Abstract
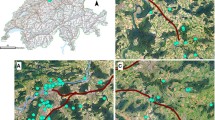
Roads are of major concern in conservation biology, as they are known to restrict animal movements through landscape fragmentation, and may therefore impact genetic patterns in native terrestrial organisms. We assessed the effect of two large-scale transportation infrastructures (LTIs), a 40-year-old highway and a 30 year-old high-speed railway, on the spatial genetic structure of the alpine newt Ichthyosaura alpestris, a highly nomadic amphibian. Genetic data were gathered following a targeted individual-based sampling scheme and analysed using both overlay and correlative methods. While simulations suggested that the highway may be old enough for a significant barrier effect to be detected, LTIs were never detected as barriers to gene flow: inferred genetic boundaries rather coincided with transition zones between major landscape entities. Furthermore, spatial principal component analysis, a method designed to reveal cryptic genetic spatial patterns in high gene flow species, counter-intuitively suggested that the highway may act as a potential dispersal corridor in low-quality habitats, thus challenging traditional hypotheses on road impacts in amphibians. Our study showed that considering local interactions between species, infrastructures and landscape-specific characteristics is essential for better understanding the potential impacts of roads on movement patterns in terrestrial organisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaensen F, Chardon JP, De Blust G, Swinnen E, Villalba S, Gulinck H, Matthysen E (2003) The application of ‘least-cost’ modelling as a functional landscape model. Landsc Urban Plan 64(4):233–247. doi:10.1016/s0169-2046(02)00242-6
Anderson CD, Epperson BK, Fortin MJ, Holderegger R, James PMA, Rosenberg MS, Scribner KT, Spear S (2010) Considering spatial and temporal scale in landscape-genetic studies of gene flow. Mol Ecol 19(17):3565–3575. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04757.x
Balkenhol N, Waits LP (2009) Molecular road ecology: exploring the potential of genetics for investigating transportation impacts on wildlife. Mol Ecol 18(20):4151–4164. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04322.x
Bartoszek J, Greenwald KR (2009) A population divided: railroad tracks as barriers to gene flow in an isolated population of marbled salamanders (Ambystoma opacum). Herpetol Conserv Biol 4(2):191–197
Beebee TJC (2013) Effects of road mortality and mitigation measures on amphibian populations. Conserv Biol 27(4):657–668. doi:10.1111/cobi.12063
Beerli P (2004) Effect of unsampled populations on the estimation of population sizes and migration rates between sampled populations. Mol Ecol 13(4):827–836. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02101.x
Blair C, Weigel DE, Balazik M, Keeley ATH, Walker FM, Landguth E, Cushman S, Murphy M, Waits L, Balkenhol N (2012) A simulation-based evaluation of methods for inferring linear barriers to gene flow. Mol Ecol Resour 12(5):822–833. doi:10.1111/j.1755-0998.2012.03151.x
Bonte D, Van Dyck H, Bullock JM, Coulon A, Delgado M, Gibbs M, Lehouck V, Matthysen E, Mustin K, Saastamoinen M, Schtickzelle N, Stevens VM, Vandewoestijne S, Baguette M, Barton K, Benton TG, Chaput-Bardy A, Clobert J, Dytham C, Hovestadt T, Meier CM, Palmer SCF, Turlure C, Travis JMJ (2012) Costs of dispersal. Biol Rev 87:290–312. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2011.00201.x
Borcard D, Legendre P (2012) Is the Mantel correlogram powerful enough to be useful in ecological analysis? A simulation study. Ecology 93(6):1473–1481
Brisson J, de Blois S, Lavoie C (2010) Roadside as invasion pathway for common reed (Phragmites australis). Invasive Plant Sci Manag 3(4):506–514. doi:10.1614/ipsm-09-050.1
Broquet T, Ray N, Petit E, Fryxell JM, Burel F (2006) Genetic isolation by distance and landscape connectivity in the American marten (Martes americana). Landsc Ecol 21(6):877–889. doi:10.1007/s10980-005-5956-y
Broquet T, Berset-Braendli L, Emaresi G, Fumagalli L (2007) Buccal swabs allow efficient and reliable microsatellite genotyping in amphibians. Conserv Genet 8(2):509–511. doi:10.1007/s10592-006-9180-3
Brown GP, Phillips BL, Webb JK, Shine R (2006) Toad on the road: use of roads as dispersal corridors by cane toads (Bufo marinus) at an invasion front in tropical Australia. Biol Conserv 133(1):88–94. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2006.05.020
Chen C, Durand E, Forbes F, Francois O (2007) Bayesian clustering algorithms ascertaining spatial population structure: a new computer program and a comparison study. Mol Ecol Notes 7(5):747–756. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01769.x
Cosentino BJ, Schooley RL, Phillips CA (2011) Connectivity of agroecosystems: dispersal costs can vary among crops. Landsc Ecol 26(3):371–379. doi:10.1007/s10980-010-9563-1
Cushman SA, McKelvey KS, Hayden J, Schwartz MK (2006) Gene flow in complex landscapes: testing multiple hypotheses with causal modeling. Am Nat 168(4):486–499
Cushman SA, Wasserman TN, Landguth EL, Shirk AJ (2013) Re-evaluating causal modeling with Mantel tests in landscape genetics. Diversity 5(1):51–72. doi:10.3390/d5010051
Denoel M (2005) Persistence and dispersion of an introduced population of alpine newt (Triturus alpestris) in the limestone plateau of Larzac (Southern France). Revue d’Ecologie-La Terre et la Vie 60:139–148
Dodd CK, Barichivich WJ, Smith LL (2004) Effectiveness of a barrier wall and culverts in reducing wildlife mortality on a heavily traveled highway in Florida. Biol Conserv 118(5):619–631. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2003.10.011
Drescher K, Henderson J, McNamara K (2001) Farmland prices determinants. In: American Agricultural Economics Association Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL
Dunning JB, Danielson BJ, Pulliam HR (1992) Ecological processes that affect populations in complex landscapes. Oikos 65(1):169–175. doi:10.2307/3544901
Dutilleul P, Stockwell JD, Frigon D, Legendre P (2000) The Mantel test versus Pearson’s correlation analysis: assessment of the differences for biological and environmental studies. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 5(2):131–150. doi:10.2307/1400528
Emaresi G, Pellet J, Dubey S, Hirzel A, Fumagalli L (2011) Landscape genetics of the alpine newt (Mesotriton alpestris) inferred from a strip-based approach. Conserv Genet 12(1):41–50. doi:10.1007/s10592-009-9985-y
Emel SL, Storfer A (2012) A decade of amphibian population genetic studies: synthesis and recommendations. Conserv Genet 13(6):1685–1689. doi:10.1007/s10592-012-0407-1
Epperson BK (2003) Geographical genetics. Monographs in population biology, vol 38. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Epps CW, Palsboll PJ, Wehausen JD, Roderick GK, Ramey RR, McCullough DR (2005) Highways block gene flow and cause a rapid decline in genetic diversity of desert bighorn sheep. Ecol Lett 8(10):1029–1038. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00804.x
Forman RTT, Sperling D, Bissonette JA, Clevenger AP, Cutshall CD, Dale VH, Fahrig L, France R, Goldman CR, Heanue K, Jones JA, Swanson FJ, Turrentine T, Winter TC (2003) Road ecology. Science and solutions. Island Press, Washington, DC
Frantz AC, Bertouille S, Eloy MC, Licoppe A, Chaumont F, Flamand MC (2012) Comparative landscape genetic analyses show a Belgian motorway to be a gene flow barrier for red deer (Cervus elaphus), but not wild boars (Sus scrofa). Mol Ecol 21(14):3445–3457. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05623.x
Garcia JDD, Arevalo JR, Fernandez-Palacios JM (2007) Road edge effect on the abundance of the lizard Gallotia galloti (Sauria : Lacertidae) in two Canary Islands forests. Biodivers Conserv 16(10):2949–2963. doi:10.1007/s10531-007-9154-x
Garner TWJ, Schmidt BR (2003) Relatedness, body size and paternity in the alpine newt, Triturus alpestris. Proc Biol Sci 270(1515):619–624. doi:10.1098/rspb 2002.2284
Garner TWJ, Schmidt BR, Hoeck P, Van Buskirk J (2003) Di- and tetranucleotide microsatellite markers for the Alpine newt (Triturus alpestris): characterization and cross-priming in five congeners. Mol Ecol Notes 3(2):186–188. doi:10.1046/j.1471-8286.2003.00394.x
Gauffre B, Estoup A, Bretagnolle V, Cosson JF (2008) Spatial genetic structure of a small rodent in a heterogeneous landscape. Mol Ecol 17(21):4619–4629. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03950.x
Goldberg CS, Waits LP (2010) Comparative landscape genetics of two pond-breeding amphibian species in a highly modified agricultural landscape. Mol Ecol 19(17):3650–3663. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04673.x
Goudet J, Perrin N, Waser P (2002) Tests for sex-biased dispersal using bi-parentally inherited genetic markers. Mol Ecol 11(6):1103–1114. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01496.x
Graves TA, Beier P, Royle JA (2013) Current approaches using genetic distances produce poor estimates of landscape resistance to interindividual dispersal. Mol Ecol 22(15):3888–3903. doi:10.1111/mec.12348
Guillot G, Rousset F (2013) Dismantling the Mantel tests. Method Ecol Evol 4(4):336–344. doi:10.1111/2041-210x.12018
Hepenstrick D, Thiel D, Holderegger R, Gugerli F (2012) Genetic discontinuities in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) coincide with fenced transportation infrastructure. Basic Appl Ecol 13(7):631–638. doi:10.1016/j.baae.2012.08.009
Hoeck PEA, Garner TWJ (2007) Female alpine newts (Triturus alpestris) mate initially with males signalling fertility benefits. Biol J Linn Soc 91(3):483–491
Holderegger R, Di Giulio M (2010) The genetic effects of roads: a review of empirical evidence. Basic Appl Ecol 11(6):522–531. doi:10.1016/j.baae.2010.06.006
Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA (2007) CLUMPP: a cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 23(14):1801–1806. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm233
Janin A, Lena JP, Ray N, Delacourt C, Allemand P, Joly P (2009) Assessing landscape connectivity with calibrated cost-distance modelling: predicting common toad distribution in a context of spreading agriculture. J Appl Ecol 46(4):833–841. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2009.01665.x
Jodoin Y, Lavoie C, Villeneuve P, Theriault M, Beaulieu J, Belzile F (2008) Highways as corridors and habitats for the invasive common reed Phragmites australis in Quebec, Canada. J Appl Ecol 45(2):459–466. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01362.x
Joly P, Grolet O (1996) Colonization dynamics of new ponds, and the age structure of colonizing alpine newts (Triturus alpestris). Acta Oecol 17(6):599–608
Joly P, Miaud C (1993) How does a newt find its pond—the role of chemical cues in migrating newts (Triturus alpestris). Ethol Ecol Evol 5(4):447–455
Joly P, Miaud C, Lehmann A, Grolet O (2001) Habitat matrix effects on pond occupancy in newts. Conserv Biol 15(1):239–248
Jombart T, Devillard S, Dufour AB, Pontier D (2008) Revealing cryptic spatial patterns in genetic variability by a new multivariate method. Heredity 101(1):92–103. doi:10.1038/hdy.2008.34
Kimura M, Weiss GH (1964) The stepping stone model of population structure and the decrease of genetic correlation with distance. Genetics 49(4):561–576
Knapp M, Saska P, Knappova J, Vonicka P, Moravec P, Kurka A, Andel P (2013) The habitat-specific effects of highway proximity on ground-dwelling arthropods: implications for biodiversity conservation. Biol Conserv 164:22–29. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2013.04.012
Kopecky O, Vojar J, Denoel M (2010) Movements of Alpine newts (Mesotriton alpestris) between small aquatic habitats (ruts) during the breeding season. Amphib Reptil 31(1):109–116
Kopecky O, Vojar J, Denoel M (2012) Sex-specific effect of pool desiccation on the movement of alpine newts, Mesotriton alpestris (LAURENTI, 1768), among breeding sites (Caudata: Salamandridae). Herpetozoa 24(3–4):127–134
Kovar R, Brabec M, Vita R, Bocek R (2009) Spring migration distances of some Central European amphibian species. Amphib Reptil 30(3):367–378
Kuehn R, Hindenlang KE, Holzgang O, Senn J, Stoeckl B, Sperisen C (2007) Genetic effect of transportation infrastructure on roe deer populations (Capreolus capreolus). J Hered 98(1):13–22. doi:10.1093/jhered/esl056
Landguth EL, Cushman SA (2010) CDPOP: a spatially explicit cost distance population genetics program. Mol Ecol Resour 10(1):156–161. doi:10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02719.x
Landguth EL, Cushman SA, Schwartz MK, McKelvey KS, Murphy M, Luikart G (2010) Quantifying the lag time to detect barriers in landscape genetics. Mol Ecol 19(19):4179–4191. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04808.x
Landguth EL, Fedy BC, Oyler-McCance SJ, Garey AL, Emel SL, Mumma M, Wagner HH, Fortin MJ, Cushman SA (2012) Effects of sample size, number of markers, and allelic richness on the detection of spatial genetic pattern. Mol Ecol Resour 12(2):276–284. doi:10.1111/j.1755-0998.2011.03077.x
Le Viol I, Chiron F, Julliard R, Kerbiriou C (2012) More amphibians than expected in highway stormwater ponds. Ecol Eng 47:146–154
Lesbarreres D, Fahrig L (2012) Measures to reduce population fragmentation by roads: what has worked and how do we know? Trends Ecol Evol 27(7):347–380
Lesbarreres D, Lode T, Merila J (2004) What type of amphibian tunnel could reduce road kills? Oryx 38(2):220–223. doi:10.1017/s0030605304000389
Lesbarreres D, Primmer CR, Lode T, Merila J (2006) The effects of 20 years of highway presence on the genetic structure of Rana dalmatina populations. Ecoscience 13(4):531–538
Lowe WH, Allendorf FW (2010) What can genetics tell us about population connectivity? Mol Ecol 19(15):3038–3051. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04688.x
Mata C, Hervas I, Herranz J, Suarez F, Malo JE (2008) Are motorway wildlife passages worth building? Vertebrate use of road-crossing structures on a Spanish motorway. J Environ Manag 88(3):407–415. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.03.014
McGregor RL, Bender DJ, Fahrig L (2008) Do small mammals avoid roads because of the traffic? J Appl Ecol 45(1):117–123. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01403.x
Meunier FD, Verheyden C, Jouventin P (1999) Bird communities of highway verges: influence of adjacent habitat and roadside management. Acta Oecol 20(1):1–13. doi:10.1016/s1146-609x(99)80010-1
Miaud C, Guyetant R, Faber H (2000) Age, size, and growth of the alpine newt, Triturus alpestris (Urodela: Salamandridae), at high altitude and a review of life-history trait variation throughout its range. Herpetologica 56(2):135–144
Miller MP (2005) Alleles In Space (AIS): computer software for the joint analysis of interindividual spatial and genetic information. J Hered 96(6):722–724. doi:10.1093/jhered/esi119
Monmonier M (1973) Maximum-difference barriers: an alternative numerical regionalization method. Geogr Anal 5(3):245–261
Murphy MA, Dezzani R, Pilliod DS, Storfer A (2010) Landscape genetics of high mountain frog metapopulations. Mol Ecol 19(17):3634–3649. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04723.x
Osikowski A (2007) Sperm transport after insemination in the Alpine newt (Triturus alpestris, Caudata, Salamandridae). Folia Biol (Krakow) 55(3–4):109–114
Pabijan M, Babik W (2006) Genetic structure in northeastern populations of the Alpine newt (Triturus alpestris): evidence for post-Pleistocene differentiation. Mol Ecol 15(9):2397–2407. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02954.x
Pebesma EJ (2004) Multivariable geostatistics in S: the gstat package. Comput Geosci 30:683–691
Perret N, Pradel R, Miaud C, Grolet O, Joly P (2003) Transience, dispersal and survival rates in newt patchy populations. J Anim Ecol 72(4):567–575
Pompanon F, Bonin A, Bellemain E, Taberlet P (2005) Genotyping errors: causes, consequences and solutions. Nat Rev Genet 6(11):847–859. doi:10.1038/nrg1707
Prunier J, Kaufmann B, Grolet O, Picard D, Pompanon F, Joly P (2012) Skin swabbing as a new efficient DNA sampling technique in amphibians, and 14 new microsatellite markers in the alpine newt (Ichthyosaura alpestris). Mol Ecol Resour 12(3):524–531. doi:10.1111/j.1755-0998.2012.03116.x
Prunier JG, Kaufmann B, Fenet S, Picard D, Pompanon F, Joly P, Lena JP (2013) Optimizing the trade-off between spatial and genetic sampling efforts in patchy populations: towards a better assessment of functional connectivity using an individual-based sampling scheme. Mol Ecol 22(22):5516–5530
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Riley SPD, Pollinger JP, Sauvajot RM, York EC, Bromley C, Fuller TK, Wayne RK (2006) A southern California freeway is a physical and social barrier to gene flow in carnivores. Mol Ecol 15(7):1733–1741. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02907.x
Safner T, Miller MP, McRae BH, Fortin M-J, Manel S (2011) Comparison of bayesian clustering and edge detection methods for inferring boundaries in landscape genetics. Int J Mol Sci 12(2):865–889. doi:10.3390/ijms12020865
Say L, Devillard S, Léger F, Pontier D, Ruette S (2012) Distribution and spatial genetic structure of European wildcat in France. Anim Conserv 15:18–27
Schäfer H-J (1993) Ausbreitung und entwicklung von amphibien-populationen in der agrarlandschaft. Universität Bonn, Bonn
Schalk CM, Luhring TM (2010) Vagility of aquatic salamanders: implications for wetland connectivity. J Herpetol 44(1):104–109
Schmidt P, Weddeling K, Thomas M, Rottscheidt R, Tarkhnishvili DN, Hachtel M (2006) Dispersal of Triturus alpestris and T. vulgaris in agricultural landscapes—comparing estimates from allozyme markers and capture–mark–recapture analysis. Paper presented at the 13th Congress of the Societas Europaea Herpetologica, Bonn, Germany
Schwartz MK, McKelvey KS (2009) Why sampling scheme matters: the effect of sampling scheme on landscape genetic results. Conserv Genet 10(2):441–452. doi:10.1007/s10592-008-9622-1
Selkoe KA, Watson JR, White C, Ben Horin T, Iacchei M, Mitarai S, Siegel DA, Gaines SD, Toonen RJ (2010) Taking the chaos out of genetic patchiness: seascape genetics reveals ecological and oceanographic drivers of genetic patterns in three temperate reef species. Mol Ecol 19(17):3708–3726. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04658.x
Semlitsch RD (2008) Differentiating migration and dispersal processes for pond-breeding amphibians. J Wildl Manag 72(1):260–267. doi:10.2193/2007-082
Smouse PE, Peakall R (1999) Spatial autocorrelation analysis of individual multiallele and multilocus genetic structure. Heredity 82:561–573
Spear SF, Peterson CR, Matocq MD, Storfer A (2005) Landscape genetics of the blotched tiger salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum melanostictum). Mol Ecol 14(8):2553–2564. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02573.x
Tikka PM, Hogmander H, Koski PS (2001) Road and railway verges serve as dispersal corridors for grassland plants. Landsc Ecol 16(7):659–666
Trombulak SC, Frissell CA (2000) Review of ecological effects of roads on terrestrial and aquatic communities. Conserv Biol 14(1):18–30. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.2000.99084.x
Van Buskirk J (2012) Permeability of the landscape matrix between amphibian breeding sites. Ecol Evol 2(12):3160–3167. doi:10.1002/ece3.424
Van Strien MJ, Keller D, Holderegger R (2012) A new analytical approach to landscape genetic modelling: least-cost transect analysis and linear mixed models. Mol Ecol 21(16):4010–4023. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05687.x
Von der Lippe M, Kowarik I (2007) Long-distance dispersal of plants by vehicles as a driver of plant invasions. Conserv Biol 21(4):986–996. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1739.2007.00722.x
Wagner A, Schabetsberger R, Sztatecsny M, Kaiser R (2011) Skeletochronology of phalanges underestimates the true age of long-lived alpine newts (Ichthyosaura alpestris). Herpetol J 21(2):145–148
Woltz HW, Gibbs JP, Ducey PK (2008) Road crossing structures for amphibians and reptiles: informing design through behavioral analysis. Biol Conserv 141(11):2745–2750. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2008.08.010
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche et de la Technologie (ANRT, agreement 2/2009), Réseau Ferré de France (RFF), Autoroutes Paris-Rhin-Rhône (APRR) and the ECOSPHERE company. It was conducted in accordance with French laws and with the approval of the Préfectures de Saône-et-Loire, de Côte-d’Or and de l’Yonne. We warmly thank T. Jombart for helpful comments about sPCA results, P. Allemand for his help in Matlab programing, E. Landguth for clues as to the use of CDPOP and J. Van Buskirk for details about his own study. We gratefully acknowledge support from the CNRS/IN2P3 Computing Center (Lyon/Villeurbanne - France), for providing part of the computing ressources needed for this work. In addition, we thank C. De Fazio, G. Perez, F. Revollon, F. Ribette, J. Mangin and O. Grolet for their precious help and support in the field and laboratory, A. Corrigan for proofreading, and two anonymous reviewers for comments that greatly improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prunier, J.G., Kaufmann, B., Léna, JP. et al. A 40-year-old divided highway does not prevent gene flow in the alpine newt Ichthyosaura alpestris . Conserv Genet 15, 453–468 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-013-0553-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-013-0553-0