Abstract
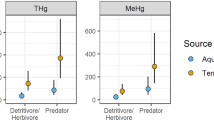
Mercury (Hg) bioaccumulation in salamanders has received little attention despite widespread Hg contamination of aquatic ecosystems and worldwide amphibian declines. Here we report concentrations of methyl Hg (MeHg) and total Hg in larval northern two-lined salamanders (Eurycea bislineata bislineata) collected from streams in Acadia National Park (ANP), Maine, and Bear Brook Watershed, Maine (BBWM; a paired, gauged watershed treated with bimonthly applications (25 kg/ha/yr) of ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4]) since 1989), and Shenandoah National Park (SNP), Virginia. MeHg comprised 73–97% of total Hg in the larval salamander composite samples from ANP. At BBWM we detected significantly higher total Hg levels in larvae from the (NH4)2SO4 treatment watershed. At ANP total Hg concentrations in salamander larvae were significantly higher from streams in unburned watersheds in contrast with larval samples collected from streams located in watersheds burned by the 1947 Bar Harbor fire. Additionally, total Hg levels were significantly higher in salamander larvae collected at ANP in contrast with SNP. Our results suggest that watershed-scale attributes including fire history, whole-catchment (NH4)2SO4 additions, wetland extent, and forest cover type influence mercury bioaccumulation in salamanders inhabiting lotic environments. We also discuss the use of this species as an indicator of Hg bioaccumulation in stream ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Amirbahman P.L. Ruck I.J. Fernandez T.A. Haines J.S. Kahl (2004) ArticleTitleThe effect of fire on mercury cycling in the soils of forested watersheds: Acadia National Park, Maine, USA Water Air and Soil Poll. 152 315–31
Bank, M.S., Burgess, J.R., Evers, D.C. and Loftin, C.S. (2005). Mercury contamination of biota from Acadia National Park, Maine, USA: a review. Env. Mon. & Assess
Brigham, M.E., Krabbenhoft, D.P. and Hamilton, P.A. (2003). Mercury in Stream Ecosystems – New Studies Initiated by the U.S. Geological Survey. USGS, Department of the Interior Fact Sheet 016–03
A.J.K. Calhoun J.E. Cormier R.B. Owen SuffixJr. C.E. Roman A.F. O’Connell SuffixJr. R.W. Tiner (1994) The wetlands of Acadia National Park and vicinity U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, National wetlands Inventory Newton Corner, MA
K.L. Clark R.L. Hall (1985) ArticleTitleEffects of elevated hydrogen ion and aluminum concentrations on the survival of amphibian embryos and larvae Can. J. Zool. 63 116–23 Occurrence Handle10.1139/z85-020 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhvF2ju78%3D
K.L. Clark B.D. LaZerte (1985) ArticleTitleA laboratory study of the effects of aluminum and pH on amphibian eggs and tadpoles Can. J. Fish. Aq. Sci. 42 1544–51 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXltlKks74%3D
G. Compeau R. Bartha (1985) ArticleTitleSulfate reducing bacteria: principal methylators of mercury in anoxic estuarine sediments Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 50 498–502 Occurrence Handle16346866 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlvVehsrY%3D
R. Devereux M.R. Winfrey J. Winfrey D.A. Stahl (1996) ArticleTitleDepth profile of sulfate reducing bacterial ribosomal RNA and Hg methylation in an estuarine sediment FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 20 23–31 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjsVOktbo%3D
C.G. Gilmour E.A. Henry (1991) ArticleTitleMercury methylation in aquatic systems affected by acid deposition Environ. Pollut. 71 131–69 Occurrence Handle15092118 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXksFKnurc%3D
C.G. Gilmour E.A. Henry R. Mitchell (1992) ArticleTitleSulfate stimulation of mercury methylation in freshwater sediments Env. Sci. Tech. 26 2281–7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlslOrurs%3D
D.F. Grigal (2002) ArticleTitleInputs and outputs of mercury from terrestrial watersheds: a review Environ. Rev. 10 1–39 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjtFChtLs%3D
N.B. Grimm W.E. Gergel W.H. McDoll E.W. Boyer C.L. Dent P. Groffman S.C. Hart J. Harvey C. Johnston E. Mayorga M.E. McClain J. Pinay (2003) ArticleTitleMerging aquatic and terrestrial perspectives of nutrient biogeochemistry Oecologia 442 485–501
Harmon, S.M., King, J.K., Chandler, G.T., Newman, L.A. and Gladden, J.B. (2003). Mercury body burdens in Gambusia holbrooki and Erimyzon sucetta in a wetland mesocosm amended with sulfate. United States Department of Energy Report #WSRC- MS-2003-00374
J.E. Houlahan C.S. Findlay B.R. Schmidt A.H. Meyer S.L. Kuzmin (2000) ArticleTitleQuantitative evidence for global amphibian declines Nature 404 752–55 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35008052 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjtVWntL0%3D Occurrence Handle10783886
Johnson, K.B., Haines, T.A., Kahl, J.S., Norton, S.A. and Amirbahman, A. (2005). Fire and its effects on mercury and methylmercury inputs. Environ. Monit. Assess
Kahl, J.S., Fernandez, I., Manski, D., Haines, T.A. and Lent, R. (2002). Study of Atmospheric Deposition Effects on Surface Waters and Watershed Resources: Paired-gauged watershed research at Acadia National Park. USGS-BRD Technical Report
M. Lucotte R. Schetagne N. Thérien C. Langlois A. Tremblay (Eds) (1999) Mercury in the Biogeochemical Cycle Springer-Verlag Germany
G. Mierle (1990) ArticleTitleAqueous inputs of mercury to pre-cambrian shield lakes in Ontario Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9 843–51 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXltVejtrk%3D
F.M.M. Morel A.M.L. Kraepiel M. Amyot (1998) ArticleTitleThe chemical cycle and bioaccumulation of mercury Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 29 543–66
R.J. Naiman H. Décamps (1997) ArticleTitleThe ecology of interfaces – riparian zones Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 28 621–58
InstitutionalAuthorNameNational Academy of Sciences (NAS) (2000) Toxicological Effects of Methylmercury National Research Council, National Academy Press Washington, DC
National Atmospheric Deposition Program / Mercury Deposition Network (NADP/MDN). (2004). NADP Program Office, Illinois State Water Survey, 2204 Griffith Drive, Champaign, IL 61820, http://nadp.sws.uiuc.edu/
J.W. Petranka (1984) ArticleTitleOntogeny of the diet and feeding behavior of Eurycea bislineata larvae J. Herp. 18 48–55
J.W. Petranka (1998) Salamanders of the United States Smithsonian Institution Press Washington, D.C
R. Relyea N.A. Mills (2001) ArticleTitlePredator-induced stress makes the pesticide carbaryl more deadly to grey treefrog tadpoles (Hyla versicolor) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98 2491–6 Occurrence Handle11226266 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhslKmsrY%3D
J.D. Rouse C.A. Bishop J. Struger (1999) ArticleTitleNitrogen pollution: an assessment of the impact on amphibians Environ. Health Persp. 107 1–6
D.W. Sparling G. Linder C. Bishop (Eds) (2000) Ecotoxicology of Amphibians and Reptiles SETAC Press Pensacola, FL, USA
R.C. Stebbins N.W. Cohen (1995) A Natural History of Amphibians Princeton University Press Princeton, New Jersey, USA
SYSTAT Software Inc. (2002). SYSTAT 10.2. Richmond, CA
United States Department of Energy (USDOE). (1999). Energy Information Administration. International Energy Annual 1997. Washington, D.C
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (1991). Methods for the Determination of Metals in Environmental Samples. EPA-600/4-91-010
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2001). Method 1630: Methyl Mercury in Water by Distillation, Aqueous Ethylation, Purge and Trap, and CVAFS. EPA-821-R-01-020
H.M. Webber T.A. Haines (2003) ArticleTitleMercury effects on predator avoidance behavior of a forage fish, golden shiner (Notemigonus crysoleucas) Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 22 1556–61 Occurrence Handle12836981 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXot1Wrtbk%3D
J.G. Wiener W.F. Fitzgerald C.J. Watras R.G. Rada (1990) ArticleTitlePartitioning and bioavailability of mercury in an experimentally acidified Wisconsin lake Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9 909–18 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXltVejt74%3D
Wiener, J.G., Krabbenhoft, D.P., Heinz, G.H. and Scheuhammer, A.M. (2003). Ecotoxicology of mercury. In: Hoffman, D.J., Rattner, B.A., Burton, G.A. Jr., and Cairns J.(eds) Handbook of Ecotoxicology, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Chapter 16
J.G. Wiener D.J. Spry (1996) Toxicological significance of mercury in freshwater fish W.N. Beyer G.H. Heinz A.W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife: Interpreting Tissues Concentrations Boca Raton FL, USA 297–339
M.S. Wipfli (1997) ArticleTitleTerrestrial invertebrates as salmonid prey and nitrogen sources in streams: contrasting old growth and young-growth riparian forests in south-eastern Alaska USA Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 54 1259–69
W.L. Witt (1993) ArticleTitleAnnotated checklist of the amphibians and reptiles of Shenandoah National Park, Virginia Catesbeiana 13 26–35
J.H. Zar (1999) Biostatistical analysis EditionNumber4 th ed. Prentice Hall Press Upper Saddle River, NJ
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bank, M.S., Loftin, C.S. & Jung, R.E. Mercury Bioaccumulation in Northern Two-lined Salamanders from Streams in the Northeastern United States. Ecotoxicology 14, 181–191 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-004-6268-8
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-004-6268-8