Abstract
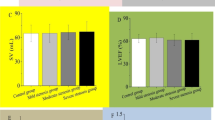
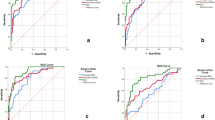
To investigate the relationship between left ventricular (LV) myocardial mechanics evaluated by three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (3D-STE) and degree of coronary artery stenosis in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). Ninety-seven suspected CAD patients without LV regional wall motion abnormality (RWMA) observed visually form traditional echocardiography were divided into four groups according to coronary artery angiography (CAG): 23 patients in slight stenosis group [stenosis rate (SR) ≤25%], 26 patients in mild stenosis group (25< SR ≤50%), 28 patients in moderate stenosis group (50< SR ≤75%), and 20 patients in severe stenosis group (SR >75%). Global longitudinal strain (GLS), circumferential strain (GCS), radial strain (GRS), area strain (AS) and three dimensional strain (3D-Strain) were obtained. The parameters from 3D-STE were compared between different groups and then the diagnostic value of global strains indicating different graded coronary artery stenosis was analyzed by the receiver operating characteristic curve. (1) There were significant difference in GLS, GCS, GRS, GAS and 3D-Strain between the severe stenosis group and any other group while all 3D-STE parameters except GCS in the moderate stenosis group were remarkably different from those respectively in mild group. (2) Receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC) analysis showed that the area under the curve of GLS, GRS, GCS, GAS, 3D-Strain were 0.899, 0.873, 0.723, 0.856 and 0.863 respectively for the identification of stenosis rate >50%, and 0.896, 0.866, 0.797, 0.909 and 0.899 respectively for the identification of severe stenosis. GAS less than −29.13% allowed a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 71.4%, while 3D strain less than 41.35% allowed a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 80.5% for evaluating serve coronary artery stenosis. The myocardial mechanics from 3D-STE in the CAD patients were characteristic. It could be expected to identify serve coronary stenosis with a good sensitivity and an acceptable specificity by using GAS or 3D-strain especially in the suspected CAD patients without RWMA on conventional echocardiography.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V et al (2012) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet 380:2095–2128
Gaemperli O (2013) Role of noninvasive imaging in cardiology. Praxis 102:29–37
Kawagishi T (2008) Speckle tracking for assessment of cardiac motion and dyssynchrony. Echocardiography 25:1167–1171
Health Quality O (2010) Stress echocardiography for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease: an evidence-based analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser 10:1–61
Leitman M, Lysyansky P, Sidenko S, Shir V, Peleg E, Binenbaum M et al (2004) Two-dimensional strain-a novel software for real-time quantitative echocardiographic assessment of myocardial function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 17:1021–1029
Perk G, Tunick PA, Kronzon I (2007) Non-Doppler two-dimensional strain imaging by echocardiography—from technical considerations to clinical applications. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 20:234–243
Saito K, Okura H, Watanabe N, Hayashida A, Obase K, Imai K et al (2009) Comprehensive evaluation of left ventricular strain using speckle tracking echocardiography in normal adults: comparison of three-dimensional and two-dimensional approaches. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 22:1025–1030
Biswas M, Sudhakar S, Nanda NC, Buckberg G, Pradhan M, Roomi AU et al (2013) Two- and three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography. Echocardiography 30:88–105
Sun YJ, Wang F, Zhang RS, Wang HY, Yang CG, Cai J et al (2015) Incremental value of resting three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in detecting coronary artery disease. Exp Ther Med 9:2043–2046
Altman M, Bergerot C, Aussoleil A, Davidsen ES, Sibellas F, Ovize M et al (2014) Assessment of left ventricular systolic function by deformation imaging derived from speckle tracking: a comparison between 2D and 3D echo modalities. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 15:316–323
Maffessanti F, Nesser HJ, Weinert L, Steringer-Mascherbauer R, Niel J, Gorissen W et al (2009) Quantitative evaluation of regional left ventricular function using three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with and without heart disease. Am J Cardiol 104:1755–1762
Nagata Y, Takeuchi M, Wu VC, Izumo M, Suzuki K, Sato K et al (2015) Prognostic value of LV deformation parameters using 2D and 3D speckle-tracking echocardiography in asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis and preserved LV ejection fraction. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 8:235–245
Chen R, Wu X, Shen LJ, Wang B, Ma MM, Yang Y et al (2014) Left ventricular myocardial function in hemodialysis and nondialysis uremia patients: a three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography study. PLoS ONE 9:e100265
Li CM, Li C, Bai WJ, Zhang XL, Tang H, Qing Z et al (2013) Value of three-dimensional speckle-tracking in detecting left ventricular dysfunction in patients with aortic valvular diseases. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 26:1245–1252
Hoffmann R, Borges AC, Kasprzak JD, von Bardeleben S, Firschke C, Greis C et al (2007) Analysis of myocardial perfusion or myocardial function for detection of regional myocardial abnormalities. An echocardiographic multicenter comparison study using myocardial contrast echocardiography and 2D echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr 8:438–448
Hoit BD (2011) Strain and strain rate echocardiography and coronary artery disease. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 4:179–190
Rostamzadeh A, Shojaeifard M, Rezaei Y, Dehghan K (2015) Diagnostic accuracy of myocardial deformation indices for detecting high risk coronary artery disease in patients without regional wall motion abnormality. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:9412–9420
Stanton T, Leano R, Marwick TH (2009) Prediction of all-cause mortality from global longitudinal speckle strain: comparison with ejection fraction and wall motion scoring. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2:356–364
Biere L, Donal E, Terrien G, Kervio G, Willoteaux S, Furber A et al (2014) Longitudinal strain is a marker of microvascular obstruction and infarct size in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 9:e86959
Fang LL, Zhang PY, Wang C, Wang LM, Ma XW, Shi HW et al (2011) Two-dimensional strain combined with adenosine stress echocardiography assessment of viable myocardium. Heart Vessels 26:206–213
Seo Y, Ishizu T, Aonuma K (2014) Current status of 3-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: a review from our experiences. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 22:49–57
Kleijn SA, Aly MF, Terwee CB, van Rossum AC, Kamp O (2011) Three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography for automatic assessment of global and regional left ventricular function based on area strain. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24:314–321
Serri K, Reant P, Lafitte M, Berhouet M, Le Bouffos V, Roudaut R et al (2006) Global and regional myocardial function quantification by two-dimensional strain: application in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:1175–1181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committees of Nanjing First Hospital of the Ministry of Health (Nanjing, China) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zhang, PY., Ran, H. et al. Evaluation of left ventricular myocardial mechanics by three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography in the patients with different graded coronary artery stenosis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 33, 1513–1520 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-017-1147-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-017-1147-6