Abstract
Background
Pegylated interferon (PEGIFN) and ribavirin combination is the standard of care for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Studies comparing the efficacy and safety of PEGIFN alfa-2a and PEGIFN alfa-2b in treatment-naïve HCV-infected patients have shown conflicting results.
Aim
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies comparing the efficacy and safety of PEGIFN alfa-2a and PEGIFN alfa-2b in HCV-infected patients naïve to treatment.
Methods
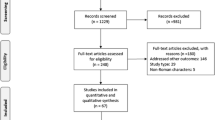
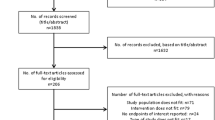
Nine studies (five abstracts) with 3,546 patients (1,771 treated with PEGIFN alfa-2a) comparing PEGIFN alfa-2a and PEGIFN alfa-2b in treatment-naïve HCV patients were analyzed. Efficacy outcomes were sustained virologic response (SVR) and treatment discontinuation rates due to serious adverse effects (SAE).
Results
Pooled data on outcomes (reported as odds ratios [ORs] with 95% confidence intervals [CIs]: [OR (95% CI)]) showed higher SVR in patients treated with PEGIFN alfa-2a as compared to treatment with PEGIFN alfa-2b [1.36 (1.07–1.73); P = 0.01]. Subgroup analysis of good quality studies on SVR in genotypes 2 and 3 also favored PEGIFN alfa-2a over PEGIFN alfa-2b (1.91 [1.09–3.37]; P = 0.02). SVR results obtained with the two types of IFN showed no impact of viral load and the presence or absence of cirrhosis. Treatment discontinuation rates due to SAE, reported in six studies (two abstracts) on 3,211 patients (1,604 treated with PEGIFN alfa-2a), were similar in the two types of PEGIFN [0.66 (0.37–1.16); P = 0.15].
Conclusions
PEGIFN alfa-2a has superior efficacy with higher SVR as compared to PEGIFN alfa-2b in treatment-naïve HCV-infected patients. The safety profile of the two types of PEGIFN was similar.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:705–714.
Kim WR. The burden of hepatitis C in the United States. Hepatology. 2002;36:S30–S34.
Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology. 2009;49:1335–1374.
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958–965.
Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P, Ramadori G, Bodenheimer H Jr, Bernstein D, Rizzetto M, Zeuzem S, Pockros PJ, Lin A, Ackrill AM. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:346–355.
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Gonçales FL Jr, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, Craxi A, Lin A, Hoffman J, Yu J. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982.
Zeuzem S, Welsch C, Herrmann E. Pharmacokinetics of peginterferons. Semin Liver Dis. 2003;23:23–28.
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12.
Rumi MG, Aghemo A, Prati GM, D’Ambrosio R, Donato MF, Soffredini R, Del Ninno E, Russo A, Colombo M. Randomized study of peginterferon-alpha2a plus ribavirin vs peginterferon-alpha2b plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:108–115.
McHutchison JG, Lawitz EJ, Shiffman ML, Muir AJ, Galler GW, McCone J, Nyberg LM, Lee WM, Ghalib RH, Schiff ER, Galati JS, Bacon BR, Davis MN, Mukhopadhyay P, Koury K, Noviello S, Pedicone LD, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Sulkowski MS. Peginterferon alfa-2b or alfa-2a with ribavirin for treatment of hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:580–593.
Ascione A, De Luca M, Tartaglione MT, Lampasi F, Di Costanzo GG, Lanza AG, Picciotto FP, Marino-Marsilia G, Fontanella L, Leandro G. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin is more effective than peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for treating chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:116–122.
Awad T, Thorlund K, Hauser G, Stimac D, Mabrouk M, Gluud C. Peginterferon alpha-2a is associated with higher sustained virological response than peginterferon alfa-2b in chronic hepatitis C: systematic review of randomized trials. Hepatology. 2010;51:1176–1184.
Hopewell S, Loudon K, Clarke MJ, Oxman AD, Dickersin K. Publication bias in clinical trials due to statistical significance or direction of trial results. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;1:MR000006.
Berenguer J, Alvarez-Pellicer J, Martín PM, López-Aldeguer J, Von-Wichmann MA, Quereda C, Mallolas J, Sanz J, Tural C, Bellón JM, González-García J. Sustained virological response to interferon plus ribavirin reduces liver-related complications and mortality in patients coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2009;50:407–413.
Singal AG, Volk ML, Jensen D, Di Bisceglie AM, Schoenfeld PS. A sustained viral response is associated with reduced liver-related morbidity and mortality in patients with hepatitis C virus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:280–288. 288.e1.
Singal AK, Singh A, Jaganmohan S, Guturu P, Mummadi R, Kuo YF, Sood GK. Antiviral therapy reduces risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:192–199.
McHutchison JG. Hepatitis C advances in antiviral therapy: what is accepted treatment now? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:431–441.
Foster GR. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: pharmacological and clinical differences between peginterferon-alpha-2a and peginterferon-alpha-2b. Drugs. 2010;70:147–165.
Bruno R, Sacchi P, Scagnolari C, Torriani F, Maiocchi L, Patruno S, Bellomi F, Filice G, Antonelli G. Pharmacodynamics of peginterferon alpha-2a and peginterferon alpha-2b in interferon-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C: a randomized, controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26:369–376.
Sinha S, Gulur P, Patel V, Hage-Nassar G, Tenner S. A randomized prospective clinical trial comparing pegylated interferon alpha 2a/ribavirin versus pegylated interferon alpha 2b/ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:S77–S78.
Yenice N, Mehtap O, Gümrah M, Arican N. The efficacy of pegylated interferon alpha 2a or 2b plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2006;17:94–98.
Khan AQ, Awan A, Shahbuddin S, Iqbal Q. Peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin versus peginterferon alfa-2b/ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C genotype 3. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:A200.
Kolakowska-Rzadzka A, Berak H, Wasilewski M, Horban A. Relevance between fibrosis and response to treatment with peginterferon alfa2A vs. alfa2B with ribaviin in chronic hepatitis C genotype 3 patients. Randomized open label study. Hepatology. 2008;48:A878.
Kamal S, Ghoraba D, Nabegh L, et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2A vs. pegylated interferon alfa-2B, plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C genotype 4 patients: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 2009;50:A1025–A1026.
Magni C, Niero F, Argenteri B, et al. Antiviral activity and tolerability between pegylated alpha-2A and alpha-2B in naive patients with chronic hepatitis C: results of a prospective monocentric randomized trial. Hepatology. 2009;50:A720.
Conflict of interest
No financial or any other kind of assistance was received for this study. None of the authors have any disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singal, A.K., Jampana, S.C. & Anand, B.S. Peginterferon Alfa-2a Is Superior to Peginterferon Alfa-2b in the Treatment of Naïve Patients with Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Dig Dis Sci 56, 2221–2226 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1765-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1765-0