Abstract
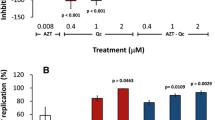
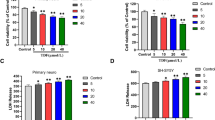
Efavirenz is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and an active constituent of the highly active antiretroviral therapy regime. It has significantly contributed in control and management of human immunodeficiency virus propagation. However, EFV administration has also led to severe adverse effects, several reports highlighted the role of EFV in mitochondrial dysfunction and toxicity but the molecular mechanism has been poorly understood. In present study, human hepatoma cells Huh 7.5 were treated with clinically relevant concentrations of EFV and parameters like cytotoxicity, mitochondrial transmembrane potential, mitochondrial morphology, cytochrome c release, mitochondria-mediated apoptosis, mtDNA and mtRNA levels and EFV distribution into mitochondrial compartment were evaluated to understand sequence of events leading to cell death in EFV-treated cells. EFV at its clinically relevant concentration was significantly toxic after 48 and 72 h of treatments. EFV-mediated toxicity is initiated with the permeabilization of mitochondrial outer membrane and change in mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) which triggers a series of events like cytochrome c release, alteration in mitochondrial morphology and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Total mitochondrial content is reduced after 48 h of EFV treatment at IC50 concentration which is also reflected in reduced mitochondrial DNA and RNA levels. After detecting EFV in mitochondrial compartment after 12 h of incubation with EFV, we hypothesize that EFV being a lipophilic molecule is internalized into the mitochondrial compartment causing depolarization of Δψm which subsequently leads to a cascade of events causing cell death.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almond LM, Hoggard PG, Edirisinghe D, Khoo SH, Back DJ. Intracellular and plasma pharmacokinetics of efavirenz in HIV-infected individuals. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56:738–44.
Annex BH, Williams RS. Mitochondrial DNA structure and expression in specialized subtypes of mammalian striated muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:5671–8.
Antonetti DA, Reynet C, Kahn CR. Increased expression of mitochondrial-encoded genes in skeletal muscle of humans with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1995;95:1383–8.
Barreiro P, Rodriguez-Novoa S, Labarga P, Ruiz A, Jimenez-Nacher I, Martin-Carbonero L, Gonzalez-Lahoz J, Soriano V. Influence of liver fibrosis stage on plasma levels of antiretroviral drugs in HIV-infected patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Infect Dis. 2007;195:973–9.
Beatrice MC, Palmer JW, Pfeiffer DR. The relationship between mitochondrial membrane permeability, membrane potential, and the retention of Ca2+ by mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1980;255(18):8663–71.
Blas-Garcia A, Apostolova N, Ballesteros D, Monleon D, Morales JM, Rocha M, Victor VM, Esplugues JV. Inhibition of mitochondrial function by efavirenz increases lipid content in hepatic cells. Hepatology. 2010;52:115–25.
Carr A, Cooper DA. Adverse effects of antiretroviral therapy. Lancet. 2000;356:1423–30.
Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Ponsoda X, Bort R. The use of cultured hepatocytes to investigate the mechanisms of drug. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1997;13:331–8.
Chaitanya GV, Steven AJ, Babu PP. PARP-1 cleavage fragments: signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell Commun Signal. 2010;8:31.
Chan DC. Mitochondria: dynamic organelles in disease, aging, and development. Cell. 2006;125:1241–52.
Chazotte B. Labeling mitochondria with JC-1. Cold Spring Harb Protocol. 2011;2011.
Chipuk JE, Bouchier-Hayes L, Green DR. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the innocent bystander scenario. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(8):1396–402.
Choi S, Sainz Jr B, Corcoran P, Uprichard S, Jeong H. Characterization of increased drug metabolism activity in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated Huh7 hepatoma cells. Xenobiotica. 2009;39:205–17.
Cote HC, Brumme ZL, Craib KJ, Alexander CS, Wynhoven B, Ting L, Wong H, Harris M, Harrigan PR, O’shaughnessy MV, Montaner JS. Changes in mitochondrial DNA as a marker of nucleoside toxicity in HIV-infected patients. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:811–20.
de Clercq E. New developments in anti-HIV chemotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1587:258–75.
de Mendoza C, Martin-Carbonero L, Barreiro P, de Baar M, Zahonero N, Rodriguez-Novoa S, Benito JM, Gonzalez-Lahoz J, Soriano V. Mitochondrial DNA depletion in HIV-infected patients with chronic hepatitis C and effect of pegylated interferon plus ribavirin therapy. AIDS. 2007;21:583–8.
Detels R, Tarwater P, Phair JP, Margolick J, Riddler SA, Munoz A, Multicenter ACS. Effectiveness of potent antiretroviral therapies on the incidence of opportunistic infections before and after AIDS diagnosis. AIDS. 2001;15:347–55.
Donaldson JG. Immunofluorescence staining. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2015;69:4.
Figueiredo, A., Moore, K. L., Mak, J., Sluis-Cremer, N., de Bethune, M. P. & Tachedjian, G. 2006. Potent nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors target HIV-1 Gag-Pol. PLoS Pathog. 2006;2:1051–59.
Frezza C, Cipolat S, Scorrano L. Measuring mitochondrial shape changes and their consequences on mitochondrial involvement during apoptosis. In: Leister D, Herrmann J, editors. Mitochondria: Humana Press; 2007a.
Frezza C, Cipolat S, Scorrano L. Organelle isolation: functional mitochondria from mouse liver, muscle and cultured fibroblasts. Nat Protoc. 2007b;2:287–95.
Gallagher, S., Winston, S. E., Fuller, S. A. & Hurrell, J. G. 2011. Immunoblotting and immunodetection. Curr Protoc Cell Biol, Chapter 6, Unit 6 2.
Gilbert, J. R. & Vance, J. M. 2001. Isolation of genomic DNA from mammalian cells. Curr Protoc Hum Genet, Appendix 3, Appendix 3B.
Gomez-Sucerquia LJ, Blas-Garcia A, Marti-Cabrera M, Esplugues JV, Apostolova N. Profile of stress and toxicity gene expression in human hepatic cells treated with efavirenz. Antivir Res. 2012;94:232–41.
Gottlieb E, Armour SM, Harris MH, Thompson CB. Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:709–17.
Gunthard HF, Aberg JA, Eron JJ, Hoy JF, Telenti A, Benson CA, Burger DM, Cahn P, Gallant JE, Glesby MJ, Reiss P, Saag MS, Thomas DL, Jacobsen DM, Volberding PA, International Antiviral Society, U. S. A. P. Antiretroviral treatment of adult HIV infection: 2014 recommendations of the International Antiviral Society—USA Panel. JAMA. 2014;312:410–25.
Gutierrez ME, Canton A, Sosa N, Puga E, Talavera L. Disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with AIDS in Panama: a review of 104 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:1199–202.
Habtewold, A., Akillu, E., Makonnen, E., Amogne, W., Yimer, G., Aderaye, G., Bertilsson, L., Owen, J. S. & Burhenne, J. 2016. Long-term effect of rifampicin-based anti-TB regimen co-administration on the pharmacokinetic parameters of efavirenz and 8-hydroxy-efavirenz in HIV infected and TB-HIV co-infected Ethiopian patients. J Clin Pharmacol.
Han J, Lee TH, Tung CH, Lee DY. Design and synthesis of a mitochondria-targeting carrier for small molecule drugs. Org Biomol Chem. 2014;12:9793–6.
Hecht M, Harrer T, Buttner M, Schwegler M, Erber S, Fietkau R, Distel LV. Cytotoxic effect of efavirenz is selective against cancer cells and associated with the cannabinoid system. AIDS. 2013;27:2031–40.
Heiskanen KM, Bhat MB, Wang HW, Ma J, Nieminen AL. Mitochondrial depolarization accompanies cytochrome c release during apoptosis in PC6 cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:5654–8.
Heller A, Brockhoff G, Goepferich A. Targeting drugs to mitochondria. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;82:1–18.
Hori R, Okumura K, Yoshida H. Binding of basic drugs to rat lung mitochondria. Pharm Res. 1987;4:142–6.
Janneh O, Chandler B, Hartkoorn R, Kwan WS, Jenkinson C, Evans S, Back DJ, Owen A, Khoo SH. Intracellular accumulation of efavirenz and nevirapine is independent of P-glycoprotein activity in cultured CD4 T cells and primary human lymphocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;64:1002–7.
Jouvenet N, Simon SM, Bieniasz PD. Visualizing HIV-1 assembly. J Mol Biol. 2011;410:501–11.
Karamchand L, Dawood H, Chuturgoon AA. Lymphocyte mitochondrial depolarization and apoptosis in HIV-1-infected HAART patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008;48:381–8.
King J, Aberg JA. Clinical impact of patient population differences and genomic variation in efavirenz therapy. AIDS. 2008;22:1709–17.
Kwara A, Lartey M, Sagoe KW, Kenu E, Court MH. CYP2B6, CYP2A6 and UGT2B7 genetic polymorphisms are predictors of efavirenz mid-dose concentration in HIV-infected patients. AIDS. 2009a;23:2101–6.
Kwara A, Lartey M, Sagoe KW, Rzek NL, Court MH. CYP2B6 (c.516G-->T) and CYP2A6 (*9B and/or *17) polymorphisms are independent predictors of efavirenz plasma concentrations in HIV-infected patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009b;67:427–36.
Lewis W, Day BJ, Copeland WC. Mitochondrial toxicity of NRTI antiviral drugs: an integrated cellular perspective. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:812–22.
Lopez S, Miro O, Martinez E, Pedrol E, Rodriguez-Santiago B, Milinkovic A, Soler A, Garcia-Viejo MA, Nunes V, Casademont J, Gatell JM, Cardellach F. Mitochondrial effects of antiretroviral therapies in asymptomatic patients. Antivir Ther. 2004;9:47–55.
Ly JD, Grubb DR, Lawen A. The mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis. 2003;8:115–28.
Maggiolo F. Efavirenz: a decade of clinical experience in the treatment of HIV. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;64:910–28.
Marzolini C, Telenti A, Decosterd LA, Greub G, Biollaz J, Buclin T. Efavirenz plasma levels can predict treatment failure and central nervous system side effects in HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS. 2001;15:71–5.
Matthews CZ, Woolf EJ, Mazenko RS, Haddix-Wiener H, Chavez-Eng CM, Constanzer ML, Doss GA, Matuszewski BK. Determination of efavirenz, a selective non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, in human plasma using HPLC with post-column photochemical derivatization and fluorescence detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002;28:925–34.
Montgomery ER, Edmanson AL, Cook SC, Hovsepian PK. Development and validation of a reverse-phase HPLC method for analysis of efavirenz and its related substances in the drug substance and in a capsule formulation. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2001;25:267–84.
Nachega JB, Hislop M, Dowdy DW, Gallant JE, Chaisson RE, Regensberg L, Maartens G. Efavirenz versus nevirapine-based initial treatment of HIV infection: clinical and virological outcomes in Southern African adults. AIDS. 2008;22:2117–25.
Olson, B. J. & Markwell, J. 2007. Assays for determination of protein concentration. Curr Protoc Protein Sci, Chapter 3, Unit 3 4.
Ott M, Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Zhivitovsky B, Orrenius S. Cytochrome c release from mitochondria proceeds by a two-step process. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2002;99(3):1259–63.
Palella Jr FJ, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–60.
Pedersen OS, Pedersen EB. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: the NNRTI boom. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2000;10:285–314.
Pessayre D, Mansouri A, Haouzi D, Fromenty B. Hepatotoxicity due to mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1999;15:367–73.
Pilon AA, Lum JJ, Sanchez-Dardon J, Phenix BN, Douglas R, Badley AD. Induction of apoptosis by a nonnucleoside human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:2687–91.
Pinti M, Nasi M, Gibellini L, Roat E, de Biasi S, Bertoncelli L, Cossarizza A. The role of mitochondria in HIV infection and its treatment. J Exp Clin Med. 2010;2:145–55.
Pocernich CB, Boyd-Kimball D, Poon HF, Thongboonkerd V, Lynn BC, Klein JB, Calebrese V, Nath A, Butterfield DA. Proteomics analysis of human astrocytes expressing the HIV protein Tat. Mol Brain Res. 2005;133:307–16.
Ramachandran G, Hemanth Kumar AK, Rajasekaran S, Kumar P, Ramesh K, Anitha S, Narendran G, Menon P, Gomathi C, Swaminathan S. CYP2B6 G516T polymorphism but not rifampin coadministration influences steady-state pharmacokinetics of efavirenz in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in South India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:863–8.
Ricci JE, Waterhouse N, Green DR. Mitochondrial functions during cell death, a complex (I-V) dilemma. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:488–92.
Soldani C, Scovassi AI. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update. Apoptosis. 2002;7:321–8.
Sordet O, Rebe C, Leroy I, Bruey JM, Garrido C, Miguet C, Lizard G, Plenchette S, Corcos L, Solary E. Mitochondria-targeting drugs arsenic trioxide and lonidamine bypass the resistance of TPA-differentiated leukemic cells to apoptosis. Blood. 2001;97:3931–40.
Stahle L, Moberg L, Svensson JO, Sonnerborg A. Efavirenz plasma concentrations in HIV-infected patients: inter- and intraindividual variability and clinical effects. Ther Drug Monit. 2004;26:267–70.
Stankov MV, Lucke T, Das AM, Schmidt RE, Behrens GM. Mitochondrial DNA depletion and respiratory chain activity in primary human subcutaneous adipocytes treated with nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:280–7.
Tanaka R, Hanabusa H, Kinai E, Hasegawa N, Negishi M, Kato S. Intracellular efavirenz levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:782–5.
Tebas P, Sension M, Arribas J, Duiculescu D, Florence E, Hung CC, Wilkin T, Vanveggel S, Stevens M, Deckx H, Echo & Groups, T. S. Lipid levels and changes in body fat distribution in treatment-naive, HIV-1-infected adults treated with rilpivirine or efavirenz for 96 weeks in the ECHO and THRIVE trials. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:425–34.
Telenti A, Zanger UM. Pharmacogenetics of anti-HIV drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;48:227–56.
Wasilewski M, Scorrano L. The changing shape of mitochondrial apoptosis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20:287–94.
Zou H, Yang R, Hao J, Wang J, Sun C, Fesik SW, Wu JC, Tomaselli KJ, Armstrong RC. Regulation of the Apaf-1/caspase-9 apoptosome by caspase-3 and XIAP. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:8091–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant No. BT/PR10319/GBD/27/97/2007 from the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India. The authors also acknowledge facilities used at the Centre for Nanoscience and Technology and Interdisciplinary Program for Life Science (IPLS) at the University of Calcutta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 219 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganta, K.K., Mandal, A. & Chaubey, B. Depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential is the initial event in non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor efavirenz induced cytotoxicity. Cell Biol Toxicol 33, 69–82 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9362-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9362-9