Abstract
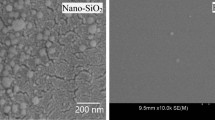
Water responsive SiO2/cellulose nanocomposite hydrogels and films were constructed, for the first time, by dispersing SiO2 nanoparticles into cellulose solution in LiOH/urea solvent, and then by crosslinking with epichlorohydrin or regeneration in coagulation bath, respectively. The cellulose nanocomposite materials were characterized by Field emission scanning electron microscopy, FTIR, dynamic rheology, wide angle X-ray diffraction and mechanical test. The SiO2/cellulose nanocomposites at wet state or in water displayed unique behaviors, showing higher light transmittance than those before contacting with water. The results revealed that strong hydrogen-bonding interaction among water, cellulose and SiO2 led the good dispersion of SiO2 nanoparticles in the cellulose matrix. The incorporation of SiO2 nanoparticles improved the transmittance and mechanical strength of the cellulose hydrogels, and also enhanced the mechanical strength of the films. Especially, the cellulose/SiO2 nanocomposite films were milky at dry state, and changed to transparent after being soaked in water, different from the cellulose film without the SiO2 nanoparticles. In our findings, SiO2 and cellulose with water could form strong hydrogen bonding to create a homogenous network structure. The cellulose/SiO2 composite as a smart material exhibited moisture and solvent responsiveness, showing potential applications in moisture detection.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apetz R, Bruggen MP (2003) Transparent alumina: a light-scattering model. J Am Ceram Soc 86(3):480–486
Balazs AC, Emrick T, Russell TP (2006) Nanoparticle polymer composites: where two small worlds meet. Science 314(5802):1107–1110
Cai J, Liu Y, Zhang L (2006) Dilute solution properties of cellulose in LiOH/urea aqueous system. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 44(21):3093–3101
Cai J, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S, Zhang L (2008) Cellulose aerogels from aqueous alkali hydroxide–urea solution. ChemSusChem 1(1–2):149–154
Chen M, Wu L, Zhou S, You B (2004) Synthesis of raspberry-like PMMA/SiO2 nanocomposite particles via a surfactant-free method. Macromolecules 37(25):9613–9619
Chen D, Huang F, Cheng YB, Caruso RA (2009) Mesoporous anatase TiO2 beads with high surface areas and controllable pore sizes: a superior candidate for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv Mater 21(21):2206–2210
de las Heras Alarcón C, Pennadam S, Alexander C (2005) Stimuli responsive polymers for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 34(3):276–285
Feng J, Peng L, Wu C, Sun X, Hu S, Lin C, Dai J, Yang J, Xie Y (2012) Giant moisture responsiveness of VS2 ultrathin nanosheets for novel touchless positioning interface. Adv Mater 24(15):1969–1974
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Fujii S, Read ES, Binks BP, Armes SP (2005) Stimulus-responsive Emulsifiers Based on nanocomposite microgel particles. Adv Mater 17(8):1014–1018
Garnweitner G, Smarsly B, Assink R, Ruland W, Bond E, Brinker CJ (2003) Self-assembly of an environmentally responsive polymer/silica nanocomposite. J Am Chem Soc 125(19):5626–5627
Han J, Dou Y, Yan D, Ma J, Wei M, Evans DG, Duan X (2011) Biomimetic design and assembly of organic–inorganic composite films with simultaneously enhanced strength and toughness. Chem Commun 47(18):5274–5276
Hu J, Liu S (2010) Responsive polymers for detection and sensing applications: current status and future developments. Macromolecules 43(20):8315–8330
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44(22):3358–3393
Koo J, Hong K, Park J, Shin D (2004) Effect of grain size on transmittance and mechanical strength of sintered alumina. Mater Sci Eng A 374(1):191–195
Langan P, Nishiyama Y, Chanzy H (2001) X-ray structure of mercerized cellulose II at 1 Å resolution. Biomacromolecules 2:410–416
Li L, Aoki Y (1997) Rheological images of poly (vinyl chloride) gels. 1. the dependence of sol–gel transition on concentation. Macromolecules 30(25):7835–7841
Liu S, Zhang L (2009) Effects of polymer concentration and coagulation temperature on the properties of regenerated cellulose films prepared from LiOH/urea solution. Cellulose 16(2):189–198
Ma M, Guo L, Anderson DG, Langer R (2013) Bio-inspired polymer composite actuator and generator driven by water gradients. Science 339(6116):186–189
Nan C-W, Fan L, Lin Y, Cai Q (2003) Enhanced Ionic Conductivity of Polymer Electrolytes Containing Nanocomposite S i O 2 Particles. Phys Rev Lett 91(26):266104
Ogihara H, Xie J, Okagaki J, Saji T (2012) Simple method for preparing superhydrophobic paper: spray-deposited hydrophobic silica nanoparticle coatings exhibit high water-repellency and transparency. Langmuir 28(10):4605–4608
Pei Y, Wang X, Huang W, Liu P, Zhang L (2013) Cellulose-based hydrogels with excellent microstructural replication ability and cytocompatibility for microfluidic devices. Cellulose 20(4):1897–1909
Sidorenko A, Krupenkin T, Taylor A, Fratzl P, Aizenberg J (2007) Reversible switching of hydrogel-actuated nanostructures into complex micropatterns. Science 315(5811):487–490
Song H, Zheng L (2013) Nanocomposite films based on cellulose reinforced with nano-SiO2: microstructure, hydrophilicity, thermal stability, and mechanical properties. Cellulose 20(4):1737–1746
Stuart MAC, Huck WT, Genzer J, Müller M, Ober C, Stamm M, Sukhorukov GB, Szleifer I, Tsukruk VV, Urban M (2010) Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat Mater 9(2):101–113
Wang Z, Han E, Ke W (2006) Effect of acrylic polymer and nanocomposite with nano-SiO2 on thermal degradation and fire resistance of APP–DPER–MEL coating. Polym Degrad Stab 91(9):1937–1947
Wang Q, Cai J, Zhang L, Xu M, Cheng H, Han CC, Kuga S, Xiao J, Xiao R (2013) A bioplastic with high strength constructed from a cellulose hydrogel by changing the aggregated structure. J Mater Chem A 1(22):6678–6686
Wu J, Sailor MJ (2009) Chitosan hydrogel-capped porous SiO2 as a pH responsive nano-valve for triggered release of insulin. Adv Funct Mater 19(5):733–741
Yang X, Liu Q, Chen X, Yu F, Zhu Z (2008) Investigation of PVA/ws-chitosan hydrogels prepared by combined γ-irradiation and freeze-thawing. Carbohydr Polym 73(3):401–408
Yang J, Han C-R, Duan J-F, Xu F, Sun R-C (2013) Interaction of silica nanoparticle/polymer nanocomposite cluster network structure: revisiting the reinforcement mechanism. J Phys Chem C 117(16):8223–8230
Yuvaraj H, Shim JJ, Lim KT (2010) Organic–inorganic polypyrrole-surface modified SiO2 hybrid nanocomposites: a facile and green synthetic approach. Polym Adv Technol 21(6):424–429
Zarzar LD, Aizenberg J (2013) Stimuli-responsive chemomechanical actuation: a hybrid materials approach. Acc Chem Res 47:530–539
Zeng J, Liu S, Cai J, Zhang L (2010) TiO2 immobilized in cellulose matrix for photocatalytic degradation of phenol under weak UV light irradiation. J Phys Chem C 114(17):7806–7811
Zhang Y, Yu J, Zhou C, Chen L, Hu Z (2010) Preparation, morphology, and adhesive and mechanical properties of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene/SiO2 nanocomposite fibers. Polym Compos 31(4):684–690
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2010CB732203), the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (21334005) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20874079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, M., Duan, B., Xu, D. et al. Moisture and solvent responsive cellulose/SiO2 nanocomposite materials. Cellulose 22, 553–563 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0527-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0527-5