Summary
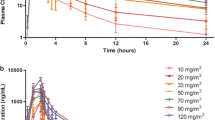
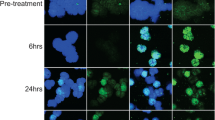
Purpose The aim of the present study was to assess the safety, maximum tolerated dose (MTD), pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy of single and multiple doses of intravenous CG200745, a novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Experimental Design Two to six patients received intravenous CG200745 according to the 2 + 4 dose-escalating method. This first-in-human trial was comprised of two parts: Part 1 was a single ascending dose, and Part 2 was multiple ascending doses weekly for 3 weeks, and then 1 week off. For the first cycle, pharmacokinetic sampling for CG200745 and pharmacodynamic sampling for acetylated histone H4 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were performed on day 1 for Part 1 and on days 1 and 15 for Part 2. Examination of acetylated histone H4 in pre- and post-biopsy samples was performed in accessible patients. Results In all, 28 patients were treated at 13 dose levels (1.8–250 mg/m2) and received a total of 71 cycles of CG200745. Hematologic toxicities included grade 3/4 neutropenia (22.2 %) that did not last a week and non-hematologic toxicities included fatigue (22.2 %) and anorexia (16.7 %) that did not exceed grade 2. No dose-limiting toxic effects were noted. Dose proportionality was observed for both the maximum concentration and area under the curve. The elimination half-life was 5.67 ± 2.69 h (mean ± standard deviation). An increase in PBMC acetylated histone H4 was observed at dose levels up to 51 mg/m2, which plateaued at higher dose levels. At 24 h, 75 % of patients (6/8) showed higher relative acetylation in tumor tissue compared to PBMCs. Although there was no partial or complete response, 57.1 % of patients (16/28) had stable disease that lasted at least 6 weeks. Conclusions CG200745 can be safely administered at effective dose levels that inhibit HDAC in PBMCs and tumor tissue. Although MTD was not reached, further escalation was not performed because acetylated histone H4 plateaued at dose levels higher than 51 mg/m2. Additional phase II trials are recommended at 250 mg/m2.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW (2006) Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:769–784
Na YS, Kim SM, Jung KA et al (2010) Effects of the HDAC inhibitor CG2 in combination with irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, or oxaliplatin on HCT116 colon cancer cells and xenografts. Oncol Rep 24:1509–1514
Oh ET, Park MT, Choi BH et al (2012) Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor CG200745 induces clonogenic cell death by modulating acetylation of p53 in cancer cells. Invest New Drugs 30:435–442
Hyun Y-L, Kim HJ, Kim YE et al. Abstract #4561: Preclinical studies of CG200745, novel histone deacetylase inhibitor discovered using structure-based drug discovery technologies. AACR Meeting Abstracts 2009; 2009: 4561-
Berry SM, Carlin BP, Lee JJ, Muller P (2010) Bayesian adaptive methods for clinical trials. CRC press
Derelanko MJ, Auletta CS (2014) Handbook of toxicology. CRC press
Thurn KT, Thomas S, Moore A, Munster PN (2011) Rational therapeutic combinations with histone deacetylase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Future Oncol 7:263–283
Subramanian S, Bates SE, Wright JJ et al (2010) Clinical toxicities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 3:2751–2767
Ali A, Bluteau O, Messaoudi K et al (2013) Thrombocytopenia induced by the histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat involves p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Cell Death Dis 4:e738
Ro S, Kong G-S, Lee S-K et al (2012) Abstract LB-359: Extended accumulation of acetylated histone in tumor tissues obtained from the phase I study of CG200745. Cancer Res 72:LB-359
Chung EJ, Lee MJ, Lee S, Trepel JB (2006) Assays for pharmacodynamic analysis of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2:213–230
Weber JS, Levit LA, Adamson PC et al. (2014) American society of clinical oncology policy statement update: the critical role of phase I trials in cancer research and treatment. J Clin Oncol
Tampakis A, Tampaki EC, Nebiker CA, Kouraklis G (2014) Histone deacetylase inhibitors and colorectal cancer: what is new? Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 14:1220–1227
Schulze-Bergkamen H, Jaeger D, Kopp H-G et al (2013) Phase I dose escalation of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi) resminostat in combination with FOLFIRI in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients: the SHORE trial. J Clin Oncol 31:3625
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health &Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number : HI06C0868, HI14C1731). Crystal Genomics for support.
Conflict of interest
Hyunju Cha, Sool-Ki Kwon, Seonggu Ro, and JoongMyung Cho are current employees of Crystal Genomics. The remaining authors have reported no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Kp., Park, S.J., Kim, JE. et al. First-in-human study of the toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of CG200745, a pan-HDAC inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid malignancies. Invest New Drugs 33, 1048–1057 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0262-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0262-2