Abstract
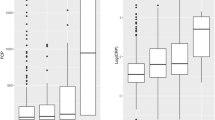
The aim of this study was to prospectively evaluate the correlation between clinical scoring systems and C-reactive protein (CRP) in inflammatory bowel disease. The modified Harvey-Bradshaw index was used in 40 patients (58 assessments) with Crohn’s disease, and the Lichtiger score in 29 patients (36 assessments) with ulcerative colitis. In ulcerative colitis, CRP was elevated in 14%, 42%, 64%, and 83%, respectively, of subjects with quiescent, mild, moderate, and severe disease. There was a linear correlation of log(CRP) with clinical score except for proctitis. In Crohn’s disease, CRP was elevated in 54%, 70%, 75%, and 100%, respectively, of subjects with quiescent, mild, moderate, and severe disease. We conclude that the clinical score has a good correlation with CRP in ulcerative colitis except for proctitis, whereas clinical score has a poor correlation with CRP in Crohn’s disease, particularly in those with clinically quiescent, fibrostenotic, and ileal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camilleri M, Proana M (1989) Advances in the assessment of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Mayo Clin Proc 64:800–807
Gomes P, du Boulay C, Smith CL, Holdstock G (1986) Relationship between disease activity indices and colonoscopic findings in patients with colonic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 27:92–95
Saverymuttu SH, Camilleri M, Rees H, Lavender JP, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS (1986) Indium 111-granulocyte scanning in the assessment of disease extent and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease: a comparison with colonoscopy, histology, and fecal indium 111-granulocyte excretion. Gastroenterology 90:1121–1128
Papi C, Ciaco A, Bianchi M, Montani S, Koch M, Capurso L (1996) Correlation of various Crohn’s disease activity indexes in subgroups of patients with primarily inflammatory or fibrostenosing clinical characteristics. J Clin Gastroenterol 23:40–43
Sachar DB, Smith H, Chan S, Cohen LB, Lichtiger S, Messer J (1986) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate as a measure of clinical activity in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 8:647–650
Prantera C, Davoli M, Lorenzetti R, Pallone F, Marcheggiano A, Iannoni C, Mariotti S (1988) Clinical and laboratory indicators of extent of ulcerative colitis. Serum C-reactive protein helps the most. J Clin Gastroenterol 10:41–45
Fagan EA, Dyck RF, Maton PN, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS, Petrie A, Pepys MB (1989) Serum levels of C-reactive peptide in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Eur J Clin Invest 12:351–359
Sachar DB, Luppescu NE, Bodian C, Shlien RD, Fabry TL, Gumaste VV (1990) Erythrocyte sedimentation as a measure of Crohn’s disease activity: opposite trends in ileitis versus colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 12:643–646
Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern Jr F (1976) Development of a Crohn’s disease activity index: National Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study. Gastroenterology 70:439–444
Lichtiger S, Present DH, Kornbluth A, Gelernt I, Bauer J, Galler G, Michelassi F, Hanauer S (1994) Cyclosporine in severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy. N Engl J Med 330:1841–1845
Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM (1980) A simple index of Crohn’s disease activity. Lancet 1:514
Talstad I, Gjone E (1976) The disease activity of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 11:403–408
Dearing WH, McGuckin WH, Elveback LR (1986) Serum alpha 1-acid glycoprotein in chronic ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 56:295–303
Cooke WT, Prior P (1984) Determining disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 6:17–25
Talstasd I, Gjone E (1976) The disease activity of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 11:403–408
Florin TH, Paterson EW, Fowler EV, Radford-Smith GL (2006) Clinically active Crohn’s disease in the presence of a low C-reactive protein. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:306–311
Savermyuttu SH, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS, Pepys MB (1986) Differing acute phase responses in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut 27:809–813
Vermeire S, Van Assche G, Rutgeerts P (2006) Laboratory markers in IBD: Useful magic, or unnecessary toys? Gut 55:426–432
Chamouard P, Richert Z, Meyer N, Rahmi G, Bauman R (2006) Diagnostic value of C-reactive protein for predicting activity level of Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:882–887
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodgers, A.D., Cummins, A.G. CRP Correlates with Clinical Score in Ulcerative Colitis but Not in Crohn’s Disease. Dig Dis Sci 52, 2063–2068 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9691-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9691-2