Abstract
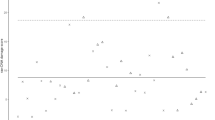
This study, performed at the behest of ranchers living and working down-prevailing wind from industrial facilities located in Calhoun County, Texas investigated locational risks to ecosystem health associated with proximity to specific industrial complexes. Concerns expressed were for potential genotoxicity in cattle resulting from the release of complex chemical mixtures. The Comet Assay and flow cytometric evaluation of variations in DNA content were utilized to evaluate DNA damage. Bayesian geo-statistical analysis revealed the presence of important spatial processes. The Comet assay’s optical density provided a strong indication of increased damage down-prevailing wind from the industrial complexes. Results indicated that proximity to and location down-prevailing winds from industrial facilities increased the locational risk of genotoxicity in this sentinel species.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
ArcGIS®Version 9.1, Environmental Systems Research Institute, Redlands, Ca.
ArcGIS®Version 9.1, Environmental Systems research Institute, Redlands, Ca.
References
Albertini RJ, Anderson D, Douglas GR, Hagmar L, Hemminki K, Merlo F et al (2000) IPCS guidelines for the monitoring of genotoxic effects of carcinogens in humans. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 463:111–172. doi:10.1016/S1383-5742(00)00049-1
Baciuchka-Palmaro A, Orsiere T, Duffaud F, Sari-Minodier I, Pompili J, Bellon L et al (2002) Acentrometric micronuclei are increased in peripheral blood lymphocytes of untreated cancer patients. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 520:189–198. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00206-1
Best N, Richardson S, Thomson A (2005) A comparison of Bayesian spatial models for disease mapping. Stat Methods Med Res 14:35–59. doi:10.1191/0962280205sm388oa
Bickham JW, Mazet JA, Blake J, Smolen MJ, Lou YG, Ballachey BE (1998) Flow cytometric determination of genotoxic effects of exposure to petroleum in mink and sea otters. Ecotoxicology 7:191–199. doi:10.1023/A:1008930626834
Biggeri A, Dreassi E, Catelan D, Rinaldi L, Lagazio C, Cringoli G (2006) Disease mapping in veterinary epidemiology: a Bayesian geostatistical approach. Stat Methods Med Res 15:337–352. doi:10.1191/0962280206sm455oa
Blasiak J, Jaloszynski P, Trzeciak A, Szyfter K (1999) In vitro studies on the genotoxicity of the organophosphorous insecticide malathion and its two analogues. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 445:275–283. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(99)00132-1
Blasiak J, Arabski M, Krupa R, Wozniak K, Rykala J, Kolacinska A et al (2004a) Basal, oxidative and alkylative DNA damage, DNA repair efficacy and mutagen sensitivity in breast cancer. Mutat Res Fund Mol Mech Mutagen 554:139–148. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.04.001
Blasiak J, Arabski M, Krupa R, Wozniak K, Zadrozny M, Kasznicki J et al (2004b) DNA damage and repair in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mutat Res Fund Mol Mech Mutagen 554:297–304. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.05.011
Boyd HA, Flanders WD, Addiss DG, Waller LA (2005) Residual spatial correlation between geographically referenced observations—a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach. Epidemiology 16:532–541. doi:10.1097/01.ede.0000164558.73773.9c
Chen XY, Li N, Shen L, Li YY (2003) Genetic structure along a gaseous organic pollution gradient: a case study with Poa annua L. Environ Pollut 124:449–455. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00042-3
Clark DR, Bickham JW, Baker DL, Cowman DF (2000) Environmental contaminants in Texas, USA, wetland reptiles: evaluation using blood samples. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2259–2265. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2000)019<2259:ECITUW>2.3.CO;2
Custer TW, Custer CM, Hines RK, Sparks DW, Melancon MJ, Hoffman DJ et al (2000) Mixed-function oxygenases, oxidative stress, and chromosomal damage measured in lesser scaup wintering on the Indiana Harbor Canal. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 38:522–529. doi:10.1007/s002449910068
Darzynkiewicz Z, Juan G (1997) DNA content measurements for DNA ploidy and cell cycle analysis. Current protocols in cytometry. Wiley, Hoboken NJ, pp 7.5.1–7.5.24
Diggle PJ, Ribeiro PJ (2007) Model-based geostatistics. Springer Science, New York, NY
Fairbairn DW, Olive PL, O’Neill KL (1995) The comet assay: a comprehensive review. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 339:37–59
Fernandez C, Green PJ (2002) Modelling spatially correlated data via mixtures: a Bayesian approach. J R Stat Soc B 64:805–826. doi:10.1111/1467-9868.00362
Formosa Plastics (2007) Our operations—point comfort, TX. Available: http://www.fpcusa.com/company/operations/point_comfort_tx.html. Accessed 15 November 2007
Frenzilli G, Nigro M, Scarcelli V, Gorbi S, Regoli F (2001) DNA integrity and total oxyradical scavenging capacity in the Mediterranean mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis: a field study in a highly eutrophicated coastal lagoon. Aquat Toxicol 53:19–32. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(00)00159-4
Gabelova A, Valovicova Z, Horvathova E, Slamenova D, Binkova B, Sram RJ et al (2004) Genotoxicity of environmental air pollution in three European cities: Prague, Kosice and Sofia. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 563:49–59. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2004.05.014
Janssen NAH, van Vliet PHN, Aarts F, Harssema H, Brunekreef B (2001) Assessment of exposure to traffic related air pollution of children attending schools near motorways. Atmos Environ 35:3875–3884. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00144-3
Lawson AB, Browne WJ, Vidal Rodeiro CL (2003) Disease mapping with WinBUGS and MLwiN. Wiley, Hoboken NJ
Lemiere S, Cossu-Leguille C, Bispo A, Jourdain MJ, Lanhers MC, Burnel D et al (2004) Genotoxicity related to transfer of oil spill pollutants from mussels to mammals via food. Environ Toxicol 19:387–395. doi:10.1002/tox.20045
Lowcock LA, Sharbel TF, Bonin J, Ouellet M, Rodrigie J, Desgranges J-L (1997) Flow cytometric assay for in vivo genotoxic effects of pesticides in Green frogs (Rana clamitans). Aquat Toxicol 38:241–255. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(96)00846-6
Marlin DJ, Johnson L, Kingston DA, Smith NC, Deaton CM, Mann S et al (2004) Application of the comet assay for investigation of oxidative DNA damage in equine peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Nutr 134:2133S–2140S
Matson CW, Franson JC, Hollmen T, Kilpi M, Hario M, Flint PL et al (2004) Evidence of chromosomal damage in common eiders (Somateria mollissima) from the Baltic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 49:1066–1071. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.07.014
Matson CW, Palatnikov G, Islamzadeh A, McDonald TJ, Autenrieth RL, Donnelly KC et al (2005a) Chromosomal damage in two species of aquatic turtles (Emys orbicularis and Mauremys caspica) inhabiting contaminated sites in Azerbaijan. Ecotoxicology 14:513–525. doi:10.1007/s10646-005-0001-0
Matson CW, Palatnikov GM, McDonald TJ, Autenrieth RL, Donnelly KC, Anderson TA et al (2005b) Patterns of genotoxicity and contaminant exposure: Evidence of genomic instability in the marsh frogs (Rana ridibunda) of Sumgayit, Azerbaijan. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2055–2064. doi:10.1897/04-250R1.1
Maywald LF (2001) Handbook of Texas online, s.v. The Texas State Historical Association. Available: http://www.tsha.utexas.edu/handbook/online/. Accessed 6 March 2007
Merk O, Speit G (1999) Detection of crosslinks with the comet assay in relationship to genotoxicity and cytotoxicity. Environ Mol Mutagen 33:167–172. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(1999)33:2<167::AID-EM9>3.0.CO;2-D
Nacci DE, Cayula S, Jackim E (1996) Detection of DNA damage in individual cells from marine organisms using the single cell gel assay. Aquat Toxicol 35:197–210. doi:10.1016/0166-445X(96)00016-1
Neuparth T, Bickham JW, Theodorakis CW, Costa FO, Costa MH (2006) Endosulfan-induced genotoxicity detected in the gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata, by means of flow cytometry and micronuclei assays. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 76:242–248. doi:10.1007/s00128-006-0913-2
Scott HM, Soskolne CL, Martin SW, Ellehoj EA, Coppock RW, Guidotti TL et al (2003) Comparison of two atmospheric-dispersion models to assess farm-site exposure to sour-gas processing-plant emissions. Prev Vet Med 57:15–34. doi:10.1016/S0167-5877(02)00207-6
Shugart L, Bickham JW, Jackim G, McMahon G, Ridley W, Stein J, et al. (1989) DNA alterations. In: Huggert R (ed) Biomarkers. Lewis Publishers, pp 125–153
Speit G, Schutz P, Merk O (2000) Induction and repair of formaldehyde-induced DNA-protein crosslinks in repair-deficient human cell lines. Mutagenesis 15:85–90. doi:10.1093/mutage/15.1.85
Spiegelhalter DJ, Best N, Carlin BP, van der Linde A (2002) Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J R Stat Soc B 64:583–639. doi:10.1111/1467-9868.00353
Spiegelhalter D, Thomas A, Best N, Lunn D (2003) WinBUGS 1.4. [1.4]. Cambridge, UK, Imperial College of Science, Technology, and Medicine. Ref Type: Computer Program
Sram RJ, Podrazilova K, Dejmek J, Mrackova G, Pilcik T (1998) Single cell gel electrophoresis assay: sensitivity of peripheral white blood cells in human population studies. Mutagenesis 13:99–103
Thompson JA, Brown SE, Riddle WT, Seahorn JC, Cohen ND (2005) Use of a bayesian risk-mapping technique to estimate spatial risks for mare reproductive loss syndrome in Kentucky. Am J Vet Res 66:17–20. doi:10.2460/ajvr.2005.66.17
Thompson JA, Scott HM (2007) Bayesian kriging of seroprevalence to Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis and Neospora caninum in Alberta beef and dairy cattle. Can Vet J 48:1281–1285
Tice R, Vacquez M (1999) Protocol for the application of the pH >13 alkaline single cell gel (SCG) assay to the detection of DNA damage in mammalian cells. Comet Assay Interest Group, Integrated Laboratory Systems
USEPA (2004) Tri explorer: facility report. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Available: http://www.epa.gov/triexplorer/. Accessed 2 August 2004
USEPA (2007) Integrated risk information system. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Available: http://www.epa.gov/iris/. Accessed 15 March 2007
Wickliffe JK, Bickham JW (1998) Flow cytometric analysis of hematocytes from brown pelicans (Pelecanus occidentalis) exposed to planar halogenated hydrocarbons and heavy metals. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 61:239–246. doi:10.1007/s001289900754
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the Vivian L. Smith Foundation and the Point Comfort, Texas ALCOA facility for providing the financial resources for completion of this project. Also, to our colleagues in Texas A&M University’s Food Animal Medicine and Surgery Service, your support and encouragement are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bissett, W., Smith, R., Adams, L.G. et al. Geostatistical analysis of biomarkers of genotoxicity in cattle, Bos taurus and Bos taurus × Bos indicus, sentinels near industrial facilities. Ecotoxicology 18, 87–93 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0261-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0261-6