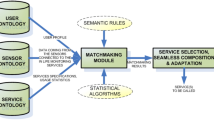
Abstract
Ambient assisted living (AAL) environments are augmented with sensing and communication technologies to support elderly people with personalized, adaptive and anticipatory requirements. A plethora of heterogeneous devices and services appear and disappear, which expose different behavior with the changing contexts in these environments. Therefore, a service matchmaking mechanism that attempts to identify relevant services in order to fulfill the user needs, has to deal with the heterogeneity of devices and services along with their dynamic behavior. Existing service specifications, such as semantic web services, are often used to abstract the environment’s functionalities and the user tasks without incorporating context-aware properties, which makes them unsuitable for service matchmaking in pervasive and ambient environment. To deal with these issues, we introduce a contExt Aware web Service dEscription Language (wEASEL) that is an abstract service model to represent services and user tasks in AAL environments. Also, we present a set of wEASEL-based service matching algorithms and evaluate them for their suitability. The proposed service matchmaking mechanism can incorporate services that are available in local AAL environment as well as in the cloud computing marketplace.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Semantic Markup for Web Services (OWL-S): http://www.w3.org/Submission/OWL-S/
Web Service Modeling Ontology (WSMO): http://www.w3.org/Submission/WSMO/
Semantic Web Rule Language (SWRL): http://www.w3.org/Submission/SWRL/
Rule Markup Language (RuleML): http://ruleml.org/
Semantic Web Services Framework (SWSF): http://www.w3.org/Submission/SWSF/
Semantic Annotation for WSDL and XML Schema (SAWSDL): http://www.w3.org/2002/ws/sawsdl/
The word Resource has been shortened to Rsc in order to save space
Available at http://tinyurl.com/wEASEL-site
In IR, precision is defined the proportion of retrieved material that is actually relevant. On the other hand, the recall of the system is the proportion of relevant material actually retrieved in answer to a search request [12].
Precision macro-averaging refers to the mean precision values for answer sets retrieved by the matchmaker for all queries in the test collection at specific recall values.
References
Armbrust, M., Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A.D., Katz, R., Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D., Rabkin, A., Stoica, I., et al.: A view of cloud computing. Commun. ACM 53(4), 50–58 (2010)
Battle, S., Bernstein, A., Boley, H., Grosof, B., Gruninger, M., Hull, R., Kifer, M., Martin, D., McIlraith, S., McGuinness, D.: Semantic web services framework (swsf). Tech. Rep. W3C Member Submission - 9 (2005)
Bellur, U., Kulkarni, R.: Improved matchmaking algorithm for semantic web services based on bipartite graph matching. In: IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), pp. 86–93. (2007)
Bellur, U., Vadodaria, H.: On extending semantic matchmaking to include preconditions and effects. In: IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), pp. 120–128. (2008)
Bener, A.B., Ozadali, V., Ilhan, E.S.: Semantic matchmaker withprecondition and effect matching using swrl. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(5), 9371–9377 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2009.01.010
Ben Mokhtar, S., Preuveneers, D., Georgantas, N., Issarny, V., Berbers, Y.: Easy: efficient semantic service discovery in pervasive computing environments with qos and context support. J. Syst. Softw. 81(5), 785–808 (2008)
Ben Mokhtar, S., Raverdy, P.G., Urbieta, A., Cardoso, R.: Interoperable semantic and syntactic service discovery for ambient computing environments. Innovative Applications of Ambient Intelligence: Advances in Smart Systems (2012)
Berners-Lee, T., Hendler, J.: The semantic web. Sci. Am. 284(5), 28–37 (2001)
Botelho, L., Fernandez, A., Fries, B., Klusch, M., Pereira, L., Santos, T., Pais, P., Vasirani, M.: Service Discovery, Chap. 10. CASCOM—Intelligent Service Coordination in the SemanticWeb. Springer, New York (2008)
Bottaro, A., Bourcier, J., Escoffier, C., Lalanda, P.: Autonomic context-aware service composition. In: 2nd IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Services (ICPS’07). Istanbul, Turkey (2007)
Champion, M., Ferris, C., Newcomer, E., Orchard, D.: Web services architecture. W3C Tehnical Report (2002)
Cleverdon, C., Mills, J., Keen, M.: Aslib Cranfield research project-Factors determining the performance of indexing systems; Volume 2, Test results. Cranfield (1966)
Du, K., Zhang, D., Zhou, X., Hariz, M.: Handling conflicts of context-aware reminding system in sensorised home. Cluster Computing 14(1), 81–89 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10586-009-0091-1
Filho, J.G.P., van Sinderen, M.: Web service architectures—semantics and context-awareness issues in web services platforms. Tech. rep, Telematica Instituut (2003)
Fujii, K., Suda, T.: Semantics-based context-aware dynamic service composition. ACM Trans. Auton. Adapt. Syst. 4(2), 12 (2009)
Guinard, D., Trifa, V., Karnouskos, S., Spiess, P., Savio, D.: Interacting with the soa-based internet of things: Discovery, query, selection, and on-demand provisioning of web services. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 3(3), 223–235 (2010)
Gwang-hun, K., Do-hyun, K., XuanTung, H., Younghee, L.: Group-aware service discovery using effect ontology for conflict resolution in ubiquitous environment. In: 10th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT) (2008)
Gwang-hun, K., Do-hyun, K., XuanTung, H., Younghee, L., Gab-soo, L.: Semantic service discovery using effect ontology for appliance service in ubiquitous environment. In: International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Technologies and Applications (ICUT) (2008)
Hasswa, A., Hassanein, H.: A smart spaces architecture based on heterogeneous contexts, particularly social contexts. Clust. Comput. 15(4), 373–390 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10586-011-0157-8
Hossain, M.A., Alamri, A., Almogren, A.S., Hossain, S., Parra, J.: A framework for a context-aware elderly entertainment support system. Sensors 14(6), 10538–10561 (2014)
Hossain, M.A., Parra, J., Atrey, P.K., El Saddik, A.: A framework for human-centered provisioning of ambient media services. Multimed. Tools Appl. 44(3), 407–431 (2009)
Hossain, M.S.: Adaptive media service framework for health monitoring. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, pp. 70–73. ACM (2011)
Hossain, M.S., Muhammad, G.: Cloud-based collaborative media service framework for healthcare. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks (2014)
Keller, U., Lara, R., Lausen, H., Polleres, A., Fensel, D.: Automatic location of services. In: Proceedings of the 2nd European Semantic Web Conference (ESWC 2005), pp. 38–49. Springer (2005)
Klusch, M., Fries, B., Sycara, K.: Automated semantic web service discovery with owls-mx. In: AAMAS ’06: Proceedings of the 5th int. joint conf. on Autonomous agents and multiagent systems, pp. 915–922. ACM, New York (2006). doi:10.1145/1160633.1160796
Klusch, M., Fries, B., Sycara, K.: OWLS-MX: a hybrid Semantic Web service matchmaker for OWL-S services. Web Semant. 7(2), 121–133 (2009)
Klusch, M., Kapahnke, P.: Owls-mx3: An adaptive hybrid semantic service matchmaker for owl-s. In: Proceedings of 3rd International Workshop on Service Matchmaking and Resource Retrieval in the Semantic Web. CEUR-WS.org (2009)
Klusch, M., Kapahnke, P., Fries, B.: Hybrid semantic web service retrieval: A case study with OWLS-MX. In: IEEE Second International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC’08) (2008)
Klusch, M., Khalid, M., Kapahnke, P., Fries, B., Vasileski, M.: Owls-tc owl-s service retrieval test collection—version 4.0—user manual (2010)
Kourtesis, D., Paraskakis, I.: Combining sawsdl, owl-dl and uddi for semantically enhanced web service discovery. In: 5th European Semantic Web Conference (ESWC 2008), vol. 5021, pp. 614–628. Springer (2008)
Kumar, A., Neogi, A., Pragallapati, S., Ram, D.J.: Raising programming abstraction from objects to services. In: International Conference on Web Services (ICWS) (2007)
Kuster, U., Konig-Ries, B., Stern, M., Klein, M.: Diane: an integrated approach to automated service discovery, matchmaking and composition. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 1033–1042 (2007)
Lausen, H., Innsbruck, D.: Semantic annotations for WSDL and XML schema (sawsdl) (2006)
Majithia, S., Walker, D.W., Gray, W.A.: A framework for automated service composition in service-oriented architecture. In: 1st European Semantic Web Symposium (2004)
Martin, D., Burstein, M., Hobbs, J., Lassila, O., McDermott, D., McIlraith, S., Narayanan, S., Paolucci, M., Parsia, B., Payne, T.: Owl-s: Semantic markup for web services. W3C Memb. Submiss. 22 (2004)
McIlraith, S.A., Zeng, T.C., Zeng, H.: Semantic web services. IEEE Intell. Syst. Appl. 16(2), 46–53 (2001)
Paolucci, M., Kawamura, T., Payne, T.R., Sycara, K.: Semantic matching of Web services capabilities. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2342, 333–347 (2002). http://link.springer-ny.com/link/service/series/0558/bibs/2342/23420333.htm; http://link.springer-ny.com/link/service/series/0558/papers/2342/23420333.pdf
Rasch, K., Li, F., Sehic, S., Ayani, R., Dustdar, S.: Context-driven personalized service discovery in pervasive environments. World Wide Web 14(4), 295–319 (2011). URL http://www.springerlink.com/index/10.1007/s11280-011-0112-x
Remagnino, P., Foresti, G.L.: Ambient intelligence: a new multidisciplinary paradigm. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A 35(1), 1–6 (2005)
Roman, D., Lausen, H., Keller, U.: Web service modeling ontology standard (wsmo-standard) (2004)
Ruyter, B.d., Pelgrim, E.: Ambient assisted-living research in carelab. interactions, Interactions 14(4), 30–33 (2007)
Saehoon, K., Woohyun, K., Dongman, L., Younghee, L.: Group context-aware service discovery for supporting continuous service availability. In: Proceedings of the First Internaltional Workshop on Personalized Context Modeling and Management for UbiComp Applications (ubiPCMM 2005) (2005)
Sirin, E., Parsia, B., Hendler, J.: Template-based composition of semantic web services. In: AAAI Fall Symposium on Agents and the Semantic Web (2005)
Stollberg, M., Keller, U., Lausen, H., Heymans, S.: Two-phase web service discovery based on rich functional descriptions. In: 4th European Semantic Web Conference, ESWC 2007, vol. 4519, pp. 99–113. Springer (2007)
Sycara, K., Lu, J., Klusch, M., Widoff, S.: Matchmaking among heterogeneous agents on the internet. In: Proceedings of the 1999 AAAI Spring Symposium on Intelligent Agents in Cyberspace (1999)
Sycara, K., Paolucci, M., Ankolekar, A., Srinivasan, N.: Automated discovery, interaction and composition of semantic web services. Web Semant. 1(1), 27–46 (2003)
Trastour, D., Bartolini, C., Gonzalez-Castillo, J.: A semantic web approach to service description for matchmaking of services. In: Proceedings of the International Semantic Web Working Symposium (SWWS) (2001). http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/trastour01semantic.html
Urbieta, A.: An integrated approach for context-aware modelling, matchmaking and composition of semantic services, based on preconditions and effects, oriented to intelligent environments. Ph.D. Thesis, Mondragon Unibertsitatea (MU) (2010)
Urbieta, A., Azketa, E., Gomez, I., Parra, J., Arana, N.: Analysis of effects- and preconditions-based service representation in ubiquitous computing environments. In: IEEE Second International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC’08) (2008)
Urbieta, A., Azketa, E., Gomez, I., Parra, J., Arana, N.: Bridging the gap between services and context in ubiquitous computing environments using an effects- and conditions-based model. In: 3th International Symposium on Ubiquitous Computing and Ambient Intelligence (UCAm I), Advances in Soft Computing Series. Springer (2008)
Urbieta, A., Azketa, E., Gomez, I., Parra, J., Arana, N.: Towards effects-based service description and integration in pervasive environments. In: ACM Service Integration in Pervasive Environments (SIPE’08) Workshop on International Conference on Pervasive Services (ICPS’08) (2008)
Wang, H., Li, Z., Fan, L.: Capability matchmaking of semantic web services with preconditions and effects. In: The Third Chinese Semantic Web Symposium (CSWS) (2009)
Yau, S.S., Liu, J.: Hierarchical situation modeling and reasoning for pervasive computing. In: SEUS-WCCIA ’06: Proceedings of the The Fourth IEEE Workshop on Software Technologies for Future Embedded and Ubiquitous Systems, and the Second International Workshop on Collaborative Computing, Integration, and Assurance (SEUS- CCIA’06), pp. 5–10 (2006). doi:10.1109/SEUS-WCCIA.2006.25
Yau, S.S., Liu, J.: Incorporating situation awareness in service specifications. In: ISORC ’06: Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Symposium on Object and Component-Oriented Real-Time Distributed Computing, pp. 287–294. (2006). doi:10.1109/ISORC.2006.39
Zaremski, A.M., Wing, J.M.: Signature matching: a tool for using software libraries. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 4(2), 146–170 (1995). http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/zaremski95signature.html
Zaremski, A.M., Wing, J.M.: Specification matching of software components. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 6(4), 333–369 (1997)
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through the research group Project No. RGP-VPP-049.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Urbieta, A., González-Beltrán, A., Ben Mokhtar, S. et al. Hybrid service matchmaking in ambient assisted living environments based on context-aware service modeling. Cluster Comput 18, 1171–1188 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-015-0469-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-015-0469-1