Summary
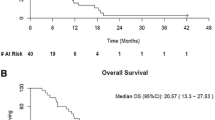
Purpose: To assess the activity and toxicity of interferon-α (IFN-α), capecitabine, and thalidomide in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (MRCC). Patients and methods: Twenty-seven patients were enrolled in a pilot study to receive oral capecitabine 1,900 mg/m2/day in 2 daily doses, 2 weeks on, l week off; daily subcutaneous IFN-α 1 mIU without interruption; and daily oral thalidomide 200 mg/day for the first seven days, then escalated to 400 mg/day without interruption. Dosages were reduced for toxicity as necessary. Results: Two patients discontinued treatment during the first week of the study, leaving 25 patients evaluable. There were 5 (20%) partial responses (PRs), 1 (4%) minor response (MR), 6 (24%) cases of stable disease (SD) ≥ 6 months, and 13 (52%) cases of progressive disease (PD). The interval from first response to disease progression varied from 0–23 months: 17 patients progressed in 0–6 months; 4 progressed in 7–12 months; and 4 progressed in 12–24 months. Median survival was >22 months, 14 months, and 1 month, respectively, for patients with PR, SD, and PD. Grade 3/4 toxicities consisted of hand-foot syndrome, neuropathy, fatigue, anemia, and deep venous thrombosis were common. Conclusion: This study demonstrates antitumor activity of combination IFN-α/capecitabine/thalidomide in MRCC. The 20% PR rate was notable, as the patient population had advanced disease and inferior performance status. Treatment was generally well tolerated, and further research is warranted to explore the efficacy of this combination for treating MRCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T, Thun M: Cancer statistics, 2004. CA: Cancer J Clin 54: 8–29, 2004.
Motzer RJ, Bahnson RR, Carducci MA, et al. National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Kidney Caner NCCN 1: 1–16, 2003.
Linehan WM, Zbar B, Bates SE, et al.: Cancer of the kidney and ureter. In Cancer: Principles and Practice, 6th ed.; DeVita VT Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA (eds): Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001.
Hernberg M, Pyrhonen S, Muhonen T: Regimens with or without interferon-alpha as treatment for metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma: An overview of randomized trials. J Immunother 22: 145–154, 1999.
Xeloda® (capecitabine) tablets [package insert]. Nutley, NJ: Roche Laboratories, 2003.
Chang DZ, Olencki T, Budd TG, Peereboom D, Ganapathi R, Osterwalder B, Bukowski R: Phase I trial of capecitabine in combination with interferon alpha in patients with metastatic renal cancer: toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 48: 493–498, 2001.
Padrik P, Leppik K, Arak A: A phase II study of combination therapy with capecitabine and interferon-alfa2A (IFNa) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22: 405, 2003 (abstr 1626).
Amato R: Thalidomide for recurrent renal-cell cancer in a 40-year-old man. Oncology 14(Suppl 13): 33–36, 2000.
Daliani DD, Papandreou CN, Thall PF, Wang X, Perez C, Oliva R, Pagliaro L, Amato R: A pilot study of thalidomide in patients with progressive metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 95: 758–765, 2002.
Eisen T, Boshoff C, Mak I, Sapunar F, Vaughan MM, Pyle L, Johnston SR, Ahern R, Smith IE, Gore ME: Continuous low dose thalidomide: A phase II study in advanced melanoma, renal cell, ovarian and breast cancer. Br J Cancer 82: 812–817, 2000.
Minor DR, Monroe D, Damico LA, Meng G, Suryadevara U, Elias L: A phase II study of thalidomide in advanced metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 20: 389–393, 2002.
Stebbing J, Benson C, Eisen T, Pyle L, Smalley K, Bridle H, Mak I, Sapunar F, Ahern R, Gore ME: The treatment of advanced renal cell cancer with high-dose oral thalidomide. Br J Cancer 85: 953–958. 2001.
Amato RJ, Schell J, Thompson N, Moore R, Miles B: Phase II study of thalidomide and interleukin-2 (IL-2) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (MRCC). Presented at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), 2003 (abstr 1556).
Rabinowitz M, Elias L, Lee F-C: Phase I/II trial of 5-fluorouricil, interferon-a, interleukin-2, and thalidomide for metastatic renal cell cancer. Presented at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), 2003 (abstr 1788).
Sella A, Sternberg C, Yarom N, Sava T, Calabry F, Zisman A, Lindner A, Cetto GL: Phase II study of low dose thalidomide and interferon-alfa in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Presented at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), 2003 (abstr 1614).
Nathan PD, Gore ME, Eisen TG: Unexpected toxicity of combination thalidomide and interferon alfa-2a treatment in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 20: 1429–1430, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amato, R.J., Rawat, A. Interferon-α plus capecitabine and thalidomide in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A pilot study. Invest New Drugs 24, 171–175 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-005-2938-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-005-2938-5