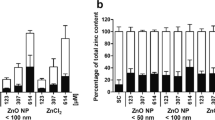
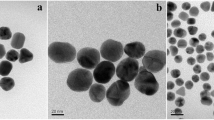
Abstract
The effects of ingestion of engineered nanoparticles (NPs), especially via drinking water, are unknown. Using NPs spiked into synthetic water and cell culture media, we investigated cell death, oxidative stress, and inflammatory effects of silver (Ag), titanium dioxide (TiO2), and zinc oxide (ZnO) NPs on human intestinal Caco-2 and SW480 cells. ZnO NPs were cytotoxic to both cell lines, while Ag and TiO2 NPs were toxic only at 100 mg/L to Caco-2 and SW480, respectively. ZnO NPs led to significant cell death in synthetic freshwaters with 1 % phosphate-buffered saline in both cell lines, while Ag and TiO2 NPs in buffered water led to cell death in SW480 cells. NP exposures did not yield significant increased reactive oxygen species generation but all NP exposures led to increased IL-8 cytokine generation in both cell lines. These results indicate cell stress and cell death from NP exposures, with a varied response based on NP composition.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott Chalew TE. Emerging contaminants and public health: Evaluation of the stability, toxicity, and treatment of engineered nanoparticles in drinking water. Ph.D. 3533276, The Johns Hopkins University; 2012
Abdelhay A, Carmen-Mihaela T, Christophe M, Cédric M, Hélène G, Ghouti M, et al. Physicochemical properties and cellular toxicity of (poly)aminoalkoxysilanes-functionalized ZnO quantum dots. Nanotechnol. 2012;23(33):335101.
AshaRani PV, Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano. 2008;3(2):279–90.
Baker RD, Baker SS, Larosa K. Polarized caco-2 cells. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40(3):510–8.
Barone F, de Berardis B, Bizzarri L, Degan P, Andreoli C, Zijno A, et al. Physico-chemical characteristics and cyto-genotoxic potential of ZnO and TiO 2 nanoparticles on human colon carcinoma cells. J Phys Conf Ser. 2011;304(1):012047.
Benn TM, Westerhoff P. Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environ Sci Technol. 2008;42(11):4133–9.
Blaser SA, Scheringer M, Macleod M, Hungerbuhler K. Estimation of cumulative aquatic exposure and risk due to silver: contribution of nano-functionalized plastics and textiles. Sci Total Environ. 2008;390:396–406.
Brogna A, Ferrara R, Bucceri AM, Lanteri E, Catalano F. Influence of aging on gastrointestinal transit time: an ultrasonographic and radiologic study. Invest Radiol. 1999;34:357–9.
Brun E, Jugan M-L, Herlin-Boime N, Jaillard D, Fayard B, Flank AM, et al. Investigation of TiO2 nanoparticles translocation through a caco-2 monolayer. J Phys Conf Ser. 2011;304(1):012048.
Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle KL, Hess KL, Jones RL, et al. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112(43):13608–19.
Crabtree JE, Farmery SM, Lindley IJ, Figura N, Peichl P, Tompkins DS. CagA/cytotoxic strains of Helicobacter pylori and interleukin-8 in gastric epithelial cell lines. J Clin Pathol. 1994;47(10):945–50.
De Berardis B, Civitelli G, Condello M, Lista P, Pozzi R, Arancia G, et al. Exposure to ZnO nanoparticles induces oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;246(3):116–27.
de Jong WH, Park MVDZ. Nanotoxicology - in vitro studies: what do you need to know? In: Nanoimpactnet, editor. 1st NanoImpactNet conference. Lausanne: NanoImpactNet; 2009.
Desai MP, Labhasetwar V, Walter E, Levy RJ, Amidon GL. The mechanism of uptake of biodegradable microparticles in caco-2 cells is size dependent. Pharm Res. 1997;14(11):1568–73.
Finamore A, Massimi M, Conti Devirgiliis L, Mengheri E. Zinc deficiency induces membrane barrier damage and increases neutrophil transmigration in caco-2 cells. J Nutr. 2008;138(9):1664–70.
Gaiser BK, Fernandes TF, Jepson MA, Lead JR, Tyler CR, Baalousha M, et al. Interspecies comparisons on the uptake and toxicity of silver and cerium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2012;31(1):144–54.
Gerloff K, Albrecht C, Boots AW, Förster I, Schins RPF. Cytotoxicity and oxidative DNA damage by nanoparticles in human intestinal caco-2 cells. Nanotoxicol. 2009;3(4):355–64.
Gerloff K, Fenoglio I, Carella E, Kolling J, Albrecht C, Boots AW, et al. Distinctive toxicity of TiO2 rutile/anatase mixed phases nanoparticles on caco-2 cells. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012;25(3):646–55.
Gottschalk F, Nowack B. The release of engineered nanomaterials to the environment. J Environ Monitor. 2011;13(5):1145–55.
Handy RD, Jha AN, Al-Jubory A. In vitro techniques and their application to nanoparticles. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2009;153(2, Supplement 1):S87–S.
Hu X, Cook S, Wang P, Hwang H-M. In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of engineered metal oxide nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ. 2009a;407(8):3070–2.
Hu Z, Pan Y, Wang J, Chen J, Li J, Ren L. Meso-tetra (carboxyphenyl) porphyrin (TCPP) nanoparticles were internalized by SW480 cells by a clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway to induce high photocytotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother. 2009b;63(2):155–64.
Huang H, O’Melia CR. Direct-flow microfiltration of aquasols II. On the role of colloidal natural organic matter. J Membr Sci. 2008;325:903–13.
Hyung H, Kim J-H. Dispersion of C60 in natural water and removal by conventional drinking water treatment processes. Water Res. 2009;43(9):2463–70.
Jepson MA. Gastrointestinal tract. In: Fadeel B, Pietroiusti A, Shvedova AA, editors. Adverse effects of engineered nanomaterials: exposure, toxicology, and impact on human health. New York: Elsevier; 2012. p. 209–24.
Ji Z, Jin X, George S, Xia T, Meng H, Wang X, et al. Dispersion and stability optimization of TiO2 nanoparticles in cell culture media. Environ Sci Technol. 2010;44(19):7309–14.
Jiang J, Oberdörster G, Biswas P. Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nanoparticle Res. 2009;11(1):77–89.
Jobin C, Haskill S, Mayer L, Panja A, Sartor R. Evidence for altered regulation of I kappa B alpha degradation in human colonic epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1997;158(1):226–34.
Johnston H, Hutchison G, Christensen F, Peters S, Hankin S, Stone V. Identification of the mechanisms that drive the toxicity of TiO2 particulates: the contribution of physicochemical characteristics. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2009;6(1):1–27.
Johnston HJ, Hutchison G, Christensen FM, Peters S, Hankin S, Stone V. A review of the in vivo and in vitro toxicity of silver and gold particulates: particle attributes and biological mechanisms responsible for the observed toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2010;40(4):328–46.
Jung HC, Eckmann L, Yang SK, Panja A, Fierer J, Morzycka-Wroblewska E, et al. A distinct array of proinflammatory cytokines is expressed in human colon epithelial cells in response to bacterial invasion. J Clin Investig. 1995;95(1):55–65.
Jung T, Kamm W, Breitenbach A, Kaiserling E, Xiao JX, Kissel T. Biodegradable nanoparticles for oral delivery of peptides: is there a role for polymers to affect mucosal uptake? Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50(1):147–60.
Kaegi R, Sinnet B, Zuleeg S, Hagendorfer H, Mueller E, Vonbank R, et al. Release of silver nanoparticles from outdoor facades. Environ Pollut. 2010;158(9):2900–5.
Kilari S, Pullakhandam R, Nair KM. Zinc inhibits oxidative stress-induced iron signaling and apoptosis in caco-2 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;48(7):961–8.
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJJ, Batley GE, Fernandes TF, Handy RD, Lyon DY, et al. Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2008;27(9):1825–51.
Koeneman B, Zhang Y, Westerhoff P, Chen Y, Crittenden J, Capco D. Toxicity and cellular responses of intestinal cells exposed to titanium dioxide. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2010;26(3):225–38.
Kroll A, Pillukat M, Hahn D, Schnekenburger J. Interference of engineered nanoparticles with in vitro toxicity assays. Arch Toxicol. 2012;86(7):1123–36.
Li Q, Mahendra S, Lyon DY, Brunet L, Liga MV, Li D, et al. Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential applications and implications. Water Res. 2008;42(18):4591–602.
Limbach LK, Bereiter R, Mueller E, Krebs R, Gaelli R, Stark WJ. Removal of oxide nanoparticles in a model wastewater treatment plant: influence of agglomeration and surfactants on clearning efficiency. Environ Sci Technol. 2008;42(15):5828–33.
Liu W, Wu Y, Wang C, Li HC, Wang T, Liao CY, et al. Impact of silver nanoparticles on human cells: effect of particle size. Nanotoxicol. 2010;4(3):319–30.
Mahendra S, Li Q, Lyon DY, Brunet L, Alvarez PJJ. Nanotechnology-enabled water disinfection and microbial control: merits and limitations. In: Nora S, Mamadou D, Jeremiah D, Anita S, Richard S, editors. Nanotechnology applications for clean water. Boston: William Andrew; 2009. p. 157–66.
Mueller NC, Nowack B. Exposure modeling of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Sci Technol. 2008;42(12):4447–53.
Nowack B. The behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut. 2009;157:1063–4.
Oyanedel-Craver VA, Smith JA. Sustainable colloidal-silver-impregnated ceramic filter for point-of-use water treatment. Environ Sci Technol. 2007;42(3):927–33.
Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies (PEN). Consumer products inventory. Washington, D.C.: Woodrow Wilson Institute; 2013. http://www.nanotechproject.org/inventories/consumer/. Accessed 2011
Piret J-P, Vankoningsloo S, Mejia J, Noël F, Boilan E, Lambinon F, et al. Differential toxicity of copper (II) oxide nanoparticles of similar hydrodynamic diameter on human differentiated intestinal caco-2 cell monolayers is correlated in part to copper release and shape. Nanotoxicol. 2011;0(0):1–15.
Powell JJ, Thoree V, Pele LC. Dietary microparticles and their impact on tolerance and immune responsiveness of the gastrointestinal tract. Br J Nutr. 2007;98:S59–63.
Powers K, Palazuelos M, Brown SC, Roberts SM. Characterization of nanomaterials for toxicological evaluation. In: Sahu S, Casciano D, editors. Nanotoxicology: from in vivo and in vitro models to health risks. New York: Wiley; 2009. p. 1–27.
Rao AL, Sankar GG. Caco-2 cells: an overview. JPRHC. 2009;1(2):260–75.
Reed RB, Ladner DA, Higgins CP, Westerhoff P, Ranville JF. Solubility of nano-zinc oxide in environmentally and biologically important matrices. Environ Sci Technol. 2012;31(1):93–9.
Reijnders L. Cleaner nanotechnology and hazard reduction of manufactured nanoparticles. J Clean Prod. 2006;14(2):124–33.
Stone V, Johnston H, Schins RPF. Development of in vitro systems for nanotoxicology: methodological considerations. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2009;39(7):613–26.
Thubagere A, Reinhard BM. Nanoparticle-induced apoptosis propagates through hydrogen-peroxide-mediated bystander killing: insights from a human intestinal epithelium in vitro model. ACS Nano. 2010;4(7):3611–22.
Wang L, Nagesha DK, Selvarasah S, Dokmeci MR, Carrier RL. Toxicity of CdSe nanoparticles in caco-2 cell cultures. J Nanobiotechnol. 2008;6:11.
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Mädler L, Gilbert B, Shi H, et al. Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano. 2008;2(10):2121–34.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Westerhoff P, Hristovski K, Crittenden JC. Stability of commercial metal oxide nanoparticles in water. Water Res. 2008;42(8–9):2204–12.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge Dr. DeLisa Fairweather for her advice on the cytokine experiments, Dr. Joe Bressler for his advice about Caco-2 cell lines, and Rebecca Pinekenstein for her help in maintaining the cell lines. This research was supported in part by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) Training Program in Environmental Health Sciences (grant #: T32ES007141), the Osprey Foundation of Maryland, and the Johns Hopkins University Global Water Program.
Declaration of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
DOC 2,099 kb
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbott Chalew, T.E., Schwab, K.J. Toxicity of commercially available engineered nanoparticles to Caco-2 and SW480 human intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 29, 101–116 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-013-9241-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-013-9241-6