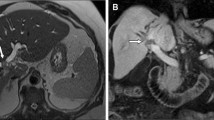
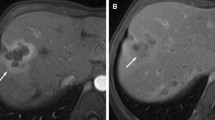
Abstract
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) can lead to the development of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). The tumor may present as an intrahepatic focal cholangiocellular carcinoma but more often as a ductal infiltrating desmoplastic lesion. CCA is found synchronously with the diagnosis of PSC in 20–30% and within 1 year in 50%. During later follow-up, the yearly developmental rate of CCA is 0.5–1.5%. Most patients with PSC and CCA do not yet have cirrhosis but present with a severe stenosis at the hilum of the liver. This type of tumor is difficult to diagnose by imaging techniques.18F-FDG-PET scanning and CEA or CA 19-9 are not early diagnostic tools. Regular MRI, multislice CT, and repeated endoscopically obtained brush cytology of stenotic lesions are recommended. The recent use of more extensive surgical resection techniques in patients with CCA results in 5-year survival rates of ≥50%. If tumors are small or incidental findings, liver transplantation leads to a 3- to 5-year survival rate of 35%. Pretransplant radiotherapy with 5-FU chemosensitization followed by endoscopic brachytherapy with iridium-192 seems to greatly improve the outcome of transplantation. Treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid may prevent development of CCA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
LaRusso NF, Wiesner RH, Ludwig J (1999) Sclerosing cholangitis. In: Bircher J et al. (eds) Oxford textbook of clinical hepatology. Oxford Medical, New York
Jayaram H, Satsangi J, Chapman RW (2001) Increased colorectal neoplasia in chronic ulcerative colitis complicated by primary sclerosing cholangitis:fact or fiction? Gut 48:430–434
Harnois DM, Gores GJ, Ludwig J, Steers JL, LaRusso NF, Wiesner RH (1997) Are patients with cirrhotic stage primary sclerosing cholangitis at risk for the development of hepatocellular cancer? J Hepatol 27:512–516
Bergquist A, Ekbom A, Olsson R, Kornfeldt D, Loof L, Danielsson A, Hultcrantz R, Lindgren S, Prytz H, Sandberg-Gertzen H, Almer S, Granath F, Broome U (2002) Hepatic and extrahepatic malignancies in primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol 36:321–327
Gores GJ (2003) Cholangiocarcinoma: current concepts and insights. Hepatology 37:961– 969
Rosen CB, Nagorney DM, Wiesner RH, Coffey Jr RJ, LaRusso NF (1991) Cholangiocarcinoma complicating primary sclerosing cholangitis. Ann Surg 213:21–25
Nashan B, Schlitt HJ, Tusch G, Oldhafer KJ, Ringe B, Wagner S, Pichlmayr R (1996) Biliary malignancies in primary sclerosing cholangitis: timing for liver transplantation. Hepatology 23:1105–1111
Bergquist A, Glaumann H, Persson B, Broomé U (1998) Risk factors and clinical presentation of hepatobiliary carcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis—a case control study. Hepatology 27:311–316
Boberg KM, Bergquist A, Mitchell S, Pares A, Rosina F, Broome U, Chapman R, Fausa O, Egeland T, Rocca G, Schrumpf E (2002) Cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis: risk factors and clinical presentation. Scand J Gastroenterol 37:1205–1211
Brandsaeter B, Isoniemi H, Broome U, Olausson M, Backman L, Hansen B, Schrumpf E, Oksanen A, Ericzon BG, Hockerstedt K, Makisalo H, Kirkegaard P, Friman S, Bjoro K (2004) Liver transplantation for primary sclerosing cholangitis; predictors and consequences of hepatobiliary malignancy. J Hepatol 40:815–822
Nakeeb A, Tran KQ, Black MJ, Erickson BA, Ritch PS, Quebbeman EJ, Wilson SD, Demeure MJ, Rilling WS, Dua KS, Pitt HA (2002) Improved survival in resected biliary malignancies. Surgery 132:555–563
Anderson, CD, Pinson CW, Berlin J, Chari RS (2004) Diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Oncologist 9:43–57
Stiehl A, Rudolph G, Kloters-Plachky P, Sauer P, Walker S (2002) Development of dominant bile duct stenoses in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis treated with ursodeoxycholic acid: outcome after endoscopic treatment. J Hepatol 36:151–156
Okolicsanyi L, Fabris L, Viaggi S, Carulli N, Podda M, Ricci G (1996) Primary sclerosing cholangitis: clinical presentation, natural history and prognostic variables: an Italian multicentre study. Eur J Gastro Hepatol 8:685–691
Lindberg B, Arnelo U, Bergquist A, Thorne A, Hjerpe A, Granqvist S, Hansson LO, Tribukait B, Persson B, Broome U (2002) Diagnosis of biliary strictures in conjunction with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreaticography, with special reference to patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Endoscopy 34:909–916
Campbell WL, Ferris JV, Holbert BL, Thaete FL, Baron RL (1998) Biliary tract carcinoma complicating primary sclerosing cholangitis: evaluation with CT, cholangiography, US, and MR imaging. Radiology 207:41–50
American Joint Committee on Cancer (2005) AJCC cancer staging. Springer Verlag, New York
Sirica AE (2005) Cholangiocarcinoma:molecular targeting strategies for chemoprevention and therapy. Hepatology 41:5–15
Jaiswal M, LaRusso NF, Shapiro RA, Billiar TR, Gores GJ (2001) Nitric oxide-mediated inhibition of DNA repair potentiates oxidative DNA damage in cholangiocytes. Gastroenterology 120:190–199
Ahrendt SA, Rashid A, Chow JT, Eisenberger CF, Pitt HA, Sidransky D (2000) p53 overexpression and K ras gene mutations in primary sclerosing cholangitis-associated biliary tract cancer. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 7:426–431
Boberg KM, Schrumpf E, Bergquist A, Broome U, Pares A, Remotti H, Schjolberg A, Spurkland A, Clausen OP (2000) Cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis: K-ras mutations and Tp53 dysfunction are implicated in the neoplastic development. J Hepatol 32:374–380
Kubicka S, Kuhnel F, Flemming P, Hain B, Kezmic N, Rudolph KL, Manns M, Meier PN (2001) K-ras mutations in the bile of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 48:403–408
Rizzi PM, Ryder SD, Portmann B, Ramage JK, Naoumov NV, Williams R (1996) p53 Protein overexpression in cholangiocarcinoma arising in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 38:265–268
Ahrendt SA, Eisenberger CF, Yip L, Rashid A, Chow JT, Pitt HA, Sidransky D (1999) Chromosome 9p21 loss and p16 inactivation in primary sclerosing cholangitis-associated cholangiocarcinoma. J Surg Res 84:88–93
Kornfeld D, Ekbom A, Ihre T (1997) Survival and risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. A population-based study. Scand J Gastroenterol 32:1042–1045
Burak K, Angulo P, Pasha TM, Egan K, Petz J, Lindor KD (2004) Incidence and risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol 99:523–526
Chalasani N, Baluyut A, Ismail A, Zaman A, Sood G, Ghalib R, McCashland TM, Reddy KR, Zervos X, Anbari MA, Hoen H (2000) Cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: a multicenter case-control study. Hepatology 31:7–11
Broome U, Lofberg R, Veress B, Eriksson LS (1995) Primary sclerosing cholangitis and ulcerative colitis: evidence for increased neoplastic potential. Hepatology 22:1404–1408
Leidenius M, Hockersted K, Broome U, Ericzon BG, Friman S, Olausson M, Schrumpf E (2001) Hepatobiliary carcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis: a case control study. J Hepatol 34:792–798
Ahrendt SA, Pitt HA, Nakeeb A, Klein AS, Lillemoe KD, Kalloo AN, Cameron JL (1999) Diagnosis and management in cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Gastrointest Surg 3:357–368
Farrant JM, Hayllar KM, Wilkinson ML, Karani J, Portmann BC, Westaby D, Williams R (1991) Natural history and prognostic variables in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology 100:1710–1717
Schrumpf E, Abdelnoor M, Fausa O, Elgjo K, Jenssen E, Kolmannskog F (1994) Risk factors in primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol 21:1061–1066
Broome U, Olsson R, Loof L, Bodemar G, Hultcrantz R, Danielsson A, Prytz H, Sandberg-Gertzen H, Wallerstedt S, Lindberg G (1996) Natural history and prognostic factors in 305 Swedish patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 38:610–615
Goss JA, Shackleton CR, Farmer DG, Arnaout WS, Seu P, Markowitz JS, Martin P, Stribling RJ, Goldstein LI, Busuttil RW (1997) Orthotopic liver transplantation for primary sclerosing cholangitis: a 12-year single centre experience. Ann Surg 225:472–483
Björnsson E, Kilander A, Olsson R (1999) CA19-9 and CEA are unreliable markers for cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Liver 19:501–508
Hultcrantz R, Olsson R, Danielsson A, Jarnerot G, Loof L, Ryden BO, Wahren B, Broome U (1999) A 3-year prospective study on serum tumor markers used for detecting cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol 30:669–673
Vleggaar FP (2000) The risk and prognostic significance of major clinical events, in particular biliary complications, in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Chapter 7 in ``Advances in classification, prognostication and treatment of immunocholangitis.'' PhD thesis, University of Rotterdam.
Kaya M, de Groen PC, Angulo P, Nagorney DM, Gunderson LL, Gores GJ, Haddock MG, Lindor KD (2001) Treatment of cholangiocarcinoma complicating primary sclerosing cholangitis: the Mayo Clinic experience. Am J Gastroenterol 96:1164–1169
Ponsioen CY, Vrouenraets SM, Prawirodirdjo W, Rajaram R, Rauws EA, Mulder CJ, Reitsma JB, Heisterkamp SH, Tytgat GN (2002) Natural history of primary sclerosing cholangitis and prognostic value of cholangiography in a Dutch population. Gut 51:562–566
Bjornsson E, Lindqvist-Ottosson J, Asztely M, Olsson R (2004) Dominant strictures in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol 99:502–508
Solano E, Khakhar A, Bloch M, Quan D, McAlister V, Ghent C, Wall W, Marotta P (2003) Liver transplantation for primary sclerosing cholangitis. Transplant Proc 35:2431–2434
Ito K, Mitchell DG, Outwater EK, Blasberg R (1999) Primary sclerosing cholangitis: MR imaging features. Am J Roentgen 172:1527–1533
Angulo P, Pearce DH, Johnson CD, Henry JJ, LaRusso NF, Petersen BT, Lindor KD (2000) Magnetic resonance cholangiography in patients with biliary disease: its role in primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol 33:520–527
Clayton RA, Clarke DL, Currie EJ, Madhavan KK, Parks RW, Garden OJ (2003) Incidence of benign pathology in patients undergoing hepatic resection for suspected malignancy. Surgeon 1:32–38
Corvera CU, Blumgart LH, Darvishian F, Klimstra DS,DeMatteo R, Fong Y, D’Angelica M, Jarnagin WR (2005) Clinical and pathologic features of proximal biliary strictures masquerading as hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 201:862–869
Zandrino F, Curone P, Benzi L, Ferretti ML, Musante F (2005) MR versus multislice CT cholangiography in evaluating patients with obstruction of the biliary tract. Abdom Imaging 30:77–85
Keiding S, Hansen SB, Rasmussen HH, Gee A, Kruse A, Roelsgaard K, Tage-Jensen U, Dahlerup JF (1998) Detection of cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis by positron emission tomography. Hepatology 28:700–706
Fevery J, Buchel O, Nevens F, Verslype C, Stroobants S, Van Steenbergen W (2005) Positron emission tomography is not a reliable method for the early diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol 43:358– 360
Anderson CD, Rice MH, Pinson CW, Chapman WC, Chari RS, Delbeke D (2004) Fluorodeoxyglucose PET imaging in the evaluation of gallbladder carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 8:90–97
Fritscher-Ravens A, Broering DC, Knoefel WT, Rogiers X, Swain P, Thonke F, Bobrowski C, Topalidis T, Soehendra N (2004) EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration of suspected hilar cholangiocarcinoma in potentially operable patients with negative brush cytology. Am J Gastroenterol 99:45–51
Eloubeidi MA, Chen VK, Jhala NC, Eltoum IE, Jhala D, Chhieng DC, Syed SA, Vickers SM, Mel Wilcox C (2004) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy of suspected cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:209–213
Nichols JC, Gores GJ, LaRusso NF, Wiesner RH, Nagorney DM, Ritts Jr RE (1993) Diagnostic role of serum CA 19-9 for cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Mayo Clin Proc 68:874–879
Ramage JK, Donaghy A, Farrant JM, Iorns R, Williams R (1995) Serum tumor markers for the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology 108:865– 869
Fisher A, Theise ND, Min A, Mor E, Emre S, Pearl A, Schwartz ME, Miller CM, Sheiner PA (1995) CA19-9 does not predict cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis undergoing liver transplantation. Liver Transpl Surg 1:94–98
Siqueira E, Schoen RE, Silverman W, Martin J, Rabinovitz M, Weissfeld JL, Abu-Elmaagd K, Madariaga JR, Slivka A, Martini J (2002) Detecting cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastrointest Endosc 56:40–47
Levy C, Lymp J, Angulo P, Gores GJ, LaRusso N, Lindor KD (2005) The value of serum CA 19-9 in predicting cholangiocarcinomas in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Dig Dis Sci 50:1734–1740
Albert MB, Steinberg WM, Henry JP (1988) Elevated serum levels of tumor marker CA 19-9 in acute cholangitis. Dig Dis Sci 33:1223–1225
Petersen-Benz C, Stiehl A (2005) Impact of dominant stenoses on the serum level of the tumor marker CA19-9 in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Z Gastroenterol. 43:587–590
Ponsioen CY, Vrouenraets SM, van Milligen de Wit AW, Sturm P, Tascilar M, Offerhaus GJ, Prins M, Huibregtse K, Tytgat GN (1999) Value of brush cytology for dominant strictures in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Endoscopy 31:305–309
Rabinovitz M, Zajko AB, Hassanein T, Shetty B, Bron KM, Schade RR, Gavaler JS, Block G, Van Thiel DH, Dekker A (1990) Diagnostic value of brush cytology in the diagnosis of bile duct carcinoma: a study in 65 patients with bile duct strictures. Hepatology 12:747–752
Lal A, Okonkwo A, Schindler S, De Frias D, Nayar R (2004) Role of biliary brush cytology in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Acta Cytol 48:9–12
Kipp BR, Stadheim LM, Halling SA, et al. (2004) A comparison of routine cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of malignant bile duct strictures. Am J Gastroenterol 99:1675–1681
Ponsioen CY, Lam K, van Milligen de Wit AW, Huibregtse K, Tytgat GN (1999) Four years experience with short term stenting in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol 94:2403–2407
Ahrendt SA, Pitt HA, Kalloo AN, Venbrux AC, Klein AS, Herlong HF, Coleman J, Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL (1998) Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Resect, dilate, or transplant? Ann Surg 227:412–423
Pichlmayr R, Weimann A, Klempnauer J, Oldhafer KJ, Maschek H, Tusch G, Ringe B (1996) Surgical treatment in proximal bile duct cancer. A single-center experience. Ann Surg 224:628–638
Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL (2000) Surgery for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: the Johns Hopkins approach. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 7:115–121
Nimura Y, Kamiya J, Kondo S, Nagino M, Uesaka K, Oda K, Sano T, Yamamoto H, Hayakawa N (2000) Aggressive preoperative management and extended surgery for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: Nagoya experience. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 7:155–162
Lee SG, Lee YJ, Park KM, Hwang S, Min PC (2000) One hundred and eleven liver resections for hilar bile duct cancer. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 7:135–141
Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, De Matteo RP, Gonen M, Burke EC, Bodniewicz J, Youssef M, Klimstra D, Blumgart LH (2001) Staging, resectability and outcome in 225 patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 234:507– 519
Ebata T, Nagino M, Kamiya J, Uesaka K, Nagasaka T, Nimura Y (2003) Hepatectomy with portal vein resection for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: audit of 52 consecutive cases. Ann Surg 238:720–727
Neuhaus P, Jonas S, Settmacher U, Thelen A, Benckert C, Lopez-Hanninen E, Hintze RE (2003) Surgical management of proximal bile duct cancer: extended right lobe resection increases resectability and radicality. Langenbecks Arch Surg 388:194–200
Hemming AW, Reed AI, Fujita S, Foley DP, Howard RJ (2005) Surgical management of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 241:693–699
Nagino M, Kamiya J, Nishio H, Ebata T, Arai T, Nimura Y (2006) Two hundred forty consecutive portal vein embolizations before extended hepatectomy for biliary cancer: surgical outcome and long-term follow-up. Ann Surg 243:364–372
Abdel Wahab AM, Fathy O, Elghwalby N, Sultan A, Elebidy E, Abdalla T, Elshobary M, Mostafa M, Foad A, Kandeel T, Abdel Raouf A, Salah T, Abu Zeid M, Abu Elenein A, Gad Elhak N, ElFiky A, Ezzat F (2006) Resectability and prognostic factors after resection of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 53:5–10
Otto G (2007) Diagnostic and surgical approaches in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis 22:101–108
Tsao JI, Nimura Y, Kamiya J, Hayakawa N, Kondo M, Uesaka K, Oda K, Rossi RL, Braasch JW, Dugan JM (2000) Management of hilar cholangiocarcinoma: comparison of an American and Japanese experience. Ann Surg 232:166–174
Zervos EE, Osborne D, Goldin SB, Villadolid DV, Thometz DP, Durkin A, Carey LC, Rosemurgy AS (2005) Stage does not predict survival after resection of hilar cholangiocarcinomas promoting an aggressive operative approach. Am J Surg 190:810– 815
Nakeeb A, Tran KQ, Black MJ, Erickson BA, Ritch PS, Quebbeman EJ, Wilson SD, Demeure MJ, Rilling WS, Dua KS, Pitt HA (2002) Improved survival in resected biliary malignancies. Surgery 132:555–563
Todoroki T, Ohara K, Kawamoto T, Koike N, Yoshida S, Kashiwagi H, Otsuka M, Fukao K (2000) Benefits of adjuvant radiotherapy after radical resection of locally advanced main hepatic duct carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:581–587
Itoh H, Nishijima K, Kurosaka Y, Takegawa S, Kiriyama M, Dohba S, Kojima Y, Saitoh Y (2005) Magnitude of combination therapy of radical resection and external beam radiotherapy for patients with carcinomas of the extrahepatic bile duct and gallbladder. Dig Dis Sci 50:2231–2242
Jan YY, Yeh CN, Yeh TS, Chen TC (2005) Prognostic analysis of surgical treatment of peripheral cholangiocarcinoma: two decades of experience at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. World J Gastroenterol 11:1779–1784
Madariaga JR, Iwatsuki S, Todo S, Lee RG, Irish W, Starzl TE (1998) Liver resection for hilar and peripheral cholangiocarcinomas: a study of 62 cases. Ann Surg 227:70–79
Graziadei IW, Wiesner RH, Marotta PJ, Porayko MK, Hay JE, Charlton MR, Poterucha JJ, Rosen CB, Gores GJ, LaRusso NF, Krom RA (1999) Long-term results of patients undergoing liver transplantation for primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 30:1121–1127
Maheshwari A, Yoo HY, Thuluvath PJ (2004) Long-term outcome of liver transplantation in patients with PSC: a comparative analysis with PBC. Am J Gastroenterol 99:538–542
Ghali P, Marotta PJ, Yoshida EM, Bain VG, Marleau D, Peltekian K, Metrakos P, Deschênes M (2005) Liver transplantation for incidental cholangiocarcinoma: analysis of the Canadian experience. Incidental CCA was documented in 8 patients with PSC, transplanted between 1996 and 2003. The 3-year survival rate was 30%. Liver Transpl 11:1412–1416
Meyer CG, Penn I, James L (2000) Liver transplantation for cholangiocarcinoma: results in 207 patients. Transplantation 69:1633–1637
Robles R, Figueras J, Turrion VS, Margarit C, Moya A, Varo E, Calleja J, Valdevieso A, Valdecasas JCG, Lopez P, Gomez M, de Vicente E, Loinaz C, Santoyo J, Fleitas M, Bernados A, Llado L, Ramirez P, Bueno FS, Jaurrieta E, Parrilla P (2004) Spanish experience in liver transplantation for hilar and peripheral cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 239:265–271
Bjøro K, Brandsæter B, Foss A, Schrumpf E (2005) Liver transplantation in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Sem Liver Dis 26:69–79
Pascher A, Jonas S, Neuhaus P (2003) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: indication for transplantation. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 10:282–287
Rea DJ, Heimbach JK, Rosen CB, Haddock MG, Alberts SR, Kremers WK, Gores GJ, Nagorney DM (2005) Liver transplantation with neoadjuvant chemoradiation is more effective than resection for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 242:451– 461
Sudan D, DeRoover A, Chinnakotla S, Fox I, Shaw Jr B, McCashland T, Sorrell M, Tempero M, Langnas A (2002) Radiochemotherapy and transplantation allow long-term survival for nonresectable hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Transplant 2:774–779
Blendis L, Lurie Y (2002) Primary sclerosing cholangitis: a premalignant condition. Gastroenterology 123:647–648
Alpini G, Glaser SS, Ueno Y, Rodgers R, Phinizy JL, Francis H, Baiocchi L, Holcomb LA, Caligiuri A, LeSage GD (1999) Bile acid feeding induces cholangiocyte proliferation and secretion: evidence for bile acid-regulated ductal secretion. Gastroenterology 116:179–186
Alpini G, Kanno N, Phinizy JL, Glaser S, Francis H, Taffetani S, LeSage G (2004) Tauroursodeoxycholate inhibits human cholangiocarcinoma growth via Ca2+-, PKC-, and MAPK-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G973–G982
Tung BY, Emond MJ, Haggitt RC, Bronner MP, Kimmey MB, Kowdley KV, Brentnall TA (2001) Ursodiol use is associated with lower prevalence of colonic neoplasia in patients with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Ann Intern Med 134:89–95
Pardi DS, Loftus Jr EV, Kremers WK, Keach J, Lindor KD (2003) Ursodeoxycholic acid as a chemopreventive agent in patients with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology 124:889–893
Serfaty L, De Leusse A, Rosmorduc O, Desaint B, Flejou JF, Chazouilleres O, Poupon RE, Poupon R (2003) Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy and the risk of colorectal adenoma in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: an observational study. Hepatology 38:203–209
Alberts DS, Martinez ME, Hess LM, Einspahr JG, Green SB, Bhattacharyya AK, Guillen J, Krutzsch M, Batta AK, Salen G, Fales L, Koonce K, Parish D, Clouser M, Roe D, Lance P, Phoenix and Tucson Gastroenterologist Networks (2005) Phase III trial of ursodeoxycholic acid to prevent colorectal adenoma recurrence. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:846–853
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fevery, J., Verslype, C., Lai, G. et al. Incidence, Diagnosis, and Therapy of Cholangiocarcinoma in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Dig Dis Sci 52, 3123–3135 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9681-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9681-4