Summary
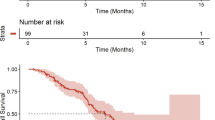
Purpose: To investigate the safety, optimal dosing, pharmacokinetics and clinical activity of a regimen of navitoclax (ABT-263) combined with gemcitabine in patients with solid tumors. Experimental Design: Patients with solid tumors for which gemcitabine was deemed an appropriate therapy were enrolled into one of two different dosing schedules (21-day dosing schedule: navitoclax administered orally on days 1–3 and 8–10,; and gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8; 28-day dosing schedule: navitoclax administrated orally on days 1–3, 8–10, and 15–17; and gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 on days 1, 8 and 15). Navitoclax doses were escalated from 150 to 425 mg. An expanded safety cohort was conducted for the 21-day dosing schedule at the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of navitoclax. Results: Forty-six patients were enrolled at three U.S. centers. The most common adverse events included: hematologic abnormalities (thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia), liver enzyme elevations (ALT and AST), and gastrointestinal disturbances (diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting). Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) observed in cycle 1 were grade 4 thrombocytopenia (2 patients), grade 4 neutropenia (1 patient), and grade 3 AST elevation (2 patients). The MTD of navitoclax was 325 mg co-administered with gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 for the 21-day schedule. No clinically significant pharmacokinetic drug–drug interactions were observed. There were no objective responses. Stable disease, reported at the end of cycle 2, was the best response in 54 % of evaluable patients (n = 39). Conclusions: The combination of navitoclax 325 mg with gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 was generally well tolerated and exhibited a favorable safety profile in patients with advanced solid tumors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azmi AS, Mohammad RM (2009) Non-peptidic small molecule inhibitors against Bcl-2 for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol 218(1):13–21
Del Gaizo Moore V (2008) and A. Letai, Rational design of therapeutics targeting the BCL-2 family: are some cancer cells primed for death but waiting for a final push? Adv Exp Med Biol 615:159–75
Kang MH, Reynolds CP (2009) Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15(4):1126–32
Leibowitz B, Yu J (2010) Mitochondrial signaling in cell death via the Bcl-2 family. Cancer Biol Ther 9(6):417–22
Tse C et al (2008) ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res 68(9):3421–8
Lin X et al (2006) /‘Seed/’ analysis of off-target siRNAs reveals an essential role of Mcl-1 in resistance to the small-molecule Bcl-2//Bcl-XL inhibitor ABT-737. Oncogene 26(27):3972–3979
Tahir SK et al (2007) Influence of Bcl-2 family members on the cellular response of small-cell Lung cancer cell lines to ABT-737. Cancer Res 67(3):1176–1183
Chen J et al (2011) The Bcl-2/Bcl-X (L)/Bcl-w inhibitor, navitoclax, enhances the activity of chemotherapeutic agents in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 10(12):2340–9
Mini E et al (2006) Cellular pharmacology of gemcitabine. Ann Oncol 17(5):7–12
Wong FY et al (2012) Combination therapy with gossypol reveals synergism against gemcitabine resistance in cancer cells with high BCL-2 expression. PLoS One 7(12):e50786
Schniewind B et al (2004) Resistance of pancreatic cancer to gemcitabine treatment is dependent on mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Int J Cancer 109(2):182–188
Okamoto K et al (2007) bcl-2-specific siRNAs restore Gemcitabine sensitivity in human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med 11(2):349–361
Banerjee S et al (2010) Preclinical studies of apogossypolone, a novel pan inhibitor of bcl-2 and mcl-1, synergistically potentiates cytotoxic effect of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas 39(3):323–31
Wong M et al (2012) Navitoclax (ABT-263) reduces Bcl-x (L)-mediated chemoresistance in ovarian cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther 11(4):1026–35
Eisenhauer EA et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–47
Oken MM et al (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin Oncol 5(6):649–55
National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 3.0. 2006 [cited 2007 December 13]; Available from: http://ctep.cancer.gov/forms/CTCAEv3.pdf.
Roberts AW et al (2012) Substantial susceptibility of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to BCL2 inhibition: results of a phase I study of navitoclax in patients with relapsed or refractory disease. J Clin Oncol 30(5):488–96
Wilson WH et al (2010) Navitoclax, a targeted high-affinity inhibitor of BCL-2, in lymphoid malignancies: a phase 1 dose-escalation study of safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and antitumour activity. Lancet Oncol 11(12):1149–59
Rudin CM et al (2012) Phase II study of single-agent navitoclax (ABT-263) and biomarker correlates in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18(11):3163–9
Gandhi L et al (2011) Phase I study of navitoclax (ABT-263), a novel Bcl-2 family inhibitor, in patients with small-cell lung cancer and other solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 29(7):909–16
Corcoran RB et al (2013) Synthetic lethal interaction of combined BCL-XL and MEK inhibition promotes tumor regressions in KRAS mutant cancer models. Cancer Cell 23(1):121–8
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by AbbVie, Inc. We thank the study teams at our respective institutions. Medical writing support was provided by Michael J. Theisen, PhD and Jamie L. Kistler, PhD, at Complete Publication Solutions, LLC; this support was funded by AbbVie, Inc. Joseph Beason and Min Tian provided statistical programming support and Keith J. Gaddie, Ph. D provided medical writing support; all are AbbVie employees.
Funding source
AbbVie Inc.
Conflict of interest/disclosure information
James Cleary, Caio Rocha-Lima, Herbert Hurwitz, Alberto J. Montero, Geoffrey Shapiro, and Hope Uronis have no conflict of interests to declare. Jianning Yang, Alison M. Graham, Todd Busman, Kyle Holen, and Mack Mabry are employees and stock owners of AbbVie. *Catherine Franklin is a former employee and stock owner of AbbVie and currently works for Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research, Inc., Cambridge, MA.
The design, study conduct, analysis, and financial support of the clinical trial were provided by AbbVie. AbbVie participated in the interpretation of data, review, and approval of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cleary, J.M., Lima, C.M.S.R., Hurwitz, H.I. et al. A phase I clinical trial of navitoclax, a targeted high-affinity Bcl-2 family inhibitor, in combination with gemcitabine in patients with solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 32, 937–945 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0110-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0110-9