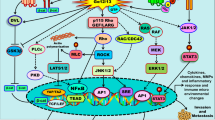
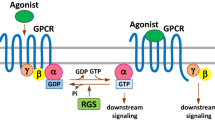
Abstract
KiSS1 and its cognate G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR54, have diverse functions. While KiSS1 and GPR54 have been intensively studied in physiology, their role in cancer is still unclear. In cancer, KiSS1 and GPR54 have been known to suppress metastasis by inhibiting cancer cell motility. However, recent studies suggest that KiSS1 and GPR54 have varied roles even in cancer development and metastasis. Here, we examine recent advances in understanding the roles of KiSS1 and GPR54 in cancer development and metastasis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, S. C., & Theodorescu, D. (2009). Learning therapeutic 9lessons from metastasis suppressor proteins. Nature Reviews Cancer, 9(4), 253–264. doi:10.1038/nrc2594.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Review]. Cell, 144(5), 646–674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013.
Fullgrabe, J., Kavanagh, E., & Joseph, B. (2011). Histone onco-modifications. Oncogene, 30(31), 3391–3403. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.121.
Sharma, S., Kelly, T. K., & Jones, P. A. (2010). Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis, 31(1), 27–36. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp220.
De Bock, K., Mazzone, M., & Carmeliet, P. (2011). Antiangiogenic therapy, hypoxia, and metastasis: Risky liaisons, or not? [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t Review]. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 8(7), 393–404. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.83.
Thiery, J. P., Acloque, H., Huang, R. Y., & Nieto, M. A. (2009). Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell, 139(5), 871–890. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.007.
Shoushtari, A. N., Szmulewitz, R. Z., & Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W. (2011). Metastasis-suppressor genes in clinical practice: Lost in translation? Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 8(6), 333–342. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.65.
Cook, L. M., Hurst, D. R., & Welch, D. R. (2011). Metastasis suppressors and the tumor microenvironment. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 21(2), 113–122. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.12.005.
Lee, J. H., & Welch, D. R. (1997). Suppression of metastasis in human breast carcinoma MDA-MB-435 cells after transfection with the metastasis suppressor gene, KiSS-1. Cancer Research, 57(12), 2384–2387.
Nash, K. T., & Welch, D. R. (2006). The KISS1 metastasis suppressor: Mechanistic insights and clinical utility. Frontiers in Bioscience, 11, 647–659.
Lee, J. H., Miele, M. E., Hicks, D. J., Phillips, K. K., Trent, J. M., Weissman, B. E., et al. (1996). KiSS-1, a novel human malignant melanoma metastasis-suppressor gene. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 88(23), 1731–1737.
Seminara, S. B., & Kaiser, U. B. (2005). New gatekeepers of reproduction: GPR54 and its cognate ligand, KiSS-1. Endocrinology, 146(4), 1686–1688. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0070.
Ohtaki, T., Shintani, Y., Honda, S., Matsumoto, H., Hori, A., Kanehashi, K., et al. (2001). Metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature, 411(6837), 613–617. doi:10.1038/35079135.
Mitchell, D. C., Abdelrahim, M., Weng, J., Stafford, L. J., Safe, S., Bar-Eli, M., et al. (2006). Regulation of KiSS-1 metastasis suppressor gene expression in breast cancer cells by direct interaction of transcription factors activator protein-2alpha and specificity protein-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(1), 51–58. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506245200.
Mitchell, D. C., Stafford, L. J., Li, D., Bar-Eli, M., & Liu, M. (2007). Transcriptional regulation of KiSS-1 gene expression in metastatic melanoma by specificity protein-1 and its coactivator DRIP-130. Oncogene, 26(12), 1739–1747. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209963.
Nash, K. T., Phadke, P. A., Navenot, J. M., Hurst, D. R., Accavitti-Loper, M. A., Sztul, E., et al. (2007). Requirement of KISS1 secretion for multiple organ metastasis suppression and maintenance of tumor dormancy. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 99(4), 309–321. doi:10.1093/jnci/djk053.
Seminara, S. B., Messager, S., Chatzidaki, E. E., Thresher, R. R., Acierno, J. S., Jr., Shagoury, J. K., et al. (2003). The GPR54 gene as a regulator of puberty. The New England Journal of Medicine, 349(17), 1614–1627. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035322.
Teles, M. G., Bianco, S. D., Brito, V. N., Trarbach, E. B., Kuohung, W., Xu, S., et al. (2008). A GPR54-activating mutation in a patient with central precocious puberty. The New England Journal of Medicine, 358(7), 709–715. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa073443.
Topaloglu, A. K., Tello, J. A., Kotan, L. D., Ozbek, M. N., Yilmaz, M. B., Erdogan, S., et al. (2012). Inactivating KISS1 mutation and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. The New England Journal of Medicine, 366(7), 629–635. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1111184.
Silveira, L. G., Noel, S. D., Silveira-Neto, A. P., Abreu, A. P., Brito, V. N., Santos, M. G., et al. (2010). Mutations of the KISS1 gene in disorders of puberty. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 95(5), 2276–2280. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2421.
Lapatto, R., Pallais, J. C., Zhang, D., Chan, Y. M., Mahan, A., Cerrato, F., et al. (2007). Kiss1−/− mice exhibit more variable hypogonadism than Gpr54−/− mice. Endocrinology, 148(10), 4927–4936. doi:10.1210/en.2007-0078.
Morelli, A., Marini, M., Mancina, R., Luconi, M., Vignozzi, L., Fibbi, B., et al. (2008). Sex steroids and leptin regulate the “first Kiss” (KiSS 1/G-protein-coupled receptor 54 system) in human gonadotropin-releasing-hormone-secreting neuroblasts. The Journal of Sexual Medicine, 5(5), 1097–1113. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00782.x.
Horikoshi, Y., Matsumoto, H., Takatsu, Y., Ohtaki, T., Kitada, C., Usuki, S., et al. (2003). Dramatic elevation of plasma metastin concentrations in human pregnancy: Metastin as a novel placenta-derived hormone in humans. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 88(2), 914–919.
Janneau, J. L., Maldonado-Estrada, J., Tachdjian, G., Miran, I., Motte, N., Saulnier, P., et al. (2002). Transcriptional expression of genes involved in cell invasion and migration by normal and tumoral trophoblast cells. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 87(11), 5336–5339.
Mead, E. J., Maguire, J. J., Kuc, R. E., & Davenport, A. P. (2007). Kisspeptins are novel potent vasoconstrictors in humans, with a discrete localization of their receptor, G protein-coupled receptor 54, to atherosclerosis-prone vessels. Endocrinology, 148(1), 140–147. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0818.
Ramaesh, T., Logie, J. J., Roseweir, A. K., Millar, R. P., Walker, B. R., Hadoke, P. W., et al. (2010). Kisspeptin-10 inhibits angiogenesis in human placental vessels ex vivo and endothelial cells in vitro. Endocrinology, 151(12), 5927–5934. doi:10.1210/en.2010-0565.
Cho, S. G., Yi, Z., Pang, X., Yi, T., Wang, Y., Luo, J., et al. (2009). Kisspeptin-10, a KISS1-derived decapeptide, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by suppressing Sp1-mediated VEGF expression and FAK/Rho GTPase activation. Cancer Research, 69(17), 7062–7070. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0476.
Muir, A. I., Chamberlain, L., Elshourbagy, N. A., Michalovich, D., Moore, D. J., Calamari, A., et al. (2001). AXOR12, a novel human G protein-coupled receptor, activated by the peptide KiSS-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(31), 28969–28975. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102743200.
Kotani, M., Detheux, M., Vandenbogaerde, A., Communi, D., Vanderwinden, J. M., Le Poul, E., et al. (2001). The metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(37), 34631–34636. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104847200.
Cho, S. G., Li, D., Stafford, L. J., Luo, J., Rodriguez-Villanueva, M., Wang, Y., et al. (2009). KiSS1 suppresses TNFalpha-induced breast cancer cell invasion via an inhibition of RhoA-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 107(6), 1139–1149. doi:10.1002/jcb.22216.
Masui, T., Doi, R., Mori, T., Toyoda, E., Koizumi, M., Kami, K., et al. (2004). Metastin and its variant forms suppress migration of pancreatic cancer cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 315(1), 85–92. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.021.
Becker, J. A., Mirjolet, J. F., Bernard, J., Burgeon, E., Simons, M. J., Vassart, G., et al. (2005). Activation of GPR54 promotes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human tumor cells through a specific transcriptional program not shared by other Gq-coupled receptors. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 326(3), 677–686. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.094.
Navenot, J. M., Fujii, N., & Peiper, S. C. (2009). Activation of Rho and Rho-associated kinase by GPR54 and KiSS1 metastasis suppressor gene product induces changes of cell morphology and contributes to apoptosis. Molecular Pharmacology, 75(6), 1300–1306. doi:10.1124/mol.109.055095.
Zhao, X., Lu, L., Pokhriyal, N., Ma, H., Duan, L., Lin, S., et al. (2009). Overexpression of RhoA induces preneoplastic transformation of primary mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Research, 69(2), 483–491. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2907.
Chang, Y. W., Marlin, J. W., Chance, T. W., & Jakobi, R. (2006). RhoA mediates cyclooxygenase-2 signaling to disrupt the formation of adherens junctions and increase cell motility. Cancer Research, 66(24), 11700–11708. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1818.
Navenot, J. M., Fujii, N., & Peiper, S. C. (2009). KiSS1 metastasis suppressor gene product induces suppression of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling to Akt, tumor necrosis factor family ligand expression, and apoptosis. Molecular Pharmacology, 75(5), 1074–1083. doi:10.1124/mol.108.054270.
Stathatos, N., Bourdeau, I., Espinosa, A. V., Saji, M., Vasko, V. V., Burman, K. D., et al. (2005). KiSS-1/G protein-coupled receptor 54 metastasis suppressor pathway increases myocyte-enriched calcineurin interacting protein 1 expression and chronically inhibits calcineurin activity. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 90(9), 5432–5440. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-0963.
Martins, C. M., Fernandes, B. F., Antecka, E., Di Cesare, S., Mansure, J. J., Marshall, J. C., et al. (2008). Expression of the metastasis suppressor gene KISS1 in uveal melanoma. Eye (London, England), 22(5), 707–711. doi:10.1038/sj.eye.6703090.
Dissanayake, S. K., Wade, M., Johnson, C. E., O’Connell, M. P., Leotlela, P. D., French, A. D., et al. (2007). The Wnt5A/protein kinase C pathway mediates motility in melanoma cells via the inhibition of metastasis suppressors and initiation of an epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(23), 17259–17271. doi:10.1074/jbc.M700075200.
Dittmer, A., Schunke, D., & Dittmer, J. (2008). PTHrP promotes homotypic aggregation of breast cancer cells in three-dimensional cultures. Cancer Letters, 260(1–2), 56–61. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.10.020.
Stark, A. M., Tongers, K., Maass, N., Mehdorn, H. M., & Held-Feindt, J. (2005). Reduced metastasis-suppressor gene mRNA-expression in breast cancer brain metastases. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 131(3), 191–198. doi:10.1007/s00432-004-0629-9.
Kostadima, L., Pentheroudakis, G., & Pavlidis, N. (2007). The missing kiss of life: Transcriptional activity of the metastasis suppressor gene KiSS1 in early breast cancer. Anticancer Research, 27(4B), 2499–2504.
Martin, T. A., Watkins, G., & Jiang, W. G. (2005). KiSS-1 expression in human breast cancer. Clinical & Experimental Metastasis, 22(6), 503–511. doi:10.1007/s10585-005-4180-0.
Marot, D., Bieche, I., Aumas, C., Esselin, S., Bouquet, C., Vacher, S., et al. (2007). High tumoral levels of Kiss1 and G-protein-coupled receptor 54 expression are correlated with poor prognosis of estrogen receptor-positive breast tumors. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 14(3), 691–702. doi:10.1677/ERC-07-0012.
Cho, S. G., Wang, Y., Rodriguez, M., Tan, K., Zhang, W., Luo, J., et al.(2011) Haploinsufficiency in the prometastasis Kiss1 receptor Gpr54 delays breast tumor initiation, progression, and lung metastasis. Cancer Research, 71(20), 6535–6546, doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0329.
Jiang, Y., Berk, M., Singh, L. S., Tan, H., Yin, L., Powell, C. T., et al. (2005). KiSS1 suppresses metastasis in human ovarian cancer via inhibition of protein kinase C alpha. Clinical & Experimental Metastasis, 22(5), 369–376. doi:10.1007/s10585-005-8186-4.
Hata, K., Dhar, D. K., Watanabe, Y., Nakai, H., & Hoshiai, H. (2007). Expression of metastin and a G-protein-coupled receptor (AXOR12) in epithelial ovarian cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 43(9), 1452–1459. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.03.004.
Prentice, L. M., Klausen, C., Kalloger, S., Kobel, M., McKinney, S., Santos, J. L., et al. (2007). Kisspeptin and GPR54 immunoreactivity in a cohort of 518 patients defines favourable prognosis and clear cell subtype in ovarian carcinoma. BMC Medicine, 5, 33. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-5-33.
Katagiri, F., Nagai, K., Kida, A., Tomita, K., Oishi, S., Takeyama, M., et al. (2009). Clinical significance of plasma metastin level in pancreatic cancer patients. Oncology Reports, 21(3), 815–819.
Nagai, K., Doi, R., Katagiri, F., Ito, T., Kida, A., Koizumi, M., et al. (2009). Prognostic value of metastin expression in human pancreatic cancer. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 28, 9. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-28-9.
Dhar, D. K., Naora, H., Kubota, H., Maruyama, R., Yoshimura, H., Tonomoto, Y., et al. (2004). Downregulation of KiSS-1 expression is responsible for tumor invasion and worse prognosis in gastric carcinoma. International Journal of Cancer, 111(6), 868–872. doi:10.1002/ijc.20357.
Yamashita, S., Tsujino, Y., Moriguchi, K., Tatematsu, M., & Ushijima, T. (2006). Chemical genomic screening for methylation-silenced genes in gastric cancer cell lines using 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine treatment and oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Science, 97(1), 64–71. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00136.x.
Lee, K. H., & Kim, J. R. (2009). Kiss-1 suppresses MMP-9 expression by activating p38 MAP kinase in human stomach cancer. Oncology Research, 18(2–3), 107–116.
Yan, C., Wang, H., & Boyd, D. D. (2001). KiSS-1 represses 92-kDa type IV collagenase expression by down-regulating NF-kappa B binding to the promoter as a consequence of Ikappa Balpha-induced block of p65/p50 nuclear translocation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(2), 1164–1172. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008681200.
Sanchez-Carbayo, M., Belbin, T. J., Scotlandi, K., Prystowsky, M., Baldini, N., Childs, G., et al. (2003). Expression profiling of osteosarcoma cells transfected with MDR1 and NEO genes: Regulation of cell adhesion, apoptosis, and tumor suppression-related genes. Laboratory Investigation, 83(4), 507–517.
Ikeguchi, M., Fukuda, K., Yamaguchi, K., Kondo, A., Tsujitani, S., & Kaibara, N. (2003). Quantitative analysis of heparanase gene expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 10(3), 297–304.
Schmid, K., Wang, X., Haitel, A., Sieghart, W., Peck-Radosavljevic, M., Bodingbauer, M., et al. (2007). KiSS-1 overexpression as an independent prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study. Virchows Archiv, 450(2), 143–149. doi:10.1007/s00428-006-0352-9.
Shengbing, Z., Feng, L. J., Bin, W., Lingyun, G., & Aimin, H. (2009). Expression of KiSS-1 gene and its role in invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Anatomical Record (Hoboken), 292(8), 1128–1134. doi:10.1002/ar.20950.
Sanchez-Carbayo, M., Capodieci, P., & Cordon-Cardo, C. (2003). Tumor suppressor role of KiSS-1 in bladder cancer: Loss of KiSS-1 expression is associated with bladder cancer progression and clinical outcome. American Journal of Pathology, 162(2), 609–617. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63854-0.
Nicolle, G., Comperat, E., Nicolaiew, N., Cancel-Tassin, G., & Cussenot, O. (2007). Metastin (KISS-1) and metastin-coupled receptor (GPR54) expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Annals of Oncology, 18(3), 605–607. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl421.
Simanovsky, M., Berlinsky, S., Sinai, P., Leiba, M., Nagler, A., & Galski, H. (2008). Phenotypic and gene expression diversity of malignant cells in human blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Differentiation, 76(8), 908–922. doi:10.1111/j.1432-0436.2008.00270.x.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute/NIH grant 1R01CA106479 and grant from National Science Foundation of China (30930055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, SG., Li, D., Tan, K. et al. KiSS1 and its G-protein-coupled receptor GPR54 in cancer development and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31, 585–591 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9367-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9367-7