Abstract
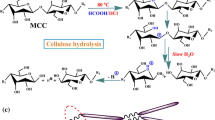
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), prepared from natural cellulose through acid hydrolysis, has been widely used in the food, chemical and pharmaceutical industries because of its high degree of crystallinity, small particle size and other characteristics. Being different from conventional mineral acids, phosphotungstic acid (H3PW12O40, HPW) was explored for hydrolyzing cellulose selectively for the preparation of MCC in this study. Various reaction parameters, such as the acid concentration, reaction time, temperature and solid-liquid ratio, were optimized. Rod-like MCC was obtained with a high yield of 93.62 % and also exhibited higher crystallinity and narrower particle diameter distribution (76.37 %, 13.77–26.17 μm) compared with the raw material (56.47 %, 32.41–49.74 μm) at 90 °C for 2 h with 58 % (w/w) HPW catalyst and a solid-liquid radio of 1:40. Furthermore, HPW can easily be extracted and recycled with diethyl ether for four runs without affecting the quality of the MCC products. The technology of protecting the crystalline region while selectively hydrolyzing the amorphous region of cellulose as much as possible by using HPW is of great significance. Due to the strong Brønsted acid sites and highest activity in solid heteropoly acid, the use of effective homogeneous HPW may offer an eco-friendly and sustainable way to selectively convert fiber resources into chemicals in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd Hamid SB, Chowdhury ZZ, Karim MZ (2014) Catalytic extraction of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) from Elaeis guineensis using central composite design (CCD). Bioresources 9:7403–7426
Adel AM, Abd El-Wahab ZH, Ibrahim AA, Al-Shemy MT (2011) Characterization of microcrystalline cellulose prepared from lignocellulosic materials: part II: physicochemical properties. Carbohydr Polym 83:676–687
Agblevor FA, Ibrahim MM, El-Zawawy WK (2007) Coupled acid and enzyme mediated production of microcrystalline cellulose from corn cob and cotton gin waste. Cellulose 14:247–256
Ciolacu D (2007) On the supramolecular structure of cellulose allomorphs after enzymatic degradation. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 9:1033–1037
Deng WP, Liu M, Zhang QH, Tan XS, Wang Y (2010) Acid-catalysed direct transformation of cellulose into methyl glucosides in methanol at moderate temperatures. Chem Commun 46:2668–2670
Deng WP, Zhang QH, Wang Y (2012) Polyoxometalates as efficient catalysts for transformations of cellulose into platform chemicals. Dalton Trans 41:9817–9831
Dhepe PL, Fukuoka A (2008) Cellulose conversion under heterogeneous catalysis. ChemSusChem 1:969–975
Donald WH, Bjorn F, Hrutfiord Sarkanen KV (1967) Kinetic study on the alkaline degradation of cotton hydrocellulose. J Appl Polym Sci 11:587–600
El-Sakhawy M, Hassan ML (2007) Physical and mechanical properties of microcrystalline cellulose prepared from agricultural residues. Carbohydr Polym 67:1–10
Fan GZ, Wang M, Liao CJ, Fang T, Li JF, Zhou RH (2013) Isolation of cellulose from rice straw and its conversion into cellulose acetate catalyzed by phosphotungstic acid. Carbohydr Polym 94:71–76
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Huang YB, Fu Y (2013) Hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose by solid acid catalysts. Green Chem 15:1095–1111
Jeoh T, Ishizawa CI, Davis MF, Himmel ME, Adney WS, Johnson DK (2007) Cellulase digestibility of pretreated biomass is limited by cellulose accessibility. Biotechnol Bioeng 98:112–122
Jiang YJ, Li XT, Wang XC, Meng LQ, Wang HS, Peng GM, Wang XY, Mu XD (2012) Effective saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass over hydrolysis residue derived solid acid under microwave irradiation. Green Chem 14:2162–2167
Jun A, Masahisa W, Shigenori K, Takeshi O (1998) Flow properties of microcrystalline cellulose suspension prepared by acid treatment of native cellulose. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 142:75–82
Kalita RD, Nath Y, Ochubiojo ME, Buragohain AK (2013) Extraction and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from fodder grass; Setaria glauca (L.) P. Beauv, and its potential as a drug delivery vehicle for isoniazid, a first line antituberculosis drug. Colloids Surf B 108:85–89
Li XT, Jiang YJ, Wang LL, Meng LQ, Wang W, Mu XD (2012) Effective low-temperature hydrolysis of cellulose catalyzed by concentrated H3PW12O40 under microwave irradiation. RSC Adv 2:6921–6925
Li JB, Zhang XR, Zhang MY, He H (2014) Optimization of selective acid hydrolysis of cellulose for microcrystalline cellulose using FeCl3. Bioresources 9:1334–1345
Li JB, Qiang DD, Zhang MY, Xiu HJ, Zhang XR (2015) Joint action of ultrasonic and Fe3+ to improve selectivity of acid hydrolysis for microcrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 129:44–49
Liao CJ, Fang T, Luo SS, Fan GZ, Song GS (2015) H3PW12O40·4H2O as an efficient catalyst for the conversion of cellulose into partially substituted cellulose acetate. J Appl Polym Sci 132:41212/1–41212/7
Liu YF, Wang HS, Yu G, Yu QX, Li B, Mu XD (2014) A novel approach for the preparation of nanocrystalline cellulose by using phosphotungstic acid. Carbohydr Polym 110:415–422
Lu P, Hsieh Y (2012) Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from rice straw. Carbohydr Polym 87:564–573
Lu QL, Tang LR, Lin FC, Wang SQ, Chen YD, Chen XR, Huang B (2014) Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals via ultrasonication-assisted FeCl3-catalyzed hydrolysis. Cellulose 21:3497–3506
Nada AMA, El-Kady MY, Abd El-Sayed ES, Amine FM (2009) Preparation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). Bioresources 4:1359–1371
Park S, Baker JO, Himmel ME, Parilla PA, Johnson DK (2010) Cellulose crystallinity index: measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:1–10
Picker-Freyer KM (2007) An insight into the process of tablet formation of microcrystalline structural changes on a nanoscale level. J Therm Anal Calorim 89:745–748
Ribeiro SJL, Messadeq Y (2008) Synthesis and characterization of cellulose acetate produced from recycled newspaper. Carbohydr Polym 73:74–82
Seehra MS, Popp BV, Goulay F, Pyapalli SK, Gullion T, Poston J (2014) Hydrothermal treatment of microcrystalline cellulose under mild conditions: characterization of solid and liquid-phase products. Cellulose 21:4483–4495
Shimizu K, Furukawa H, Kobayashi N, Itaya Y, Satsuma A (2009) Effects of Bronsted and Lewis acidities on activity and selectivity of heteropolyacid-based catalysts for hydrolysis for hydrolysis of cellobiose and cellulose. Green Chem 11:1627–1632
Siro I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17:459–494
Sun Y, Lin L, Deng HB, Li JZ, He BH, Sun RC (2008) Structural changes of bamboo cellulose in formic acid. Bioresources 3:297–315
Tang YJ, Shen XC, Zhang JH, Guo DL, Kong FG, Zhang N (2015) Extraction of cellulose nano-crystals from old corrugated container fiber using phosphoric acid and enzymatic hydrolysis followed by sonication. Carbohydr Polym 125:360–366
Tao FR, Song HL, Chou LJ (2010) Hydrolysis of Cellulose by Using Catalytic Amounts of FeCl2 in Ionic Liquids. ChemSusChem 3:1298–1303
Thygesen A, Oddershede J, Lilholt H, Thomsen AB, Stahl K (2005) On the determination of crystallinity and cellulose content in plant fibres. Cellulose 12:563–576
Tian J, Wang JH, Zhao S, Jiang CY, Zhang X, Wang XH (2010) Hydrolysis of cellulose by the heteropoly acid H3PW12O40. Cellulose 17:587–594
Tong DS, Xia X, Luo XP, Wu LM, Lin CX, Yu WH, Zhou CH, Zhong ZK (2013) Catalytic hydrolysis of cellulose to reducing sugar over acid-activated montmorillonite catalysts. Appl Clay Sci 74:147–153
Wang D, Shang SB, Song ZQ, Lee MK (2010) Evaluation of microcrystalline cellulose prepared from kenaf fibers. J Ind Eng Chem 16:152–156
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (grant no. 20126125130001) and the Doctoral Scientific Research Fund of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (grant no. BJ13-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiang, D., Zhang, M., Li, J. et al. Selective hydrolysis of cellulose for the preparation of microcrystalline cellulose by phosphotungstic acid. Cellulose 23, 1199–1207 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0858-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0858-5