Summary
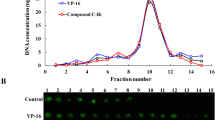
Topoisomerase II α enzyme plays a critical role in DNA replication process. It controls the topologic states of DNA during transcription and is essential for cell proliferation. Human DNA topoisomerase II α (hTopo II α) is a promising chemotherapeutic target for anticancer agents against a variety of cancer types. In the present study, andrographolide and its structurally modified analogues were investigated for their inhibitory activities on hTopo II α enzyme. Five out of nine andrographolide analogues potently reduced hTopo II α activity and inhibited cell proliferation in four mammalian cell lines (Hela, CHO, BCA-1 and HepG2 cells). IC50 values for cytotoxicity of analogues 3A.1, 3A.2, 3A.3, 1B and 2C were 4 to 7 μM. Structure-activity relationship studies revealed that both core structure of andrographolide and silicon based molecule of functional group were important for the inhibition of hTopo II α activity whereas position C-19 of analogues was required for anti-proliferation. In addition, the analogue 2C at 10 μM concentration inhibited hTopo II α, and induced apoptosis with nuclear fragmentation and formation of apoptotic bodies in HepG2 cells. The analogue 2C may, therefore, have a therapeutic potential as effective anticancer agent targeting the hTopo II α functions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodley AL, Liu LF (1998) Topoisomerases as novel targets for cancer chemotherapy. Nat Biotechnol 6:1315–1319. doi:bjp.2008.368/nbt1188-1315
Schneider E, Hsiang YH, Liu LF (1990) DNA topoisomerases as anticancer drug targets. Adv Pharmacol 21:149–183. doi:10.2174/1568011013354859
Hande KR (1998) Clinical applications of anticancer drugs targeted to topoisomerase II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1400:173–84. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(98)00134-1
Chikamori K, Grozav AG, Kozuki T, Grabowski D, Ganapathi R, Ganapathi MK (2010) DNA topoisomerase II enzymes as molecular targets for cancer chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 10:758–71. doi:10.2174/156800910793605785
Varma A, Padh H, Shrivastava N (2011) Andrographolide: new plant-derived antineoplastic entity on horizon. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 815390:1–9. doi:10.1093/ecam/nep135
Jada SR, Matthews C, Saad MS, Hamzah AS, Lajis NH, Stevens MF, Stanslas J (2008) Benzylidene derivatives of andrographolide inhibit growth of breast and colon cancer cells in vitro by inducing G(1) arrest and apoptosis. Br J Pharmacol 155:641–654. doi:bjp.2008.368/bjp.2008.368
Jada SR, Hamzah AS, Lajis NH, Saad MS, Stevens MF, Stanslas J (2006) Semisynthesis and cytotoxic activities of andrographolide analogues. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 21:145–155. doi:10.1080/147563605004999988
Nanduri S, Nyavanandi VK, Thunuguntla SS, Kasu S, Pallerla MK, Ram PS, Rajagopal S, Kumar RA, Ramanujam R, Babu JM, Vyas K, Devi AS, Reddy GO, Akella V (2004) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of andrographolide analogues as novel cytotoxic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14:4711–4717. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.06.090
Sirion U, Kasemsook S, Suksen K, Piyachaturawat P, Suksamrarn A, Saeeng R (2011) New substituted C-19-andrographolide analogues with potent cytotoxic activities. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:49–52. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.11.085
Aromdee C (2012) Modifications of andrographolide to increase some biological activities: a patent review (2006–2011). Expert Opin Ther Pat 22:169–180. doi:10.1517/13543776.2012.661718
Li J, Cheung HY, Zhang Z, Chan GK, Fong WF (2007) Andrographolide induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and cell death in HepG2 cells via alteration of reactive oxygen species. Eur J Pharm 568:31–44. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.04.027
Zhou J, Zhang S, Ong CN, Shen HM (2006) Critical role of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members in andrographolide-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 72:132–144. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.04.019
Ji L, Shen K, Jiang P, Morahan G, Wang Z (2011) Critical roles of cellular glutathione homeostasis and jnk activation in andrographolide-mediated apoptotic cell death in human hepatoma cells. Mol Carcinog 50:580–591. doi:10.1002/mc.20741
Russo A, Terrasi M, Agnese V, Santini D, Bazan V (2006) Apoptosis: a relevant tool for anticancer therapy. Ann Oncol 17(Suppl 7):vii115–vii123. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl963
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D, Warren JT, Bokesch H, Kenney S, Boyd MR (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 82(13):1107–1112. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.01.003
Pourquier P, Kohlhagen G, Ueng JM, Pommier Y (2009) Topoisomerase I and II activity assays, Form; Method in Molecular Medicine, Vol 28. In: Brown R, Böger-Brown U (eds) Cytotoxic drug resisance mechanisms. Humana Press INC, Totowa, pp 95–110
Miyata S, Wang LY, Yoshida C, Kitanaka S (2006) Inhibition of cellular proliferation by diterpenes, topoisomerase II inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem 14:2048–2051. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.10.059
Hasinoff BB, Kuschak TI, Creighton AM, Fattman CL, Allan WP, Thampatty P, Yalowich JC (1997) Characterization of a Chinese hamster ovary cell line with acquired resistance to the bisdioxopiperazine dexrazoxane (ICRF-187) catalytic inhibitor of topoisomerase II. Biochem Pharmacol 53:1843–1853. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(97)00013-0
Gong Y, Firestone GL, Bjeldanes LF (2006) 3,3′-diindolylmethane is a novel topoisomerase II alpha catalytic inhibitor that induces S-phase retardation and mitotic delay in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Mol Pharmacol 69:1320–1327. doi:10.1124/mol.105.018978
Sabisz M, Wesierska-Gadek J, Skladanowski A (2010) Increased cytotoxicity of an unusual DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor compound C-1305 toward HeLa cells with downregulated PARP-1 activity results from re-activation of the p53 pathway and modulation of mitotic checkpoints. Biochem Pharmacol 79:1387–1397. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.12.023
Bom D, Curran DP, Kruszewski S, Zimmer SG, Thompson Strode J, Kohlhagen G, Du W, Chavan AJ, Fraley KA, Bingcang AL, Latus LJ, Pommier Y, Burke TG (2000) The novel silatecan 7-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin displays high lipophilicity, improved human blood stability, and potent anticancer activity. J Med Chem 43:3970–3980. doi:10.1021/jm000144o
Parchment RE, Pessina A (1998) Topoisomerase I inhibitors and drug resistance. Cytotechnology 27:149–164. doi:10.1023/A:1008008719699
Hande KR (2006) Topoisomerase II inhibitors. Update on Cancer Therapeutics 1:3–15. doi:10.1016/j.uct.2006.04.001
Xue X, Qu XJ, Gao ZH, Sun CC, Liu HP, Zhao CR, Cheng YN, Lou HX (2012) Riccardin D, a novel macrocyclic bisbibenzyl, induces apoptosis of human leukemia cells by targeting DNA topoisomerase II. Invest New Drugs 30:212–22. doi:10.1007/s10637-010-9554-8
Onda T, Toyoda E, Miyazaki O, Seno C, Kagaya S, Okamoto K, Nishikawa K (2008) NK314, a novel topoisomerase II inhibitor, induces rapid DNA double-strand breaks and exhibits superior antitumor effects against tumors resistant to other topoisomerase II inhibitors. Cancer Lett 259:99–110. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.10.004
Acknowledgements
This research project is supported by Mahidol University, the Center of Excellence on Environmental Health, Toxicology, Science & Technology Postgraduate Education and Research Development Office (PERDO), Ministry of Education, Thailand, and the Office of the Higher Education Commission and Mahidol University under the National Research universities (NRU). We are grateful to Prof. Chumpol Pholpramool for his critical reading on the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nateewattana, J., Saeeng, R., Kasemsook, S. et al. Inhibition of topoisomerase II α activity and induction of apoptosis in mammalian cells by semi-synthetic andrographolide analogues. Invest New Drugs 31, 320–332 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9868-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9868-9