Abstract
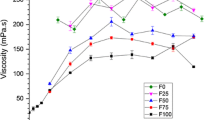
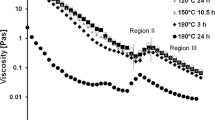
Microfibrillated Cellulose (MFC) was isolated from unbleached kraft pulp derived from kenaf bast fiber. MFC gels with different concentrations were manufactured from pulp with varying initial consistencies. The MFC was diluted to a consistency of around one percent using distilled water and was further homogenized by passing through a microfluidizer. In order to gain an understanding of the relative changes in behavior of the resulting MFC gels, their rheological properties were characterized. Results show that all of the gels exhibit a shear-thinning behavior. It was also determined that the rheological characteristics improved with increasing gel concentration, which was achieved by using higher pulp suspension consistencies. Diluted MFC that was derived from highly concentrated MFC had more variable modulus under the same strain and frequency compared to poorly concentrated MFC. But such a strong effect was not observed for viscosity. Additionally, the value of G′, ranging from 76 to 5325 Pa under the studied concentrations, was found to be fourfold the value of G″. In the low frequency range, G′ was almost independent of frequency, but was dependent on gel consistency with a coefficient of 3, indicating that MFC gels are elastic. These results show that it is possible to produce MFC gels with good rheological properties from high consistency kenaf pulp suspensions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Iwamoto S, Yano H (2007) Obtaining cellulose nanof-ibers with a uniform width of 15 nm from wood. Bio-macromolecules 8:3276–3278
Agoda-Tandjawa G, Durand S, Berot S, Blassel C, Gaillard C, Garnier C, Doublier J-L (2010) Rheological characterization of microfibrillated cellulose suspensions after freezing. Carbohydr Polym 80:677–686
Ahola S (2008) Production and interfacial behaviour of cellulose nanofibrils. TKK Reports in Forest Products Technology, Series A4. Doctoral Thesis, p 9
Almdal K, Dyre J, Hvidt S, Kramer O (1992) Towards a phenomenological definition of the term ‘gel’. Polym Gels Netw 1:5–17
Ankerfors M, Lindström T (2007) On the manufacture and use of nanocellulose. 9th International Conference on wood & biofiber plastic composites, Madison, WI (USA)
Ankerfors M, Lindström T (2010) The starting material-MFC. In: Proceedings of the SustainComp Conference, Trondheim, October 26–27
Arndt T, Meinl G, Erhard K (2011) Behaviour of cellulose fine structures in papermaking tests. Fine structure of papermaking fibres. The Final Report of COST Action E54. COST Office, Avenue Louise 149, B-1050 Brussels, Belgium. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, SLU Service/Repro, Uppsala, p 248
Aulin C, Gällstedt M, Lindström T (2010) Oxygen and oil barrier properties of microfibrillated cellulose films and coatings. Cellulose 17:559–574
Azizi Samir MAS, Alloin F, Dufresne A (2005) Review of recent research into cellulosic whiskers, their properties and their application in nanocomposite field. Biomacromolecules 6(2):612–626
Bahtoee A, Zargari K, Baniani E (2012) An investigation on fiber production of different kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus l.) genotypes. World Appl Sci J 16(1):63–66
Barnes HA (1995) A review of the slip (wall depletion) of polymer solutions, emulsions and particle suspensions in viscometers: its cause, character, and cure. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 56:221–251
Bercea M, Navard P (2000) Shear dynamics of aqueous suspensions of cellulose whiskeys. Macromolecules 33(16):6011–6016
Burchard W, Ross-Murphy SB (1990) Physical networks, polymers and gels. Elsevier, London, p 417
Derakhshandeh B, Kerekes RJ, Hatzikiriakos SG, Bennington CPJ (2011) Rheology of pulp fibre suspensions: acriticalreview. Chem Eng Sci 66:3460–3470
Dinand E, Chanzy H, Vignon M (1996) Parenchymal cell cel-lulose from sugar beet pulp: preparation and properties. Cellulose 3:183–188
Dufresne A, Dupeyre D, Vignon MR (2000) Cellulose micro-fibrils from potato tuber cells: processing and character-ization of starch–cellulose microfibril composites. J Appl Polym Sci 76:2080–2092
Faruq G, Alamgir MA, Rahman MM, Subha B, Motior MR (2011) Evaluation of genetic variability of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) from different geographic origins using morpho-agronomic traits and multivariate analysis. AJCS 5(13):1882–1890
Hassan ML, Mathew AP, Hassan EA, El-Wakil NA, Oksman K (2012) Nanofibers from bagasse and rice straw: process optimization and properties. Wood Sci Technol 46:193–205
Henriksson M, Henriksson G, Berglund LA, Lindström T (2007) An environmentally friendly method for enzyme-assisted preparation of micro fibrillated cellulose (MFC) nanofibers. Eur Polym J 43:3434–3441
Hossain MD, Hanafi MM, Jol H, Hazandy AH (2011) Growth, yield and fiber morphology of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) grown on sandy bris soil as influenced by different levels of carbon. Afr J Biotechnol 10(50):10087–10094
Iotti M, Gregersen ØW, Moe S, Lenes M (2011) Rheological studies of microfibrillar cellulose water dispersions. J Polym Environ 19:137–145
Iwamoto S, Abe K, Yano H (2008) The effect of hemicelluloses on wood pulp nanofibrillation and nanofiber network characteristics. Biomacromolecules 9:1022–1026
Jahan MS, Saeed A, He Z, Ni Y (2011) Jute as raw material for the preparation of microcrystalline cellulose. Cellulose 18:451–459
Johansson C, Bras J, Mondragon I, Nechita P, Plackett D, Šimon P, Svetec DG, Virtanen S, Baschetti MG, Breen C, Clegg F, Aucejo S (2012) Renewable fibers and bio-based materials for packaging applications- a review of recent developments. BioResources 7(2):2506–2552
Jonoobi M, Harun J, Shakeri A, Misra M, Oksman K (2009) Chemical composition, crystallinity, and thermal degradation of bleached and unbleached kenaf bast (Hibiscus cannabinus) pulp and nanofibers. BioResources 4(2):626–639
Jonoobi M, Harun J, Mathew AP, Hussein MZB, Oksman K (2010) Preparation of cellulose nanofibers with hydrophobic surface characteristics. Cellulose 17:299–307
Jonoobi M, Harun J, Tahir PM, Shakeri A, Saiful Azry S, Davoodi Makinejad M (2011) Physicochemical characterization of pulp and nanofibers from kenaf stem. Mater Lett 65:1098–1100
Kargarzadeh H, Ahmad I, Abdullah I, Dufresne A, Zainudin SY, Sheltami RM (2012) Effects of hydrolysis conditions on the morphology, crystallinity, and thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from kenaf bast fibers. Cellulose 19:855–866
Karppinen A, Vesterinen A, Saarinen T, Pietikäinen P, Seppälä J (2011) Effect of cationic polymethacrylates on the rheology and flocculation of microfibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 18:1381–1390
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Gray D, Dorri A (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5438–5546
Laine J (2006) Creating materials and specific surfaces from cellulose microfibrils. Wood Material Science Research Programme Annual Seminar, April 5, Helsinki, Finland
Lavoine N, Deslogesa I, Dufresnea A, Bras J (2012) Microfibrillated cellulose-its barrier properties and applications in cellulosic materials: a review. Carbohydr Polym 90(2):735–764
Littunen K, Hippi U, Johansson L, Österberg M, Tammelin T, Laine J, Seppälä J (2011) Free radical graft copolymeri-zation of nanofibrillated cellulose with acrylic monomers. Carbohydr Polym 84:1039–1047
Lowys MP, Desbrie`res J, Rinaudo M (2001) Rheological char-acterization of cellulosic microfibril suspensions. Role of polymeric additives. Food Hydrocoll 15:25–32
Manninen M, Kajanto I, Happonen J, Paltakari J (2011) The effect of microfibrillated cellulose addition on drying shrinkage and dimensional stability of wood-free paper. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 26:297–305
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994
Morais JPS, Rosa MF, Souza Filho MSM, Nascimentoa DM, Cassales AR (2013) Extraction and characterization of nanocellulose structures from raw cotton linter. Carbohydr Polym 91:229–235
Mossello AA, Harun J, Tahir PM, Resalati H, Ibrahim R, Fallah Shamsi SR, Mohmamed AZ (2010) A review of literatures related of using kenaf for pulp production (beating, fractionation, and recycled fiber). Mod Appl Sci 4(9):21–29
Norde W (2005) Colloids and interfaces in life sciences. Taylor & Francis e-Library. ISBN 0-203-91215-2 Master e-book, pp 354–355
Orhan M (2010) Polylactide foams reinforced with wood fibers or microfibrillated cellulose. Uppsala University, Faculty of Science and Technology. Master Thesis, p 8
Pääkkö M, Ankerfors M, Kosonen H, Nykänen A, Ahola S, Österberg M, Ruokolainen J, Laine J, Larsson PT, Ikkala O, Lindström T (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis combined with mechanical shearing and high-pressure homogenization for nanoscale cellulose fibrils and strong gels. Biomacromolecules 8:1934–1941
Ross-Murphy SB (1994) Rheological characterization of polymer gels and networks. Polym Gels Netw 2:229–237
Rudraraju VS, Wyandt CM (2005a) Rheological characterization of Microcrystalline cellulose/sodiumcarboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels using a controlled stress rheometer: part I. Int J Pharm 292:53–61
Rudraraju VS, Wyandt CM (2005b) Rheology of microcrystalline cellulose and sodiumcarboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels using a controlled stress rheometer: part II. Int J Pharm 292:63–73
Saarikoski E, Saarinen T, Salmela J, Seppälä J (2012) Flocculated flow of microfibrillated cellulose water suspensions: an imaging approach for characterization of rheological behaviour. Cellulose 19(3):647–659
Saarinen T, Lille M, Seppälä J (2009) Technical aspects on rheological characterization of microfibrillar cellulose water suspensions. Annu Trans Nord Rheol Soc 17:121–128
Saito T, Nishiyama Y, Putaux J, Vignon M, Isogai A (2006) Homogeneous suspensions of individualized microfibrils from TEMPO-catalyzed oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 7:1687–1691
Saito T, Kimura S, Nishiyama Y, Isogai A (2007) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 8:2485–2491
Sehaqui H, Liu A, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2010) Fast preparation procedure for large, flat cellulose and cellulose/inorganic nanopaper structures. Biomacromolecules 11(9):2195–2198
Shakhes J, Zeinaly F, Marandi MAB, Saghafi T (2012) Effects of harvest time and cultivar on yield and physical properties fibers of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.). Afr J Biochem Res 6(6):69–74
Shogren RL, Peterson SC, Evans KO, Kenar JA (2011) Preparation and characterization of cellulose gels from corncobs. Carbohydr Polym 86:1351–1357
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Habibi Y, Rojas OJ, Pawlak JJ (2010a) Aspects of Raw Materials and Processing Conditions on the Production and Utilization of Microfibrillated Cellulose. International conference on nanotechnology for the forest products industry. Otaniemi, Espoo, Finland
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ, Habibi Y, Pawlak JJ (2010b) The effect of chemical composition on microfibrillar cellulose films from wood pulps: water interactions and physical properties for packaging applications. Cellulose 17:835–848
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Habibi Y, Rojas OJ, Pawlak JJ (2010c) The effect of chemical composition on microfibrillar cellulose films from wood pulps: mechanical processing and physical properties. Bioresour Technol 101:5961–5968
Surip SN, Wan Jaafar WNR, Azmi NN, Anwar UMK (2012) Microscopy observation on nanocellulose from kenaf fibre. Adv Mater Res 488–489:72–75
Swerin A, Powell RL, Odberg L (1992) Linear and nonlinear dynamic viscoelas—ticity of pulp fibre suspensions. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 7(3):126–143
Syverud K, Stenius P (2009) Strength and barrier properties of MFC films. Cellulose 16:75–85
Taipale T, Österberg M, Nykänen A, Ruokolainen J, Laine J (2010) Effect of microfibrillated cellulose and fines on the drainage of kraft pulp suspension and paper strength. Cellulose 17:1005–1020
Tatsumi D (2007) Rheology of cellulose fiber disperse systems and cellulose solutions. Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi 35(5):251–256
Tatsumi D, Ishioka S, Matsumoto T (2002) Effect of fiber concentration and axial ratio on the rheological properties of cellulose fiber suspensions. J Soc Rheol 30(1):27–32 Japan
Villar JC, Revilla E, Gómez N, Carbajo JM, Simón JL (2009) Improving the use of kenaf for kraft pulping by using mixtures of bast and core fibers. Ind Crop Prod 29:301–307
Wågberg L, Winter L, Ödberg L, Lindström T (1987) On the charge stoichiometry upon adsorption of a cationic polyelectrolyte on cellulosic materials. Colloids Surf 27:163–173
Zhang J, Song H, Lin L, Zhuang J, Pang C, Liu S (2012) Microfibrillated cellulose from bamboo pulp and its properties. Biomass Bioenergy 39:78–83
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support of the INNVENTIA AB, Department of Paper Chemistry and Microbiology. We acknowledge Prof. Tom Lindström (KTH) and Dr. Ali Naderi (INNVENTIA AB) for valuable discussions, and Åsa Blademo (INNVENTIA AB) is acknowledged for valuable experimental assistance and numerous discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezayati Charani, P., Dehghani-Firouzabadi, M., Afra, E. et al. Rheological characterization of high concentrated MFC gel from kenaf unbleached pulp. Cellulose 20, 727–740 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9862-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9862-1