Abstract
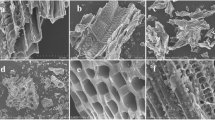
Multivalent ions take a significant role in the sorption of soluble polysaccharides on solid cellulose substrates and thus demonstrate an important principle in structural polysaccharide organisation. Sorption of Fe(III)–alginate complexes on lyocell fibres as model for the insoluble cellulose matrix has been studied between pH 3–13, at 30 and 60 °C. Sorption maximum of the Fe(III)–alginate complex was observed at pH 3 where the sorbed amounts of alginate and iron were 6,600 and 85 mg iron per kg cellulose respectively. Under the experimental conditions used, a concentration of 0.05 mM Fe(III) is sufficient to achieve surface sorption of Fe(III)–alginate complex. The alginate sorption exhibited minor dependence on molar ratio of Fe(III) to alginate. In environmental scanning electron microscopy no deposition of Fe-hydroxides on the fiber surface was detected. The thickness of the adsorbed Fe(III)–alginate layer on the fiber surface was estimated with 12–22 nm. Tensile strength and abrasion resistance of Fe(III)–alginate treated fibers were not reduced through the sorption treatment. Alginate modified cellulose is of interest as material for medical application, as sorbent and textile finish.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa AM, Granja LP, Barrias CC, Amaral FI (2005) Polysaccharides as scaffolds for bone regeneration. ITBM–RBM 26:212–217
Bechtold T, Burtscher E, Turcanu A (2002) Ca2+–Fe3+-d-gluconate-complexes in alkaline solution complex stabilities and electrochemical properties. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans 2683–2688
Bechtold T, Manian AP, Ozturk HB, Paul U, Siroka B, Siroky J, Soliman H, Vo LTT, Vu-Manh H (2013) Ion-interactions as driving force in polysaccharide assembly. Carbohydr Polym 93:316–323
Bocharova N, Zavalov O, MacVittie K, Arugula MA, Guz NV, Dokukin ME, Halámek J, Sokolov I, Privman V, Katz E (2012) Biochemical logic approach to biomarker-activated drug release. J Mater Chem 22:19709–19717
Bredereck K, Hermanutz F (2005) Man-made cellulos. Rev Progr Color Technol 35:59–75
Cain RJ, Lalgudi RS (2011) Stain-repellent compositions for textile treatment. WO2011023982A1, 261888
Chen KL, Mylon SE, Elimelech M (2006) Aggregation kinetics of alginate-coated hematite nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolytes. Environ Sci Technol 40(5):1516–1523
Chiaoprakobkij N, Sanchavanakit N, Subbalekha K, Pavasant P, Phisalaphong M (2011) Characterization and biocompatibility of bacterial cellulose/alginate composite sponges with human keratinocytes and gingival fibroblasts. Carbohydr Polym 85:548–553
Cifci C, Sanli O (2010) Crossflow filtration of iron(III), copper(II), and cadmium(II) aqueous solutions with alginic acid/cellulose composite membranes. J Appl Polym Sci 115:616–623
Cifci C, Sanli O (2011) Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)-enhanced crossflow filtration of Fe(III), Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions using alginic acid/cellulose composite membranes. Desalin Water Treat 29:87–95
Deng H, Zhou X, Wang X, Zhang C, Ding B, Zhang Q, Du Y (2010) Layer-by-layer structured polysaccharides film-coated cellulose nanofibrous mats for cell culture. Carbohydr Polym 80:474–479
Emam HE, Manian AP, Široká B, Bechtold T (2012) Copper inclusion in cellulose using sodium d-gluconate complexes. Carbohydr Polym 90:1345–1352
Ferrari E, Saladini M (2004) Iron (III) complexing ability of carbohydrate derivatives. J Inorg Biochem 98:1002–1008
Finotelli VP, Morales AM, Rocha-Leao HM, Baggio-Saitovitch ME, Rossi MA (2004) Magnetic studies of iron (III) nanoparticles in alginate polymer for drug delivery applications. Mater Sci Eng C24:625–629
Franke W (1931) Iron complexes of tartaric acid. Liebigs Ann Chem 486:242–284
Gorensek M, Bukosek V (2006) Zinc and alginate for multipurpose textiles. Acta Chem Slov 53:223–228
Griffiths B, Jacques E, Bishop SM (1998) Wound dressing comprising a blend of cellulose and alginate fibers. WO9809590A1, 169427
Hammer KD, Winter H (1991) Flat or tubular films of hydrated cellulose. DE4002083A1, 561491
Huang C–C, Lai S-H, Cheng S-L, Chang G-W (2009) Designed artificial skins prepared from modified microbial cellulose dressings for wound healing. PMSE Prepr 101:1601–1602
Jin Z, Güven G, Bocharova V, Halamek J, Tokarev I, Minko S, Melman A, Mandler D, Katz E (2012a) Electrochemically controlled drug-mimicking protein release from iron–alginate thin-films associated with an electrode. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:466–475
Jin Z, Harvey AM, Mailloux S, Halámek J, Bocharova V, Twiss MR, Katz E (2012b) Electrochemically stimulated release of lysozyme from an alginate matrix cross-linked with iron cations. J Mater Chem 22:19523–19528
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink H-P, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascination biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem 44:3358–3393
Knittel D, Schollmeyer E (2008) Unconventional textile finishes part 2: textile finishes with alginate and pectin and cellulose. Melliand Textilberichte 89:32–35
Kongdee A, Bechtold T (2004) The complexation of Fe(III)–ions in cellulose fibers: a fundamental property. Carbohydr Polym 56:47–53
Liu M, Yue X, Dai Z, Ma Y, Xing L, Zha Z, Liu S, Li Y (2009) Novel thrombo-resistant coating based on iron–polysaccharide complex multilayers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:113–123
Machida-Sano I, Matsuda Y, Namiki H (2009) In vitro adhesion of human dermal fibroblasts on iron cross-linked alginate films. Biomed Mater 4:025008
Mehltretter CL, Alexander BH, Rist CE (1953) Sequestration by sugar acids. Ind Eng Chem 45:2782
Mueller PJ, Christner A, Feustel M, Möhring U, Neudeck A (2004) Biotechnology and textile structures (part 2). Melliand Textilberichte 85:490–492
Naito N, Kawanaka S, Wada S (2005) Manufacture of water-absorption materials JP2005263858A, 1045099
Nesterova VM, Walton AS, Webb J (2000) Nanoscale iron(III) oxyhydroxy aggregates formed in the presence of functional water-soluble polymers: models for iron(III) biomineralisation processes. J Inorg Biochem 79:109–118
Paul UC, Manian AP, Široká B, Duelli H, Bechtold T (2012) Sorption of anionic polysaccharides by cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 87:695–700
Pecsok RL, Sandera J (1955) The gluconate complexes II The ferric-gluconate system. J Am Chem Soc 77(6):1489–1494
Russo R, Abbate M, Malinconico M, Santagata G (2010) Effect of polyglycerol and the crosslinking on the physical properties of a blend alginate-hydroxyethylcellulose. Carbohydr Polym 82:1061–1067
Seely RG, Hart LR (1976) Binding of aluminum and aluminum alizarin to alginate. Macromolecules 9(3):483–489
Sipos P, St Pierre GT, Tombacz E, Webb J (1995) Rod-like iron (III) oxyhydroxide particles in iron (III)–polysaccharide solutions. J Inorg Biochem 58:129–138
Somsook E, Hinsin D, Buakhrong P, Teanchai R, Mophan N, Pohmakotr M, Shiowatana J (2005) Interactions between iron (III) and sucrose, dextran, or starch in complexes. Carbohydr Polym 61:281–287
Son HJ, Jung JH, Son T-W (2012) Anionic polymer salt-coated cellulose fibers with good antibacterial and deodorization effect. KR1125253B1, 432275
Sun T, Lonsky W, Li Y, Qin J, Zhang X, Dutkiewicz J (2001) Cellulosic fibrous materials containing an activating agent for superabsorbent polymers. WO2001047570A1, 489271
Sreeram JK, Shrivastava YH, Nair UB (2004) Studies on the nature of interaction of iron (III) with alginates. Biochemica Biophysica Acta 1670:121–125
Vu-Manh H, Öztuerk H, Bechtold T (2010) Swelling and dissolution mechanism of lyocell fiber in aqueous alkaline solution containing ferric tartaric acid complex. Cellulose 17:521–532
Wagberg L (2000) Polyelectrolyte adsorption onto cellulose fibers—a review. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 15(5):586–597
Weerawarna SA, Bing S (2008) Preparation of cellulose fibers having superabsorbent particles adhered to cellulose fibers and adhering superabsorbent particles to cellulose fibers. US20080078514A1, 419453
Zhang L, Zhou D, Wang H, Cheng S (1997) Ion-exchange membranes blended by cellulose cuoxam with alginate. J Membr Sci 124:195–201
Zhang L, Zhou J, Zhou D, Tang Y (1999) Adsorption of cadmium and strontium on cellulose/alginic acid ion-exchange membrane. J Membr Sci 162:103–109
Zhang L, Cai J, Zhou J, Tang Y (2004) Adsorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+ on ion-exchange beads from cellulose/alginic acid blend. Sep Sci Technol 39:1203–1219
Acknowledgments
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme [FP7/2007–2013] under Grant Agreement No. 214015. The authors would like to acknowledge to Versuchsanstalt-Textil and the HTL-Dornbirn for the use of their facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research Institute of Textile Chemistry and Textile Physics is a member of EPNOE-European Polysaccharide Network of Excellence, www.epnoe.eu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, U.C., Manian, A.P., Široká, B. et al. Sorption of iron(III)–alginate complexes on cellulose fibres. Cellulose 20, 2481–2490 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0013-5