Abstract
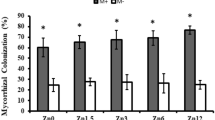
The effects of three arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi isolates on Cd uptake and accumulation by maize (Zea mays L.) were investigated in a planted pot experiment. Plants were inoculated with Glomus intraradices, Glomus constrictum and Glomus mosseae at three different Cd concentrations. The results showed that root colonization increased with Cd addition during a 6-week growth period, however, the fungal density on roots decreased after 9-week growth in the treatments with G. constrictum and G. mosseae isolates. The percentage of mycorrhizal colonization by the three arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi isolates ranged from 22.7 to 72.3 %. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculations decreased maize biomass especially during the first 6-week growth before Cd addition, and this inhibitory effect was less significant with Cd addition and growth time. Cd concentrations and uptake in maize plants increased with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonization at low Cd concentration (0.02 mM): nonetheless, it decreased at high Cd concentration (0.20 mM) after 6-week growth period. Inoculation with G. constrictum isolates enhanced the root Cd concentrations and uptake, but G. mosseae isolates showed the opposite results at high Cd concentration level after 9 week growth period, as compared to non-mycorrhizal plants. In conclusion, maize plants inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi were less sensitive to Cd stress than uninoculated plants. G. constrictum isolates enhanced Cd phytostabilization and G. mosseae isolates reduced Cd uptake in maize (Z. mays L.).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrasco L, Azcón R, Kohler J, Roldán A, Caravaca F (2011) Comparative effects of native filamentous and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the establishment of an autochthonous, leguminous shrub growing in a metal-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 409:1205–1209
Chen BD, Li XL, Tao HQ, Christie P, Wong MH (2003) The role of arbuscular mycorrhiza in zinc uptake by red clover growing in a calcareous soil spiked with various quantities of zinc. Chemosphere 50:839–846
Chen BD, Liu Y, Shen H, Li XL, Christie P (2004) Uptake of cadmium from an experimentally contaminated calcareous soil by arbuscular mycorrhizal maize (Zea mays L.). Mycorrhiza 14(6):347–354
Citterio S, Prato N, Fumagalli P, Aina R, Massa N, Santagostino A, Sgorbati S, Berta G (2005) The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae induces growth and metal accumulation changes in Cannabis sativa L. Chemosphere 59(1):21–29
de Andrade SA, da Silveira AP, Jorge RA (2008) Cadmium accumulation in sunflower plants influenced by arbuscular mycorrhiza. Int J Phytoremediation 10(1):1–13
Garg N, Bhandari P (2012) Influence of cadmium stress and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nodule senescence in Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. Int J Phytoremediation. 14:62–74
Gaur A, Adholeya A (2004) Prospects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Current Sci. 86:528–534
Glassman SI, Casper BB (2012) Biotic contexts alter metal sequestration and AMF effects on plant growth in soils polluted with heavy metals. Ecology 93:1550–1559
Göhre V, Paszkowski U (2006) Contribution of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis to heavy metal phytoremediation. Planta 223:1115–1122
González-Chávez MC, Carrillo-González R, Wright SF, Nichols KA (2004) The role of glomalin, a protein produced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, in sequestering potentially toxic elements. Environ Pollut 130(3):317–323
Guo Y, George E, Marschner H (1996) Contribution of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus to the uptake of cadmium and nickel in bean and maize plants. Plant Soil 184:195–205
Huang H, Zhang S, Chen BD, Wu N, Shan XQ, Christy P (2006) Uptake of atrazine and cadmium from soil by maize (Zea mays L.) in association with the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus etunicatum. J Agric Food Chem 54(25):9377–9382
Jankong P, Visoottiviseth P (2008) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation on plants growing on arsenic contaminated soil. Chemosphere 72:1092–1097
Janousková M, Pavlíková D, Vosátka M (2006) Potential contribution of arbuscular mycorrhiza to cadmium immobilisation in soil. Chemosphere 65:1959–1965
Koske RE, Gemma JN (1989) A modified procedure for staining roots to detect VA mycorrhizas. Mycol Res 92:486–505
Leung HM, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2007) Survival strategies of plants associated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on toxic mine tailings. Chemosphere 66(5):905–915
Leung HM, Wu FY, Cheung KC, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2010) Synergistic effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate rock on heavy metal uptake and accumulation by an arsenic hyperaccumulator. J Hazard Mater 181:497–507
Liang CC, Li T, Xiao YP, Liu MJ, Zhang HB, Zhao ZW (2009) Effects of inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on maize grown in multi-metal contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediation 11(8):692–703
Liao JP, Lin XG, Cao ZH, Shi YQ, Wong MH (2003) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizae and heavy metals under sand culture experiment. Chemosphere 50(6):847–853
Liu LZ, Gong ZQ, Zhang YL, Li PJ (2011) Growth, cadmium accumulation and physiology of marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) under the effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Pedosphere 21:319–327
Luis MC, Isabel CM, Amélia M (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance root cadmium and copper accumulation in the roots of the salt marsh plant Aster tripolium L. Plant Soil 285:161–169
Miransari M (2011) Hyperaccumulators, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and stress of heavy metals. Biotechnol Adv 29:645–653
Paul-Olivier R, Thierry B, Corinne L (2008) Influence of Glomus intraradices on Cd partitioning in a pot experiment with Medicago truncatula in four contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2710–2712
Pawlowska TE, Charvat I (2004) Heavy-metal stress and developmental patterns of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(11):6643–6649
Rashid A, Ayub N, Ahmad T, Gul J, Khan AG (2009) Phytoaccumulation prospects of cadmium and zinc by mycorrhizal plant species growing in industrially polluted soils. Environ Geochem Health 31(1):91–98
Shen H, Christie P, Li X (2006) Uptake of zinc, cadmium and phosphorus by arbuscular mycorrhizal maize (Zea mays L.) from a low available phosphorus calcareous soil spiked with zinc and cadmium. Environ Geochem Health 28:111–119
Tang M, Chen H, Huang JC (2009) AM fungi effects on the growth and physiology of Zea mays seedlings under diesel stress. Soil Biol Biochem 41:936–940
Tonin C, Wandenkoornhuyse P, Joner EJ, Straczk EJ, Leyval C (2001) Assessment of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi diversity in the rhizosphere of Viola calaminearia and effect of these fungi on heavy metal uptake by clover. Mycorrhiza 10:161–168
Veresoglou SD, Menexes G, Rillig MC (2012) Do arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affect the allometric partition of host plant biomass to shoots and roots? A meta-analysis of studies from 1990 to 2010. Mycorrhiza 22:227–235
Vogel-Mikus K, Pongrac P, Kump P, Necemer M, Regvar M (2006) Colonisation of a Zn, Cd and Pb hyperaccumulator Thlaspi praecox Wulfen with indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal mixture induces changes in heavy metal and nutrient uptake. Environ Pollut 139(2):362–371
Wang FY, Lin XG, Yin R (2007a) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculation on heavy metal accumulation of maize grown in a naturally contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediation 9(4):345–353
Wang FY, Lin XG, Yin R (2007b) Role of microbial inoculation and chitosan in phytoextraction of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd by Elsholtzia splendens—a field case. Environ Pollut 147(1):248–255
Weissenhorn I, Leyval C (1995) Root colonization of maize by a Cd-sensitive and a Cd-tolerance Glomus mosseae and cadmium uptake in sand culture. Plant Soil 175:233–238
Xu P, Christie P, Liu Y, Zhang J, Li X (2008) The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae can enhance arsenic tolerance in Medicago truncatula by increasing plant phosphorus status and restricting arsenate uptake. Environ Pollut 156:215–220
Zarei M, Hempel S, Wubet T, Schäfer T, Savaghebi G, Jouzani GS, Nekouei MK, Buscot F (2010) Molecular diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in relation to soil chemical properties and heavy metal contamination. Environ Pollut 158:2757–2765
Zhang XH, Zhu YG, Chen BD (2005) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi contribute to resistance of upland rice to combined metal contamination of soil. J Plant Nutr 28:2065–2077
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from NSFC (40930739 and 31101504) and Ministry of Environmental Protection of China, and arbuscular mycorrhizal isolates provided by Prof. Y. S. Wang (Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry, China) are gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Gong, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. Growth, cadmium uptake and accumulation of maize (Zea mays L.) under the effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecotoxicology 23, 1979–1986 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1331-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1331-6