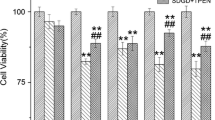
Abstract
Hypoxia is an important cause of brain injury in ischemic stroke. It is known that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an important determinant of cell survival or death during hypoxia. However, the signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms involved remain to be studied in more detail. To investigate whether inhibition of ER stress promotes neuroprotection pathways, we applied an in vitro oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) followed by reoxygenation model of human SK-N-MC neuronal cell cultures in this study. Our results showed that neuronal cell death was induced in this model during the OGD reoxygenation by the sustained ER stress, but not during OGD phase. However, treatment of the cultures with lithium with the OGD reoxygenation insult did not result in neuroprotection, whereas concomitant treatment of chemical chaperon 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) provides protective effects in ER stress-exposed cells. Moreover, 4-PBA rescued ER stress-suppressed Akt protein biosynthesis, which works cooperatively with lithium in the activation of Akt downstream signaling by inhibition of autophagy-induced cell death. Taken together, our finding provides a possible mechanism by which 4-PBA and lithium contribute to mediate neuroprotection cooperatively. This result may potentially be a useful therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bando Y, Ogawa S, Yamauchi A, Kuwabara K, Ozawa K, Hori O, Yanagi H, Tamatani M, Tohyama M (2000) 150-kDa oxygen-regulated protein (ORP150) functions as a novel molecular chaperone in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278(6):C1172–1182
Box AH, Kim SM, Demetrick DJ (2010) AKT loss in human epithelial cells treated with severe hypoxia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803(8):951–959. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.03.011
Brown KM, Tracy DK (2013) Lithium: the pharmacodynamic actions of the amazing ion. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 3(3):163–176. doi:10.1177/2045125312471963
Chuang DM, Wang Z, Chiu CT (2011) GSK-3 as a target for lithium-induced neuroprotection against excitotoxicity in neuronal cultures and animal models of ischemic stroke. Front Mol Neurosci 4:15. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2011.00015
Cole AR (2012) GSK3 as a sensor determining cell fate in the brain. Front Mol Neurosci 5:4. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2012.00004
Dohi E, Tanaka S, Seki T, Miyagi T, Hide I, Takahashi T, Matsumoto M, Sakai N (2012) Hypoxic stress activates chaperone-mediated autophagy and modulates neuronal cell survival. Neurochem Int 60(4):431–442. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2012.01.020
Donnelly N, Gorman AM, Gupta S, Samali A (2013) The eIF2alpha kinases: their structures and functions. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(19):3493–3511. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1252-6
Duvigneau JC, Kozlov AV, Zifko C, Postl A, Hartl RT, Miller I, Gille L, Staniek K, Moldzio R, Gregor W, Haindl S, Behling T, Redl H, Bahrami S (2010) Reperfusion does not induce oxidative stress but sustained endoplasmic reticulum stress in livers of rats subjected to traumatic-hemorrhagic shock. Shock 33(3):289–298. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181aef322
Freland L, Beaulieu JM (2012) Inhibition of GSK3 by lithium, from single molecules to signaling networks. Front Mol Neurosci 5:14. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2012.00014
Gao B, Zhang XY, Han R, Zhang TT, Chen C, Qin ZH, Sheng R (2013) The endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor salubrinal inhibits the activation of autophagy and neuroprotection induced by brain ischemic preconditioning. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34(5):657–666. doi:10.1038/aps.2013.34
Gold AB, Herrmann N, Lanctot KL (2010) Lithium and its neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects: potential treatment for post-ischemic stroke sequelae. Curr Drug Targets 12:243–255
Harrison LM, Muller SH, Spano D (2013) Effects of the Ras homolog Rhes on Akt/protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation in striatum. Neuroscience 236:21–30. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.062
Hetz CA (2007) ER stress signaling and the BCL-2 family of proteins: from adaptation to irreversible cellular damage. Antioxid Redox Signal 9(12):2345–2355. doi:10.1089/ars.2007.1793
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(2):89–102. doi:10.1038/nrm3270
Iannitti T, Palmieri B (2011) Clinical and experimental applications of sodium phenylbutyrate. Drugs R&D 11(3):227–249. doi:10.2165/11591280-000000000-00000
Kolb PS, Ayaub EA, Zhou W, Yum V, Dickhout JG, Ask K (2015) The therapeutic effects of 4-phenylbutyric acid in maintaining proteostasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 61:45–52. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2015.01.015
Li X, Bijur GN, Jope RS (2002) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, mood stabilizers, and neuroprotection. Bipolar Disord 4(2):137–144
Lin L, Bivard A, Parsons MW (2013) Perfusion patterns of ischemic stroke on computed tomography perfusion. J Stroke 15(3):164–173. doi:10.5853/jos.2013.15.3.164
Liu Y, Levine B (2014) Autosis and autophagic cell death: the dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ. doi:10.1038/cdd.2014.143
Liu Y, Levine B (2015) Autosis and autophagic cell death: the dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ 22(3):367–376. doi:10.1038/cdd.2014.143
Mahadevan NR, Zanetti M (2011) Tumor stress inside out: cell-extrinsic effects of the unfolded protein response in tumor cells modulate the immunological landscape of the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol 187(9):4403–4409. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1101531
Manzanero S, Santro T, Arumugam TV (2013) Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: sources and contribution to cell injury. Neurochem Int 62(5):712–718. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2012.11.009
Mizukami T, Orihashi K, Herlambang B, Takahashi S, Hamaishi M, Okada K, Sueda T (2010) Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate protects against spinal cord ischemia by inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Vasc Surg 52(6):1580–1586. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2010.06.172
Mullonkal CJ, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2007) Akt in ischemia and reperfusion. J Investig Surg 20(3):195–203. doi:10.1080/08941930701366471
Nagy T, Frank D, Katai E, Yahiro RK, Poor VS, Montsko G, Zrinyi Z, Kovacs GL, Miseta A (2013) Lithium induces ER stress and N-glycan modification in galactose-grown Jurkat cells. PLoS One 8(7):e70410. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070410
Perez-Alvarez MJ, Maza Mdel C, Anton M, Ordonez L, Wandosell F (2012) Post-ischemic estradiol treatment reduced glial response and triggers distinct cortical and hippocampal signaling in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. J Neuroinflamm 9:157. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-157
Pradeep H, Densi A, Rajanikant GK (2014) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in ischemic neuronal death. Curr Neurovasc Res 12:243–255
Puyal J, Vaslin A, Mottier V, Clarke PG (2009) Postischemic treatment of neonatal cerebral ischemia should target autophagy. Ann Neurol 66(3):378–389. doi:10.1002/ana.21714
Qi X, Hosoi T, Okuma Y, Kaneko M, Nomura Y (2004) Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate protects against cerebral ischemic injury. Mol Pharmacol 66(4):899–908. doi:10.1124/mol.104.001339
Rami A, Langhagen A, Steiger S (2008) Focal cerebral ischemia induces upregulation of Beclin 1 and autophagy-like cell death. Neurobiol Dis 29(1):132–141. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.08.005
Roussel BD, Kruppa AJ, Miranda E, Crowther DC, Lomas DA, Marciniak SJ (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in neurological disease. Lancet Neurol 12(1):105–118. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70238-7
Schonthal AH (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: its role in disease and novel prospects for therapy. Scientifica 2012:857516. doi:10.6064/2012/857516
Shao L, Sun X, Xu L, Young LT, Wang JF (2006) Mood stabilizing drug lithium increases expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins in primary cultured rat cerebral cortical cells. Life Sci 78(12):1317–1323. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2005.07.007
Shin WJ, Gwak M, Baek CH, Kim KS, Park PH (2012) Neuroprotective effects of lithium treatment following hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Childs Nerv Syst 28(2):191–198. doi:10.1007/s00381-011-1627-2
Tagliavacca L, Caretti A, Bianciardi P, Samaja M (2012) In vivo up-regulation of the unfolded protein response after hypoxia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(7):900–906. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.02.016
Wang Z, Zhang H, Xu X, Shi H, Yu X, Wang X, Yan Y, Fu X, Hu H, Li X, Xiao J (2012) bFGF inhibits ER stress induced by ischemic oxidative injury via activation of the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways. Toxicol Lett 212(2):137–146. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.05.006
Yung HW, Korolchuk S, Tolkovsky AM, Charnock-Jones DS, Burton GJ (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion-induced apoptosis through attenuation of Akt protein synthesis in human choriocarcinoma cells. FASEB J 21(3):872–884. doi:10.1096/fj.06-6054com
Zhao H (2009) Ischemic postconditioning as a novel avenue to protect against brain injury after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29(5):873–885. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.13
Zhou X, Zhou J, Li X, Guo C, Fang T, Chen Z (2011) GSK-3beta inhibitors suppressed neuroinflammation in rat cortex by activating autophagy in ischemic brain injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 411(2):271–275. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.117
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the Chung Shan Medical University-Tungs’ Taichung Metroharbor Hospital (CSMU-TTM-098-003), and from the Ministry of Science and Technology (101-2320-B-040-015-MY3). The fluorescence microscope and imaging analyzer were performed at the Instrument Center of Chung Shan Medical University, which is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, and Chung Shan Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tung, WF., Chen, WJ., Hung, HC. et al. 4-Phenylbutyric Acid (4-PBA) and Lithium Cooperatively Attenuate Cell Death during Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation (OGD) and Reoxygenation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 849–859 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0179-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0179-5