Abstract
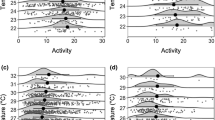
Mercury is a heavy metal that has contaminated countless ecosystems throughout the world. A large body of literature has documented reproductive, physiological, and behavioral impairments associated with mercury exposure in laboratory settings, but whether and how such effects are manifest in free-living populations remains poorly understood. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether tree swallow (Tachycineta bicolor) breeding success at a site with high mercury exposure varied with ambient temperature or precipitation at various points in the breeding cycle. Tree swallows nesting along the South River had significantly elevated blood total mercury (mean ± SE: 3.03 ± 0.15 μg/g) compared to swallows breeding on reference sites (mean ± SE: 0.16 ± 0.005 μg/g). These high levels of mercury were associated with reduced hatching and fledging success, and contaminated birds produced approximately one less fledgling per nest than their reference counterparts. The magnitude of this difference was weather-dependent: unusually high ambient temperatures encountered early in the nestling period were associated with reduced reproductive output in contaminated, but not in reference, birds. In contrast, little effect of mercury on success of nestlings was observed when temperatures were cooler, and precipitation also had no detectable interaction with mercury. These results provide insight into mechanisms underlying reproductive effects of mercury. In addition, these findings underscore the importance of considering variable environmental conditions when assessing effects of contaminants on free-living wildlife. In particular, projections about the effects of global climate change on ecotoxicological impacts must take into account the kinds of weather-mediated effect demonstrated here.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelier F, Chastel O (2010) Stress, prolactin, and parental investment in birds: a review. Gen Comp Endocrinol 163:142–148. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.03.028
Ardia DR, Wasson MF, Winkler DW (2006a) Individual quality and food availability determine yolk and egg composition in tree swallows Tachycineta bicolor. J Avian Biol 37:252–259. doi:10.1111/j.2006.0908-8857.03624.x
Ardia DR, Cooper CB, Dhondt AD (2006b) Warm temperatures lead to early onset of incubation, shorter incubation periods and greater hatching asynchrony in tree swallows Tachycineta bicolor at the extremes of their range. J Avian Biol 37:137–142. doi:10.1111/j.0908-8857.2006.03747.x
Brasso RL, Cristol DA (2008) Effects of mercury exposure on the reproductive success of tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor). Ecotoxicology 17:133–141. doi:10.1007/s10646-007-0163-z
Brasso RL, Abdel Latif MK, Cristol DA (2010) Relationship between laying sequence and mercury concentration in tree swallow eggs. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:1155–1159. doi:10.1002/etc.144
Carter LJ (1977) Chemical plants leave unexpected legacy for two Virginia rivers. Science 198:1015–1020. doi:10.1126/science.198.4321.1015
Cocking D, Hayes R, King ML, Rohrer MJ, Thomas R, Ward D (1991) Compartmentalization of mercury in biotic components of terrestrial flood plain ecosystems adjacent to the South River at Waynesboro, VA. Water Air Soil Pollut 57:159–170. doi:10.1007/BF00282879
Cornell KL, Donovan TM (2010) Effects of spatial habitat heterogeneity on habitat selection and annual fecundity for a migratory forest songbird. Landscape Ecol 25:109–122. doi:10.1007/s10980-009-9405-1
Cristol DA, Brasso RL, Condon AM, Fovargue RE, Friedman SL, Hallinger KK, Monroe AP, White AE (2008) The movement of aquatic mercury through terrestrial food webs. Science 320:335. doi:10.1126/science.1154082
Custer CM, Custer TW, Dummer PM, Munney KL (2003) Exposure and effects of chemical contaminants on tree swallows nesting along the Housatonic River, Berkshire County, Massachusetts, USA, 1998–2000. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1605–1621. doi:10.1002/etc.5620220725
Dawson RD (2008) Timing of breeding and environmental factors as determinants of reproductive performance of tree swallows. Can J Zool 86:843–850. doi:10.1139/Z08-065
Debonne M, Baarendse PJJ, Van den Brand H, Kemp B, Bruggeman V, Decuypere E (2008) Involvement of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis and its interaction with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in the ontogeny of avian thermoregulation: a review. World’s Poult Sci J 64:309–321. doi:10.1017/S0043933908000056
Evers DC, Burgess NM, Champoux L, Hoskins B, Major A, Goodale WM, Taylor RJ, Poppenga R, Daigle T (2005) Patterns and interpretation of mercury exposure in freshwater avian communities in northeastern North America. Ecotoxicology 14:193–221. doi:10.1007/s10646-004-6269-7
Franceschini MD, Lane OP, Evers DC, Reed JM, Hoskins B, Romero LM (2009) The corticosterone stress response and mercury contamination in free-living tree swallows, Tachycineta bicolor. Ecotoxicology 18:514–521. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0309-2
Frederick P, Jayasena N (2010) Altered pairing behaviour and reproductive success in white ibises exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of methylmercury. Proc Roy Soc Lond B. doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.2189
Friedman SL, Brasso RL, Condon AM (2008) An improved simple nest-box trap. J Field Ornithol 79:99–101. doi:10.1111/j.1557-9263.2008.00150.x
Gentes M, Waldner C, Papp Z, Smits JEG (2006) Effects of oil sands tailings compounds and harsh weather on mortality rates, growth and detoxification efforts in nestling tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor). Environ Pollut 142:24–33. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.09.013
Gentes M, Whitworth TL, Waldner C, Fenton H, Smits JEG (2007) Tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor) nesting on wetlands impacted by oil sands mining are highly parasitized by the bird blow fly Protocalliphora spp. J Wildl Dis 43:167–178
Hallinger KK, Zabransky DJ, Kazmer KA, Cristol DA (2010) Birdsong differs between mercury-polluted and reference sites. Auk 127:156–161. doi:10.1525/auk.2009.09058
Hallinger KK, Cornell KL, Brasso RL, Cristol DA (2011) Mercury exposure and survival in free-living tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor). Ecotoxicology 20:39–46. doi:10.1007/s10646-010-0554-4
Hawley DM, Hallinger KK, Cristol DA (2009) Compromised immune competence in free-living tree swallows exposed to mercury. Ecotoxicology 18:499–503. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0307-4
Heinz G (1979) Methylmercury: reproductive and behavioral effects on three generations of mallard ducks. J Wildl Manag 43:394–401
Heinz GH, Hoffman DJ, Klimstra JD, Stebbins KR, Kondrad SL, Erwin CA (2009) Species differences in the sensitivity of avian embryos to methylmercury. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:129–138. doi:10.1007/s00244-008-9160
Hill EF, Henney CJ, Grove RA (2008) Mercury and drought along the lower Carson River, Nevada: II. Snowy egret and black-crowned night-heron reproduction on Lahontan Reservoir, 1997–2006. Ecotoxicology 17:117–131. doi:10.1007/s10646-007-0180-y
Hoffman D, Moore J (1979) Teratogenic effects of external egg applications of methylmercury in the mallard, Anas platyrhynchos. Teratology 20:453–462. doi:10.1002/tera.1420200315
Hoyt DF (1979) Practical methods of estimating volume and fresh weight of bird eggs. Auk 96:73–77
Jones J (2003) Tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor): a new model organism? Auk 120:591–599. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2003)120[0591:TSTBAN]2.0.CO;2
Lombardo MP (1994) Nest architecture and reproductive performance in tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor). Auk 111:814–824
Ludwig GX, Alatalo RV, Helle P, Lindén H, Lindström J, Siitari H (2006) Short- and long-term population dynamical consequences of asymmetric climate change in black grouse. Proc R Soc B 273:2009–2016. doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3538
Martin JM, Branch LC, Raid RN, Beyeler SC (2010) Temporal instability of agricultural habitat reduces reproductive success of barn owls (Tyto alba). Auk 127:909–916. doi:10.1525/auk.2010.09211
McCarty JP (1995) Effects of short-term changes in environmental conditions on the foraging ecology and reproductive success of tree swallows, Tachycineta bicolor. Dissertation, Cornell University
McCarty JP (2002) Use of tree swallows in studies of environmental stress. Rev Toxicol 4:61–104
McCarty JP, Secord AL (1999) Nest-building behavior in PCB-contaminated tree swallows. Auk 116:55–63
McCarty JP, Winkler DW (1999) Relative importance of environmental variables in determining the growth of nestling tree swallows Tachycineta bicolor. Ibis 141:286–296. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.1999.tb07551.x
Mengelkoch JM, Niemi GJ, Regal RR (2004) Diet of the nestling tree swallow. Condor 106:423–429. doi:10.1650/7341
Nooker JK, Dunn PO, Whittingham LA (2005) Effects of food abundance, weather, and female condition on reproduction in tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor). Auk 122:1225–1238. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2005)122[1225:EOFAWA]2.0.CO;2
North American Bluebird Society (2010) NABS nest box specifications. http://www.nabluebirdsociety.org/nestboxspecs.htm. Accessed 26 Aug 2010
Rimmer CC, Miller EK, McFarland KP, Taylor RJ, Faccio SD (2010) Mercury bioaccumulation and trophic transfer in the terrestrial food web of a montane forest. Ecotoxicology 19:697–709. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0443-x
Robertson RJ, Stutchbury BJ, Cohen RR (1992) Tree swallow (Tachycineta bicolor). In Poole A, Stettenheim P, Gill F (eds) The birds of North America, No. 11. The Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia, and the American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington. doi:10.2173/bna.11
Saino N, Romano M, Ambronsini R, Ferrari RP, Møller AP (2004) Timing of reproduction and egg quality covary with temperature in the insectivorous barn swallow, Hirundo rustica. Funct Ecol 18:50–57. doi:10.1046/j.0269-8463.2004.00808.x
Stephenson S, Hannon S, Proctor H (2009) The function of feathers in tree swallow nests: insulation or ectoparasite barrier? Condor 111:479–487. doi:10.1525/cond.2009.090074
Stutchbury BJ, Robertson RJ (1986) A simple trap for catching birds in nest boxes. J Field Ornithol 57:64–65
Stutchbury BJ, Robertson RJ (1988) Within-season and age-related patterns of reproductive performance in female tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor). Can J Zool 66:827–834. doi:10.1139/z88-122
United Nations Environment Programme (2002) Global Mercury Assessment. United Nations Environment Programme Chemicals, Geneva
Virginia Department of Environmental Quality (2008) South River/South Fork Shenandoah River mercury monitoring update for fish tissue. http://www.deq.state.va.us/export/sites/default/fishtissue/documents/2007_Fish_Hg_Results.pdf. Accessed 26 Aug 2010
Wada H, Cristol DA, McNabb FMA, Hopkins WA (2009) Suppressed adrenocortical responses and thyroid hormone levels in birds near a mercury-contaminated river. Environ Sci Technol 43:6031–6038. doi:10.1021/es803707f
Wiener JG, Krabbenhoft DP, Heinz GH, Scheuhammer AM (2003) Ecotoxicology of mercury. In: Hoffman DJ, Rattner BA, Burton GA Jr, Cairns J Jr (eds) Handbook of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 409–463
Zanette L, Clinchy M, Smith JNM (2006) Combined food and predator effects on songbird nest survival and annual reproductive success: results from a bi-factorial experiment. Oecologia 147:632–640. doi:10.1007/s00442-005-0330-y
Acknowledgments
We thank the South River Science Team, Alena Arkhipov, Rebecka Brasso, Kjärstin Carlson-Drexler, Anne Condon, Ollie Ehlinger, Rachel Fovargue, Scott Friedman, Dana Hawley, Mikaela Howie, Ravi Jefferson-George, Sean Koebley, Elizabeth Langer, Maryse Leandre, Kevin Lonabaugh, Tom Meier, Adrian Monroe, Roshan Patel, John Schmerfeld, Haruka Wada, Ariel White and the many cooperative landowners of the Shenandoah Valley for support during this extensive field study. Funding was provided by E. I. DuPont de Nemours and Company, The Virginia Society of Ornithology, The Association of Field Ornithologists, The American Ornithologists’ Union, The Office of Vice Provost for Research at the College of William and Mary, National Science Foundation Grant UBM 0436318, and the William and Mary Undergraduate Science Education and Research Program sponsored by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Two anonymous reviewers greatly improved an earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hallinger, K.K., Cristol, D.A. The role of weather in mediating the effect of mercury exposure on reproductive success in tree swallows. Ecotoxicology 20, 1368–1377 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0694-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0694-1