Abstract
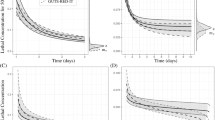
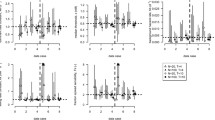
The basis of ecotoxicology lies currently in the dose–response of organisms to toxicants, as typically described by probit and logistic models. While recognising its merits, standard endpoints ignore the process of toxicity with time, and consequently our ability to predict direct toxic effects in environmental risk assessments is seriously curtailed. Although the response of toxicants with time has been studied before, its application in ecotoxicology remains underutilised. One reason is that no convincing mechanism has been proposed to explain the hyperbolic curves of such responses, whereas a variety of models have been used to describe them. The explanation of both time- and dose-dependent responses is found ultimately in the natural variability of receptor sites among individuals of populations exposed to a toxicant inhibitor with time. The process can be explained by the kinetics of inhibition, and is appropriately described by a simple mathematical expression like the Michaelis–Menten equation, though other asymptotic models (e.g. logistic model) can also be used. The advantage of the hyperbolic model is that median effect values (e.g. LC50 for dose- and ET50 for time-dependent responses) enable calculation of toxicity effects at any concentration level and/or time of exposure, thus making it especially attractive for risk assessment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Alvarez OA, Jager T, Colao BN, Kammenga JE (2006) Temporal dynamics of effect concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 40:2478–2484
Anderson PD, Weber LJ (1975) Toxic response as a quantitative function of body size. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 33:471–483
Bedaux JJM, Kooijman SALM (1994) Statistical analysis of bioassays based on hazard modelling. Environ Ecol Stat 1:303–314
Berkson J (1951) Why I prefer logits to probits. Biometrics 7:327–339
Bliss CI (1937) The calculation of the time-mortality curve. Ann Appl Biol 24:815–852
Bonnomet V, Duboudin C, Magaud H, Thybaud E, Vindimian E, Beauzamy B (2002) Modelling explicitly and mechanistically median lethal concentration as a function of time for risk assessement. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:2252–2259
Buikema AL, Niederlehner BR, Cairns J (1982) Biological monitoring part IV—toxicity testing. Wat Res 16:239–262
Cairns J, Mount DI (1990) Aquatic toxicology. Environ Sci Technol 24:154–161
Cairns J, Pratt JR (1989) The scientific basis of bioassays. Hydrobiologia 188/189:1–16
Canton JH, Adema DMM (1978) Reproducibility of short-term and reproduction toxicity experiments with Daphnia magna and comparison of the sensitivity of Daphnia magna with Daphnia pulex and Daphnia cucullata in short-term experiments. Hydrobiologia 59:135–140
Chew RD, Hamilton MA (1985) Toxicity curve estimation: fitting a compartment model to median survival times. Trans Am Fish Soc 114:403–412
Coppage DI, Matthews E (1974) Short-term effects of organophosphate pesticides on cholinesterases of estuarine fishes and pink shrimp. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 11:483–488
Dixon PM, Newman MC (1991) Analyzing toxicity data using statistical models for time-to-death: an introduction. In: Newman MC, McIntosh AW (eds) Metal ecotoxicology. Concepts and applications. Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, pp 207–242
Escher BI, Hermens JLM (2002) Modes of action in ecotoxicology: their role in body burdens, species sensitivity, QSARs, and mixture effects. Environ Sci Technol 36:4201–4217
Forbes VE, Calow P (2002) Extrapolation in ecological risk assessment: balancing pragmatism and precaution in chemical controls legislation. Bioscience 52:249–257
Forbes VE, Forbes TL (1994) Ecotoxicology in theory and practice. Chapman & Hall, London
Forbes VE, Calow P, Sibly RM (2001) Are current species extrapolation models a good basis for ecological risk assessment? Environ Toxicol Chem 20:442–447
Gaddum JH (1953) Bioassays and mathematics. Pharmacol Rev 5:87–134
Giesy JP, Graney RL (1989) Recent developments in and intercomparisons of acute and chronic bioassays and bioindicators. Hydrobiologia 188/189:21–60
Goldstein A, Aronow L, Kalman SM (1974) Principles of drug action: the basis of pharmacology. Wiley, New York
Hendriks AJ (1995) Modeling response of species to microcontaminants: comparative ecotoxicology by (sub)lethal body burdens as a function of species size and partition ratio of chemicals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 32:103–130
Hoekstra JA, Vaal MA, Notenboom J, Slooff W (1994) Variation in the sensitivity of aquatic species to toxicants. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 53:98–105
Jager T, Kooijman SALM (2005) Modeling receptor kinetics in the analysis of survival data for organophosphorus pesticides. Environ Sci Technol 39:8307–8314
Jager T, Crommentuijn T, van Gestel CAM, Kooijman SALM (2004) Simultaneous modeling of multiple end points in life-cycle toxicity tests. Environ Sci Technol 38:2894–2900
Johnson MK (1977) Improved assay of neurotoxic esterase for screening organophosphates for delayed neurotoxicity potential. Arch Toxicol 37:113–115
Kammenga JE, Riksen JAG (1996) Comparing differences in species sensitivity to toxicants: phenotypic plasticity versus concentration-response relationships. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1649–1653
Kooijman SALM (1981) Parametric analyses of mortality rates in bioassays. Water Res 15:107–119
Kooijman SALM (2000) Dynamic energy and mass budgets in biological systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kumar A, Chapman JC (1998) Profenofos toxicity to the eastern rainbow fish (Melanotaenia duboulayi). Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1799–1806
Lee NA, Kennedy IR (2001) Environmental monitoring of pesticides by immunoanalytical techniques: validation, current status, and future perspectives. J AOAC Int 84:1393–1406
Lee J-H, Landrum PF, Koh C-H (2002) Prediction of time-dependent PAH toxicity in Hyalella azteca using a damage assessment model. Environ Sci Technol 36:3131–3138
Legierse KCHM, Verhaar HJM, Vaes WHJ, de Bruijn JHM, Hermens JLM (1999) Analysis of the time-dependent acute aquatic toxicity of organophosphorus pesticides: the critical target occupation model. Environ Sci Technol 33:917–925
Maltby L, Calow P (1989) The application of bioassays in the resolution of environmental problems; past, present and future. Hydrobiologia 188/189:65–76
Matsumura F (1985) Toxicology of pesticides. Plenum Press, New York
McCarty LS, Mackay D (1993) Enhancing ecotoxicological modeling and assessment. Body residues and modes of toxic action. Environ Sci Technol 27:1719–1728
Meister R, Van den Brink PJ (2000) The analysis of laboratory toxicity experiments. In: Sparks T (ed) Statistics in ecotoxicology. Wiley, West Sussex, pp 99–118
Moriarty F (1999) Ecotoxicology—the study of pollutants in ecosystems, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London
Nacci D, Pelletier M, Lake J, Bennett R, Nichols J, Haebler R, Grear J, Kuhn A, Copeland J, Nicholson M, Walters S, Munns WR (2005) An approach to predict risks to wildlife populations from mercury and other stressors. Ecotoxicology 14:283–293
Newman MC (1998) Fundamentals of ecotoxicology. Ann Arbor Press, Chelsea
Newman MC, Aplin MS (1992) Enhancing toxicity data interpretation and prediction of ecological risk with survival time modeling: an illustration using sodium chloride toxicity to mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki). Aquat Toxicol 23:85–96
Newman MC, Jagoe RH (1996) Bioaccumulation models with time lags: dynamics and stability criteria. Ecol Model 84:281–286
Newman MC, McCloskey JT (1996) Time-to-event analyses of ecotoxicity data. Ecotoxicology 5:187–196
Newman MC, McCloskey JT (2000) The individual tolerance concept is not the sole explanation for the probit dose-effect model. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:520–526
Newman MC, McIntosh AW (1983) Slow accumulation of lead from contaminated food sources by the freshwater gastropods, Physa integra and Campeloma decisum. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 12:685–691
Newman MC, Keklak MM, Doggett MS (1994) Quantifying animal size effects on toxicity: a general approach. Aquat Toxicol 28:1–12
Nichols JW, McKim JM, Andersen ME, Gargas ML, Clewell HJ III, Erickson RJ (1990) A physiologically based toxicokinetic model for the uptake and disposition of waterborne organic chemicals in fish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 106:433–447
Pan G, Dutta HM (1998) The inhibition of brain acetylcholinesterase activity of juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides by sublethal concentrations of diazinon. Environ Res 79:133–137
Pery AR, Bedaux JJ, Zonneveld C, Kooijman SA (2001) Analysis of bioassays with time-varying concentrations. Water Res 35:3825–3832
Rand GM, Petrocelli SR (1985) Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology. Hemisphere Publishing Corp, New York
Richmonds CR, Dutta HM (1992) Effect of malathion on the brain acetylcholinesterase activity of bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus. Bull Envrion Contam Toxicol 49:431–435
Rowe CL (2003) Growth responses of an estuarine fish exposed to mixed trace elements in sediments over a full life cycle. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:229–239
Roy R, Campbell PGC (1995) Survival time modeling of exposure of juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) to mixtures of aluminum and zinc in soft water at low pH. Aquat Toxicol 33:155–176
Sánchez-Bayo F (2006) Comparative acute toxicity of organic pollutants and reference values for crustaceans. I. Branchiopoda, Copepoda and Ostracoda. Environ Pollut 139:385–420
Sánchez-Bayo F, Goka K (2006) Influence of light in acute toxicity bioassays of imidacloprid and zinc pyrithione to zooplankton crustaceans. Aquat Toxicol 78:262–271
Schimmel SC, Patrick JJM, Forester J (1976) Heptachlor: toxicity to and uptake by several estuarine organisms. J Toxicol Environ Health 1:955–965
Sibly RM (1999) Efficient experimental designs for studying stress and population density in animal populations. Ecol Appl 9:496–503
Smith S, Kwan MKH (1989) Use of aquatic macrophytes as a bioassay method to assess relative toxicity, uptake kinetics and accumulated forms of trace metals. Hydrobiologia 188/189:345–351
Soares AMVM, Baird DJ, Calow P (1992) Interclonal variation in the performance of Daphnia magna Straus in chronic bioassays. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:1477–1483
Suter GW II, Rosen AE, Linder E, Parkhurst DF (1987) Endpoints for responses of fish to chronic exposures. Environ Toxicol Chem 6:793–809
Truhaut R (1977) Ecotoxicology: objectives, principles and perspectives. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 1:151–173
Van Beelen P, Fleuren-Kemila AK, Aldenberg T (2001) The relation between extrapolated risk, expressed as potentially affected fraction, and community effects, expressed as pollution-induced community tolerance. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1133–1140
Van Ryzin J, Rai K (1987) A dose-response model incorporating nonlinear kinetics. Biometrics 43:95–105
Verhaar HJM, Wolf Wd, Dyer S, Legierse KCHM, Seinen W, Hermens JLM (1999) An LC50 vs time model for the aquatic toxicity of reactive and receptor-mediated compounds. Consequences for bioconcentration kinetics and risk assessment. Environ Sci Technol 33:758–763
Walker CH, Hopkin SP, Sibly RM, Peakall DB (2001) Principles of ecotoxicology. Taylor and Francis, Glasgow
Walthall WK, Stark JD (1997) A comparison of acute mortality and population growth rate as endpoints of toxicological effect. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 37:45–52
Wijngaarden RPAV, Brock TCM, Van den Brink PJ (2005) Threshold levels for effects of insecticides in freshwater ecosystems: a review. Ecotoxicology 14:355–380
Wogram J, Liess M (2001) Rank ordering of macroinvertebrate species sensitivity to toxic compounds by comparison with that of Daphnia magna. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 67:360–367
Zhao Y, Newman MC (2007) The theory of underlying models influences predictions for intermittent exposures. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:543–547
Zinkl JG, Lockhart WL, Kenny SA, Ward FJ (1991) The effects of cholinesterase inhibiting insecticides on fish. In: Mineau P (ed) Chemicals in agriculture: cholinesterase inhibiting insecticides—their impact on wildlife and the environment. Elsevier, London, pp 233–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Bayo, F., Goka, K. Simplified models to analyse time- and dose-dependent responses of populations to toxicants. Ecotoxicology 16, 511–523 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0158-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0158-9