries and aquaculture. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture
FAO (2013) Fishery and aquaculture country profiles: China
FAO/WHO (2010) Evaluations of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). International programme on chemical safety
Gu DF, He J, Duan XF, Reynolds K, Wu X, Chen J, Whelton PK (2006) Body weight and mortality among men and women in China. J Am Med Assoc 295:776–783
Hillwalker WE, Jepson PC, Anderson KA (2006) Selenium accumulation patterns in lotic and lentic aquatic systems. Sci Total Environ 366:367–379
Ip CCM, Li XD, Zhang G, Wong CSC, Zhang WL (2005) Heavy metal and Pb isotopic compositions of aquatic organisms in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ Pollut 138:494–504
Liu JL, Xu XR, Yu S, Cheng HF, Hong YG, Feng XB (2014a) Mercury pollution in fish from South China Sea: Levels, species-specific accumulation, and possible sources. Environ Res 131:160–164
Liu JL, Wu H, Feng JX, Li ZJ, Lin GH (2014b) Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessments in the sediments and zoo benthos of selected mangrove ecosystems, South China. Catena 119:136–142
MOH (2012) China’s Ministry of Health. Maximum levels of contaminants in seafood. GB2762-2012
Monikh FA, Safahieh A, Savari A, Ronagh MT, Doraghi A (2013) The relationship between Heavy metal (Cd Co, Cu, Ni and Pb) levels and the size of benthic, benthopelagic and pelagic fish species, Persian Gulf. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90:691–696
NBO (2012) National Bureau of Oceanography of China. Bulletin of Marine Environmental Quality
Pan K, Wang WX (2012) Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:3–16
Pintaeva ET, Bazarsadueva SV, Pertov EA, Smirnova OG (2011) Content and character of metal accumulation in fish of the Kichera River (a tributary of Lake of Baikal). Contemp Probl Ecol 4:64–68
Ptashynski MD, Pedlar RM, Evans RE, Baron CL, Klaverkamp JF (2002) Toxicology of dietary nickel in lake whitefish (Coregonus clupeaformis). Aquat Toxicol 58:229–247
Qiu YW, Yu KF, Zhang G, Wang WX (2011) Accumulation and partitioning of seven trace metals in mangroves and sediment cores from three estuarine wetlands of Hainan Island, China. J Hazard Mater 190:631–638
Rahman MS, Molla AH, Saha N, Rahman A (2012) Study on heavy metals levels and its risk assessment in some edible fishes from Bangshi River, Savar, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Food Chem 134:1847–1854
Tapia J, Vargas-Chacoff L, Bertran C, Pena-Cortes F, Hauenstein E, Schlatter R, Jimenez C, Tapia C (2012) Heavy metals in the liver and muscle of Micropogonias manni fish from Budi Lake, Araucania Region, Chile: potential risk for humans. Environ Monit Assess 184:3141–3151
Türkmen M, Türkmen A, Tepe Y, Töre Y, Ateş A (2009) Determination of metals in fish species from Aegean and Mediterranean seas. Food Chem 113:233–237
Tuzen M (2003) Determination of heavy metals in fish samples of the middle Black Sea (Turkey) by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 80:119–123
USEPA (2005) Risk-based concentration table, 2005. Region 3, Philadelphia
USFDA (1993) Guidance document for arsenic in shellfish center for food safety and applied nutrition. Washington, DC
Uysal K, Köse E, Bülbül M, Dönmez M, Erdogan Y, Koyun M, Ömeroglu Ç, Özmal F (2009) The comparison of heavy metal accumulation ratios of some fish species in Enne Dame Lake (Kutahya/Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 157:355–362
Vane CH, Harrison I, Kim AW, Moss-Hayes V, Vikers BP, Hong K (2009) Organic and metal contamination in surface mangrove sediments of South China. Mar Pollut Bull 58:134–144
Vaseem H, Banerjee TK (2013) Contamination of metals in different tissues of Rohu (Labeo rohita, Cyprinidae) collected from the Indian River Ganga. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:36–41
Wang WX, Rainbow PS (2008) Comparative approaches to understand metal bioaccumulation in aquatic animals. Comp Biochem Physiol: Part C 148:315–323
Wang SL, Xu XR, Sun YX, Liu JL, Li HB (2013) Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: A review. Mar Pollut Bull 76:7–15
Widianarko B, Van Gestel CAM, Verwejj RA, Van Straalen NM (2000) Associations between trace metals in sediment, water, and guppy, Poecilia reticulate (Peters), from urban streams of Semarang, Indonesia. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:101–107
Xia N, Xue G, Fu Y, Yang Y, Liu C, Ma R (2011) Analysis of ecological risk and the content situation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hainan Island’s inshore. Resour Environ Eng 25:244–247 (in Chinese)
Yang B, Pan XH, Li YZ, Chen YQ, Zhai FY (2009) Survey of dietary patterns and nutrients intake status of residents in Hainan. China Trop Med 9:1673–1692 (in Chinese)
Yi YJ, Zhang SH (2012) Heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn) concentrations in seven fish species in relation to fish size and location along the Yangtze River. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:3989–3996
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159:2575–2585
Zhang L, Wang WX (2007) Size-dependence of the potential for metal biomagnification in early life stages of marine fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:787–794
Zhang W, Wang WX (2012) Large-scale spatial and interspecies differences in trace elements and stable isotopes in marine wild fish from Chinese waters. J Hazard Mater 215–216:65–74
Zhao S, Feng C, Quan W, Chen X, Niu J, Shen Z (2012) Role of living environments in the accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in fishes and crabs in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1163–1171
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2012M510201), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41176090; 51378488), and Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences to Dr. X.R. Xu. We also thank Dr. Chris C. Feng for his help in revising the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled, “Heavy metals in wild marine fish from South China Sea: Levels, tissue- and species-specific accumulation and potential risk to humans”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JL., Xu, XR., Ding, ZH. et al. Heavy metals in wild marine fish from South China Sea: levels, tissue- and species-specific accumulation and potential risk to humans. Ecotoxicology 24, 1583–1592 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1451-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1451-7