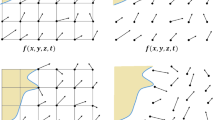
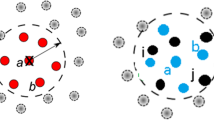
Abstract
Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a Lagrangian method based on a meshless discretization of partial differential equations. In this review, we present SPH discretization of the Navier-Stokes and advection-diffusion-reaction equations, implementation of various boundary conditions, and time integration of the SPH equations, and we discuss applications of the SPH method for modeling pore-scale multiphase flows and reactive transport in porous and fractured media.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tartakovsky, A.M., Ward, A.L., Meakin, P.: Pore-scale simulations of drainage of heterogeneous and anisotropic porous media. Phys. Fluids 19(10), 103301 (2007)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Redden, G., Lichtner, P., Scheibe, T., Meakin, P.: Mixing-induced precipitation: experimental study and multi-scale numerical analysis. Water Resour. Res. 44, W06S04 (2008)
Battiato, I., Tartakovsky, D.M., Tartakovsky, A.M., Scheibe, T.D.: Hybrid models of reactive transport in porous and fractured media. Adv. Water Resour. 34(9), 1140–1150 (2011)
Tartakovsky, A., Scheibe, T.: Dimension reduction numerical closure method for advection-diffusion-reaction systems. Adv. Water Resour. 34(12), 1616–1626 (2011)
de Anna, P., Borgne, T.L., Dentz, M., Tartakovsky, A.M., Bolster, D., Davy, P.: Flow intermittency, dispersion, and correlated continuous time random walks in porous media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(18), 184502 (2013)
Tartakovsky, A. M.: Langevin model for reactive transport in porous media. Phys. Rev. E. 82(2), 026302 (2010)
Ovaysi, S., Piri, M.: Direct pore-level modeling of incompressible fluid flow in porous media. J. Comput. Phys. 229(19), 7456–7476 (2010)
Meakin, P., Tartakovsky, A.M.: Modeling and simulation of pore scale multiphase fluid flow and reactive transport in fractured and porous media. Rev. Geophys. 47, RG3002 (2009)
Monaghan, J.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68(8), 1703 (2005)
Antuono, M., Colagrossi, A., Marrone, S., Molteni, D.: Free-surface flows solved by means of sph schemes with numerical diffusive terms. Comput. Phys. Commun. 181(3), 532–549 (2010)
Pan, W., Tartakovsky, A., Monaghan, J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics non-newtonian model for ice-sheet and ice-shelf dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 242(0), 828–842 (2013)
Monaghan, J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its diverse applications. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 44, 323–346 (2012)
Tanner, L.H.: The spreading of silicone oil drops on horizontal surfaces. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. Email Alert RSS Feed 12(9), 1473 (1979)
de Gennes, P.: Wetting: statics and dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 57(3), 827–863 (1985)
Dussan V, E.: On the spreading of liquids on solid surfaces: static and dynamic contact lines. Annu. Rev. Fluid Dyn. 11, 371–400 (1979)
Huh, C., Scriven, L.: Hydrodynamic model of steady movement of a solid/liquid/fluid contact line. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 35(1), 85–101 (1971)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Meakin, P.: Pore scale modeling of immiscible and miscible fluid flows using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Adv. Water Resour. 29(10), 1464–1478 (2006)
Quinlan, N.J., Basa, M., Lastiwka, M.: Truncation error in mesh-free particle methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 66(13), 2064–2085 (2006)
Brackbill, J., Kothe, D.B., Zemach, C.: A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 100(2), 335–354 (1992)
Kordilla, J., Tartakovsky, A., Geyer, T.: A smoothed particle hydrodynamics model for droplet and film flow on smooth and rough fracture surfaces. Adv. Water Resour. 59(0), 1–14 (2013)
Zhou, G., Ge, W., Li, J.: A revised surface tension model for macro-scale particle methods. Powder Technol. 183(1), 21–26 (2008)
Nugent, S., Posch, H.: Liquid drops and surface tension with smoothed particle applied mechanics. Phys. Rev. E 62(4), 4968 (2000)
Meleán, Y., Sigalotti, L.D.G., Hasmy, A.: On the sph tensile instability in forming viscous liquid drops. Comput. Phys. Commun. 157(3), 191–200 (2004)
Meleán, Y., Sigalotti, L.D.G.: Coalescence of colliding van der waals liquid drops. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 48(19), 4041–4061 (2005)
Bandara, U., Tartakovsky, A., Oostrom, M., Palmer, B., Grate, J., Zhang, C.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics pore-scale simulations of unstable immiscible flow in porous media, Advances in Water Resources 62, Part C (0) (2013) 356–369
Young, T.: An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 95, 65–87 (1805)
Maxwell, J.: The Scientific Papers of J.M. Maxwell, Capillary Actions, vol. 2, p. 541. Cambridge University Press (1890)
Rayleigh, L.: On the theory of surface forces. In: Collected Papers, vol. 3, Art. 176, pp. 397–425. Dover, New York (1964)
Morris, J. P.: Simulating surface tension with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 33(3), 333–353 (2000)
Hu, X., Adams, N.: A multi-phase {SPH} method for macroscopic and mesoscopic flows. J. Comput. Phys. 213(2), 844–861 (2006)
Graham, D.I., Hughes, J.P.: Accuracy of sph viscous flow models. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 56(8), 1261–1269 (2008)
Basa, M., Quinlan, N.J., Lastiwka, M.: Robustness and accuracy of sph formulations for viscous flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 60(10), 1127–1148 (2009)
Fatehi, R., Manzari, M.: Error estimation in smoothed particle hydrodynamics and a new scheme for second derivatives. Comput. Math. Appl. 61(2), 482–498 (2011)
Hashemi, M., Fatehi, R., Manzari, M.: A modified sph method for simulating motion of rigid bodies in newtonian fluid flows. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 47(6), 626–638 (2012)
Chorin, A.J.: A numerical method for solving incompressible viscous flow problems. J. Comput. Phys. 2(1), 12–26 (1967)
Tamamidis, P., Zhang, G., Assanis, D.N.: Comparison of pressure-based and artificial compressibility methods for solving 3d steady incompressible viscous flows. J. Comput. Phys. 124(1), 1–13 (1996)
Morris, J.P., Fox, P.J., Zhu, Y.: Modeling low reynolds number incompressible flows using sph. J. Comput. Phys. 136(1), 214–226 (1997)
Monaghan, J.J.: Simulating free surface flows with sph. J. Comput. Phys. 110(2), 399–406 (1994)
Lastiwka, M., Basa, M., Quinlan, N.J.: Permeable and non-reflecting boundary conditions in sph. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 61(7), 709–724 (2009)
Swegle, J., Hicks, D., Attaway, S.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics stability analysis. J. Comput. Phys. 116(1), 123–134 (1995)
Balsara, D.S.: Von neumann stability analysis of smoothed particle hydrodynamics—suggestions for optimal algorithms. J. Comput. Phys. 121(2), 357–372 (1995)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Meakin, P., Scheibe, T.D., Eichler West, R.M.: Simulations of reactive transport and precipitation with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 222(2), 654–672 (2007)
Holmes, D.W., Williams, J.R., Tilke, P.: Smooth particle hydrodynamics simulations of low reynolds number flows through porous media. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 35(4), 419–437 (2011)
Cummins, S.J., Rudman, M.: An sph projection method. J. Comput. Phys. 152(2), 584–607 (1999)
Lee, E-S, Moulinec, C., Xu, R., Violeau, D., Laurence, D., Stansby, P.: Comparisons of weakly compressible and truly incompressible algorithms for the sph mesh free particle method. J. Comput. Phys. 227(18), 8417–8436 (2008)
Xu, R., Stansby, P., Laurence, D.: Accuracy and stability in incompressible sph (isph) based on the projection method and a new approach. J. Comput. Phys. 228(18), 6703–6725 (2009)
Hosseini, S.M., Feng, J.J.: Pressure boundary conditions for computing incompressible flows with sph. J. Comput. Phys. 230(19), 7473–7487 (2011)
Litvinov, S., Ellero, M., Hu, X., Adams, N.: A splitting scheme for highly dissipative smoothed particle dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 229(15), 5457–5464 (2010)
Trask, N., Maxey, M., Kim, K., Perego, M., Parks, M. L., Yang, K., Xu, J.: A scalable consistent second-order sph solver for unsteady low reynolds number flows, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2014.12.027
Domínguez, J.M., Crespo, A.J., Valdez-Balderas, D., Rogers, B., Gómez-Gesteira, M.: New multi-gpu implementation for smoothed particle hydrodynamics on heterogeneous clusters, Computer Physics Communications
Tartakovsky, A., Meakin, P.: Modeling of surface tension and contact angles with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. E 72(2), 026301 (2005)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Meakin, P.: Simulation of free-surface flow and injection of fluids into fracture apertures using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Vadose Zone J. 4(3), 848–855 (2005)
Allen, M.P., Tildesley, D.J.: Computer simulation of liquids. Oxford university press (1989)
Monaghan, J.: Simulating free surface flows with {SPH}. J. Comput. Phys. 110(2), 399–406 (1994)
Gomez-Gesteira, M., Rogers, B.D., Crespo, A.J.C., Dalrymple, R. A., Narayanaswamy, M., Dominguez, J. M.: Sphysics - development of a free-surface fluid solver—part 1: Theory and formulations. Comput. Geosci. 48, 289–299 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2012.02.029
Liu, G. R., Liu, M.B.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: a meshfree particle method. World Scientific Publishing (2003)
Monaghan, J.J.: Sph without a tensile instability. J. Comput. Phys. 159(2), 290–311 (2000)
Maciá, F., Antuono, M., González, L.M., Colagrossi, A.: Theoretical analysis of the no-slip boundary condition enforcement in sph methods. Prog. Theor. Phys. 125(6), 1091–1121 (2011)
Takeda, H., Miyama, S.M., Sekiya, M.: Numerical simulation of viscous flow by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Prog. Theor. Phys. 92(5), 939–960 (1994)
Pan, W., Bao, J., Tartakovsky, A.M.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics continuous boundary force method for navier-stokes equations subject to a robin boundary condition. J. Comput. Phys. 259(0), 242–259 (2014)
Ryan, E.M., Tartakovsky, A.M., Amon, C.: A novel method for modeling neumann and robin boundary conditions in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 181(12), 2008–2023 (2010)
Ryan, E., Tartakovsky, A., Recknagle, K., Khaleel, M., Amon, C.: Pore-scale modeling of the reactive transport of chromium in the cathode of a solid oxide fuel cell. J. Power Sources 196(1), 287–300 (2011)
Ryan, E.M., Tartakovsky, A.M., Amon, C.: Pore-scale modeling of competitive adsorption in porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 120-121(0), 56–78 (2011)
Bocquet, L., Barrat, J-L.: Flow boundary conditions from nano-to micro-scales. Soft Matter 3(6), 685–693 (2007)
Peskin, C.S.: The immersed boundary method. Acta numerica 11, 479–517 (2002)
Li, X., Lowengrub, J., Rätz, A., Voigt, A.: Solving pdes in complex geometries: a diffuse domain approach. Commun. Math. Sci. 7(1), 81 (2009)
Pereira, G., Prakash, M., Cleary, P.: {SPH} modelling of fluid at the grain level in a porous medium. Appl. Math. Model. 35(4), 1666–1675 (2011)
Zhang, C., Oostrom, M., Wietsma, T.W., Grate, J.W., Warner, M.G.: Influence of viscous and capillary forces on immiscible fluid displacement: Pore-scale experimental study in a water-wet micromodel demonstrating viscous and capillary fingering. Energy and Fuels 25(8), 3493–3505 (2011)
Gouet-Kaplan, M., Tartakovsky, A.M., Berkowitz, B.: Interplay of resident and infiltrating water. Water Resour. Res. 45, W05416 (2009)
Du, Q., Lehoucq, R., Tartakovsky, A.: Integral approximations to classical diffusion and smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 286, 216–229 (2015). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045782514004988
Tartakovsky, G., Tartakovsky, A., Scheibe, T., Fang, Y., Mahadevan, R., Lovley, D.: Pore-scale simulation of microbial growth using a genome-scale metabolic model: implications for darcy-scale reactive transport. Adv. Water Resour. 59(0), 256–270 (2013)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Meakin, P., Scheibe, T., Wood, B.: A smoothed particle hydrodynamics model for reactive transport and mineral precipitation in porous and fractured porous media. Water Resour. Res. 43, W05437 (2007)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Scheibe, T.D., Meakin, P.: Pore-scale model for reactive transport and biomass growth. J. Porous Media 12(5), 417–434 (2009)
Tartakovsky, A., Meakin, P., Ward, A.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics model of non-aqueous phase liquid flow and dissolution. Transp. Porous Media 76, 11–34 (2009)
Pereira, G.G., Dupuy, P.M., Cleary, P.W., Delaney, G.W.: Comparison of permeability of model porous media between sph and lb, Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, an International Journal 12 (2) (2012) 176–186
Monaghan, J., Kajtar, J.: Sph particle boundary forces for arbitrary boundaries. Comput. Phys. Commun. 180(10), 1811–1820 (2009)
Peskin, C.S., McQueen, D.M.: A three-dimensional computational method for blood flow in the heart i. immersed elastic fibers in a viscous incompressible fluid. J. Comput. Phys. 81(2), 372–405 (1989)
Hérault, A., Bilotta, G., Dalrymple, R.A.: Sph on gpu with cuda. J. Hydraul. Res. 48(S1), 74–79 (2010)
Springel, V., Yoshida, N., White, S.D.: Gadget: a code for collisionless and gasdynamical cosmological simulations. New Astron. 6(2), 79–117 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tartakovsky, A.M., Trask, N., Pan, K. et al. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications for multiphase flow and reactive transport in porous media. Comput Geosci 20, 807–834 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-015-9468-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-015-9468-9