Abstract
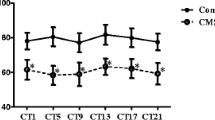
Stress is known to affect neurotrophic factor expression, which induces depression-like behavior. However, whether there are time-dependent changes in neurotrophic factor mRNA expression following stress remains unclear. In the present study, we tested whether chronic stress exposure induces long-term changes in depression-related behavior, serum corticosterone, and hippocampal proliferation as well as neurotrophic factor family mRNA levels, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), in the mouse hippocampus. The mRNA level of neurotrophic factors (BDNF, NGF, NT-3, and CNTF) was measured using the real-time PCR. The serum corticosterone level was evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and, for each subject, the hippocampal proliferation was examined by 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine immunostaining. Mice exhibited depression-like behavior in the forced-swim test (FST) and decreased BDNF mRNA and hippocampal proliferation in the middle of the stress exposure. After 15 days of stress exposure, we observed increased immobility in the FST, serum corticosterone levels, and BDNF mRNA levels and degenerated hippocampal proliferation, maintained for at least 2 weeks. Anhedonia-like behavior in the sucrose preference test and NGF mRNA levels were decreased following 15 days of stress. NGF mRNA levels were significantly higher 1 week after stress exposure. The current data demonstrate that chronic stress exposure induces prolonged BDNF and NGF mRNA changes and increases corticosterone levels and depression-like behavior in the FST, but does not alter other neurotrophic factors or performance in the sucrose preference test.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelucci F, Mathé AA, Aloe L (2004) Neurotrophic factors and CNS disorders: findings in rodent models of depression and schizophrenia. Prog Brain Res 146:151–165
Ardayfio P, Kim KS (2006) Anxiogenic-like effect of chronic corticosterone in the light-dark emergence task in mice. Behav Neurosci 120:249–256
Benelli A, Filaferro M, Bertolini A et al (1999) Influence of S-adenosyl-l-methionine on chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia in castrated rats. Br J Pharmacol 127:645–654
Chourbaji S, Hellweg R, Brandis D et al (2004) Mice with reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression show decreased choline acetyltransferase activity, but regular brain monoamine levels and unaltered emotional behavior. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 121:28–36
David DJ, Samuels BA, Rainer Q et al (2009) Neurogenesis-dependent and -independent effects of fluoxetine in an animal model of anxiety/depression. Neuron 62:479–493
de Kloet ER, Joëls M, Holsboer F (2005) Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:463–475
D’Sa C, Duman RS (2002) Antidepressants and neuroplasticity. Bipolar Disord 4:183–194
Duman RS, Monteggia LM (2006) A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 59:1116–1127
Hashimoto K, Shimizu E, Iyo M (2004) Critical role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in mood disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 45:104–114
Holmes A, Wellman CL (2009) Stress-induced prefrontal reorganization and executive dysfunction in rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:773–783
Ihne JL, Fitzgerald PJ, Hefner KR et al (2012) Pharmacological modulation of stress-induced behavioral changes in the light/dark exploration test in male C57BL/6J mice. Neuropharmacology 6:464–473
Jacobsen JP, Mørk A (2006) Chronic corticosterone decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA and protein in the hippocampus, but not in the frontal cortex, of the rat. Brain Res 1110:221–225
Jiao J, Opal MD, Dulawa SC (2013) Gestational environment programs adult depression-like behavior through methylation of the calcitonin gene-related peptide gene. Mol Psychiatry 18:1273–1280
Kawashima H, Numakawa T, Kumamaru E et al (2010) Glucocorticoid attenuates brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent upregulation of glutamate receptors via the suppression of microRNA-132 expression. Neuroscience 165:1301–1311
Kessler RC, Gruber M, Hettema JM et al (2008) Co-morbid major depression and generalized anxiety disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey follow-up. Psychol Med 38:365–374
Kim KS, Han PL (2006) Optimization of chronic stress paradigms using anxiety- and depression-like behavioral parameters. J Neurosci Res 83:497–507
Kordower JH, Isacson O, Emerich DF (1999) Cellular delivery of trophic factors for the treatment of Huntington’s disease: is neuroprotection possible? Exp Neurol 159:4–20
Lambert WM, Xu CF, Neubert TA et al (2013) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling rewrites the glucocorticoid transcriptome via glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 33:3700–3714
Lucca G, Comim CM, Valvassori SS et al (2008) Chronic mild stress paradigm reduces sweet food intake in rats without affecting brain derived neurotrophic factor protein levels. Curr Neurovasc Res 5:207–213
MacMaster FP, Mirza Y, Szeszko PR et al (2008) Amygdala and hippocampal volumes in familial early onset major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 63:385–390
McGeary JE, Gurel V, Knopik VS et al (2011) Effects of nerve growth factor (NGF), fluoxetine, and amitriptyline on gene expression profiles in rat brain. Neuropeptides 45:317–322
Nikulina EM, Arrillaga-Romany I, Miczek KA et al (2008) Long-lasting alteration in mesocorticolimbic structures after repeated social defeat stress in rats: time course of mu-opioid receptor mRNA and FosB/DeltaFosB immunoreactivity. Eur J Neurosci 27:2272–2284
Numakawa T, Kumamaru E, Adachi N et al (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor interaction with TrkB promotes BDNF-triggered PLC-gamma signaling for glutamate release via a glutamate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:647–652
Peruga I, Hartwig S, Merkler D et al (2012) Endogenous ciliary neurotrophic factor modulates anxiety and depressive-like behavior. Behav Brain Res 229:325–332
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 21:730–732
Réus GZ, Stringari RB, Ribeiro KF et al (2011) Maternal deprivation induces depressive-like behaviour and alters neurotrophin levels in the rat brain. Neurochem Res 36:460–466
Russo-Neustadt A, Ha T, Ramirez R et al (2001) Physical activity-antidepressant treatment combination: impact on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and behavior in an animal model. Behav Brain Res 120:87–95
Sakamoto Y, Ogawa T, Ogawa M et al (2015) Effects of 15-day chronic stress on behavior and neurological changes in the hippocampus of ICR mice. Yakugaku Zasshi 135:151–158
Schaaf MJM, de Kloet ER, Vreugdenhil E (2000) Corticosterone effects on BDNF expression in the hippocampus: implications for memory formation. Stress 30:201–208
Shi CG, Wang LM, Wu Y et al (2010) Intranasal administration of nerve growth factor produces antidepressant-like effects in animals. Neurochem Res 35:1302–1314
Shirayama Y, Chen AC, Nakagawa S et al (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J Neurosci 22:3251–3261
Smith MA, Makino S, Kim SY et al (1995a) Stress increases brain-derived neurotropic factor messenger ribonucleic acid in the hypothalamus and pituitary. Endocrinology 136:3743–3750
Smith MA, Makino S, Kvetnansky R (1995b) Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 15:1768–1777
Szegedi A, Jansen WT, van Willigenburg APP et al (2009) Early improvement in the first 2 weeks as a predictor of treatment outcome in patients with major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis including 6562 patients. J Clin Psychiatry 70:344–353
Takahashi T, Nowakowski RS, Caviness VS Jr (1992) BUdR as an S-phase marker for quantitative studies of cytokinetic behaviour in the murine cerebral ventricular zone. J Neurocytol 21:185–197
Torner L, Karg S, Blume A et al (2009) Prolactin prevents chronic stress-induced decrease of adult hippocampal neurogenesis and promotes neuronal fate. J Neurosci 29:1826–1833
Uchida S, Hara K, Kobayashi A et al (2011) Impaired hippocampal spinogenesis and neurogenesis and altered affective behavior in mice lacking heat shock factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1681–1686
Ueyama T, Kawai Y, Nemoto K et al (1997) Immobilization stress reduced the expression of neurotrophins and their receptors in the rat brain. Neurosci Res 28:103–110
Van Calker D, Zobel I, Dykierek P et al (2009) Time course of response to antidepressants: predictive value of early improvement and effect of additional psychotherapy. J Affect Disord 114:243–253
Wolkowitz OM, Burke H, Epel ES (2009) Glucocorticoids: mood, memory, and mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1179:19–40
Yasui-Furukori N, Tsuchimine S, Kaneda A et al (2013) Association between plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and personality traits in healthy Japanese subjects. Psychiatry Res 210:220–223
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Dr. Yoshihisa Kitamura and Dr. Kenshi Takechi for their support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashikawa, N., Ogawa, T., Sakamoto, Y. et al. Time Course of Behavioral Alteration and mRNA Levels of Neurotrophic Factor Following Stress Exposure in Mouse. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 807–817 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0174-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0174-x