Abstract
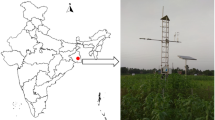
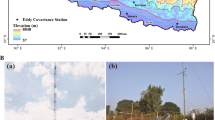
The micrometeorological technique of eddy covariance is a powerful tool for characterizing the carbon (C) budget of terrestrial ecosystems. Eddy covariance method was used for estimating Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE) of carbon dioxide between atmosphere and revegetated manganese mine spoil dump at Gumgaon, India. In this paper, we analyzed the diel CO2 flux pattern and its response to various physical environmental conditions. The carbon balance of terrestrial ecosystems is particularly sensitive to climatic changes. Study of diel pattern of CO2 flux showed that carbon uptake was dependent on sunlight. Effect of temperature and latent heat on the CO2 flux showed that rate of CO2 uptake increased proportionally, but later declined due to various factors like stomatal response, high evaporative demand, circadian rhythm and/or a combination of all three. Net ecosystem production of revegetated land was found to be 28.196 KgC/ha/day whereas average net carbon release by the ecosystem, through respiration was observed to be 5.433 KgC/ha/day. Thus, quantifying net carbon (C) storage in degraded land is a necessary step in the validation of carbon sequestration estimates and in assessing the possible role of these ecosystems in offsetting adverse impacts of fossil fuel emissions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akala VA, Lal R (2000) Potential of mine land reclamation for soil organic carbon sequestration in Ohio. Land Degrad Dev 11:289–297
Akala VA, Lal R (2001) Soil organic carbon pools and sequestration rates in reclaimed minesoils in Ohio. J Environ Qual 30:2098–2104
Aubinet A et al. (2000) Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of forest: the Euro flux methodology. Adv Ecol Res 30:117–175
Baldocchi DD (2003) Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbondioxide exchange rates of ecosystem: past, present, future. Glob Chang Biol 9:479–492
Baldocchi DD, Valentini R, Running S, Oechel WC, Dahlman R (1996) Strategies for measuring and modelling carbon dioxide and water vapour fluxes over terrestrial ecosystems. Glob Chang Biol 2:159–167
Baldocchi DD, Hicks BB, Meyers TP (1988) Measuring biosphere—atmosphere exchanges of biologically related gases with micrometeorological methods. Ecology 69(5):1331–1340
Bendfeldt ES, Burger JA, Daniels WL (2001) Quality of amended mine soils after sixteen years. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:1736–1744
Conant RT, Paustian K, Elliott ET (2001) Grassland management and conversion into grassland: effects on soil carbon. Ecol Appl 11:343–355
Crafts-Brandner SJ, Salvucci ME (2000) Rubisco activase constrains the photosynthetic potential of leaves at high temperature and CO2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(24):13430–13435
Fan S-M, Goulden ML, Munger JW, Daube BC, Bakwin PS, Wofsy SC, Amthor JS, Fitzjarrald DR, Moore KE, Moore TR (1995) Environmental controls on the photosynthesis and respiration of a boreal lichen woodland: a growing season of whole-ecosystem exchange measurements by eddy correlation. Oecologia 102:443–452
Fisher MJ, Rao IM, Ayarza MA et al (1994) Carbon storage by introduced deep-rooted grasses in the South American savannas. Nature 371:236–238
Follett RF, Kimble JM, Lal R (2001) The potential for U.S grazing lands to sequester carbon and mitigate the greenhouse effects. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Gorsell EV, Leuning R, Cleugh HA, Keith H, Suni T (2007) Tellus 59B:397–403
Goulden ML, Miller SD, da Rocha HR, Menton MC, de Freitas HC, Figueira AMS, de Sousa CAD (2004) Diel and seasonal patterns of tropical forest co2 exchange. Ecol Appl 14(4):S42–S54
Grace J, Malhi Y, Lloyd J, McIntyre J, Miranda AC, Meir P, Miranda HS (1996) The use of eddy covariance to infer the net carbon dioxide uptake of Brazilian rain forest. Glob Chang Biol 2:208–217
Jarvis PG, Leverenz JM (1983) Productivity of temperate, deciduous and evergreen forests. In: Physiological plant ecology, ecosystems processes: moneral cycling, productivity and man’s influence. Springer, Berlin, pp 233–261
Grace J, Kruijt B, Freibauer A, Benndorf R, Carr R, Dutschke M, Federici S, Mollicone D, Sanz MJ, Schlamadinger B, Sezzi E, Waterloo M, Valentini R, Verhagen J, van Putten B (2003) Scientific and technical issues in the clean development mechanism. This discussion paper originated from a workshop in Wageningen, The Netherlands, April 2003, a contribution to the project Concerted Action CarboEurope-GHG, which is part of the CarboEurope Cluster
Jones HG (1992) Plants and microclimate: a quantitative approach to environmental plant physiology, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kirschbaum MUF (2000) Will changes in soil organic carbon act as a positive ornegative feedback on global warming. Biogeochemistry 48:21–51
Krishnan SR (2004) Final Term Paper Spring CE 524
Kruijt B, Elbers JA, von Randow C, Araújo AC, Oliveiria PJ, Culf A, Manzi AO, Nobre AD, Kabat P, Moors EJ (2004) The robustness in eddy correlation fluxes for Amazon rainforest conditions. Ecol Appl 14:S101–S113
Larcher W (1995) Physiological plant ecology: ecophysiology and stress physiology of functional groups, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin
Lieth H, Whittaker RH (eds) (1975) Primary productivity of the biosphere. Springer, Berlin
Malhi Y, Nobre AD, Grace J, Kruijt B, Pereira MGP, Culf A, Scott S (1998) Carbon dioxide transfer over a Central Amazonian rain forest. J Geophys Res-Atmospheres 103:31593–31612
Massman WJ, Lee X (2002) Eddy covariance flux corrections and uncertainties in long-term studies of carbon and energy exchanges. Agric For Meteorol 113:121–144
Post WM, Kwon KC (2000) Soil carbon sequestration and land-use change: processes and potential. Glob Chang Biol 6:317–327
Reichle DE (ed) (1970) Analysis of temperate forest ecosystems. Springer, Berlin
Reichstein M, Tenhunen JD, Ourcival JM, Roupsard O, Rambal S, Meglietta F, Peressotti A, Pecchiari M et al (2002).Severe drought effects on ecosystem CO2 and H2O fluxes at three mediterranean sites: revision of current hypothesis. Glob Chang Biol 8:999–1017
Richter DD, Markewitz D, Wells CG et al (1994) Soil chemical change during three decades in an old-field loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) ecosystem. Ecology 75:1463–1473
Ruimy A, Jarvis PG, Baldocchi DD, Sauiger B (1995) CO2 fluxes over plant canopies and solar radiation: a review. Adv Ecol Res 26:1–81
Schulze ED, Wirth C, Heimann M (2000) Managing forests after Kyoto. Science 289:2058–2059
Torbert JL, Burger JA, Probert T (1995) Evaluation of techniques to improve white pine establishment on an Appalachian minesoil. J Environ Qual 24:869–873
US National Committee for the International Biological Program (1975) Productivity of world ecosystems. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC
Wang YP, Leuning R, Cleugh HA, Coppin PA (2001) Parameter estimation in surface exchange models using nonlinear inversion: how many parameters can we estimate and which measurements are most useful. Glob Chang Biol 7(5):495–510
Wofsy SC, Goulden ML, Munger JW, Fan S-M, Bakwin PS, Daube BC, Bassow SL, Bazzaz FA (1993) Net exchange of CO2 in a mid-latitude forest. Science 260:1314–1317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, R., Juwarkar, A.A., Wanjari, T. et al. Study of terrestrial carbon flux by eddy covariance method in revegetated manganese mine spoil dump at Gumgaon, India. Climatic Change 106, 609–619 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9953-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9953-z