Abstract
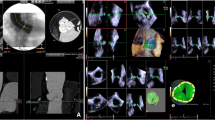
To assess the accuracy and reproducibly of cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) in the measurement of the aortic annulus and in process of valve sizing as compared to intra-operative sizing, cardiovascular computed tomography (CCT) and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE). Retrospective study on 42 patients who underwent aortic valve replacement from September 2010 to September 2015, with available records of pre surgery annulus assessment by CMR, CCT and TEE and of peri-operative assessment. In CCT and CMR, the annular plane was considered a virtual ring formed by the lowest hinge points of the valvular attachments to the aorta. In TEE the annulus was measured at the base of leaflet insertion in the mid-esophageal long-axis view using the X-plane technique. Two double-blinded operators performed the assessments for each imaging technique. Intra-operative evaluation was performed using Hegar dilators. Continuous variables were studied with within-subject ANOVA, Bland–Altman (BA) plots, Wilcoxon’s and Friedman’s tests; trends were explored with scatter plots. Categorical variables were studied with Fisher’s exact test. The intra- and inter-operator reliability was satisfying. There were no significant differences between the annulus dimensions measured by CMR and either one of the three references. Valve sizing for CoreValve by CMR had the same good agreement with CCT and TEE, with a 78 % match rate; for SAPIEN XT the agreement was slightly better (82 %) for CCT than for TEE (66 %). MR performs well when compared to the surgical reference of intra-operative sizing and stands up to the level of the most used imaging references (CCT and TEE).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nkomo VT, Gardin JM, Skelton TN, Gottdiener JS, Scott CG, Enriquez-Sarano M (2006) Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Lancet 368(9540):1005–1011
Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG et al (2010) Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med 363(17):1597–1607
Smith CR, Leon MB, Mack MJ, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG et al (2011) Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med 364(23):2187–2198
Zaman S, Gooley R, McCormick L, Harper R, Meredith IT (2015) Pre-transcatheter aortic valve implantation workup in the cardiac catheterisation laboratory. Heart Lung Circ 24(12):1162–1170
Tay ELW, Gurvitch R, Wijeysinghe N, Nietlispach F, Leipsic J, Wood DA et al (2011) Outcome of patients after transcatheter aortic valve embolization. J Am Coll Cardiol Cardiovasc Interv 4(2):228–234
Pasic M, Unbehaun A, Dreysse S, Buz S, Drews T, Kukucka M et al (2012) Rupture of the device landing zone during transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a life-threatening but treatable complication. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 5(3):424–432
Salizzoni S, Marra WG, Moretti C, D’Amico M, La Torre MW, Rinaldi M (2014) An iatrogenic atrioventricular septal defect that developed following transfemoral TAVI. J Heart Valve Dis 23(2):216–218
Kodali SK, Williams MR, Smith CR, Svensson LG, Webb JG, Makkar RR et al (2012) Two-year outcomes after transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement. N Engl J Med 366(18):1686–1695
Jabbour A, Ismail TF, Moat N, Gulati A, Roussin I, Alpendurada F et al (2011) Multimodality imaging in transcatheter aortic valve implantation and post-procedural aortic regurgitation: comparison among cardiovascular magnetic resonance, cardiac computed tomography, and echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 58(21):2165–2173
D’Onofrio A, Salizzoni S, Agrifoglio M, Cota L, Luzi G, Tartara PM et al (2013) Medium term outcomes of transapical aortic valve implantation: results from the Italian registry of trans-apical aortic valve implantation. Ann Thorac Surg 96(3):830–835; discussion 836
Jayasuriya C, Moss RR, Munt B (2011) Transcatheter aortic valve implantation in aortic stenosis: the role of echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24(1):15–27
Dashkevich A, Blanke P, Siepe M, Pache G, Langer M, Schlensak C et al (2011) Preoperative assessment of aortic annulus dimensions: comparison of noninvasive and intraoperative measurement. Ann Thorac Surg 91(3):709–714
Kempfert J, Van Linden A, Lehmkuhl L, Rastan AJ, Holzhey D, Blumenstein J et al (2012) Aortic annulus sizing: echocardiographic vs. computed tomography derived measurements in comparison with direct surgical sizing. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 42(4):627–633
Yano M, Nakamura K, Nagahama H, Matsuyama M, Nishimura M, Onitsuka T (2012) Aortic annulus diameter measurement: what is the best modality? Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 18(2):115–120
Bazeed MF, Rezk AI, Moselhy MS (2013) Value of cardiac CT in comprehensive aortic valve and root evaluation before percutaneous aortic valve replacement. Acta Radiol 54(5):498–504
Wang H, Hanna JM, Ganapathi A, Keenan JE, Hurwitz LM, Vavalle JP et al (2015) Comparison of aortic annulus size by transesophageal echocardiography and computed tomography angiography with direct surgical measurement. Am J Cardiol 115(11):1568–1573
Tsuneyoshi H, Komiya T, Shimamoto T (2016) Accuracy of aortic annulus diameter measurement: comparison of multi-detector CT, two- and three-dimensional echocardiography. J Card Surg 31(1):18–22
Pontone G, Andreini D, Bartorelli AL, Bertella E, Mushtaq S, Gripari P et al (2013) Comparison of accuracy of aortic root annulus assessment with cardiac magnetic resonance versus echocardiography and multidetector computed tomography in patients referred for transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am J Cardiol 112(11):1790–1799
Gargiulo G, Capodanno D, Sannino A, Perrino C, Capranzano P, Stabile E et al (2015) Moderate and severe preoperative chronic kidney disease worsen clinical outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: meta-analysis of 4992 patients. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 8(2):e002220
D’Ascenzo F, Moretti C, Salizzoni S, Bollati M, D’Amico M, Ballocca F et al (2013) 30 days and midterm outcomes of patients undergoing percutaneous replacement of aortic valve according to their renal function: a multicenter study. Int J Cardiol 167(4):1514–1518
La Manna A, Sanfilippo A, Capodanno D, Salemi A, Polizzi G, Deste W et al (2011) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance for the assessment of patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a pilot study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 13:82
Paelinck BP, Van Herck PL, Rodrigus I, Claeys MJ, Laborde J-C, Parizel PM et al (2011) Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging of aortic valve stenosis and aortic root to multimodality imaging for selection of transcatheter aortic valve implantation candidates. Am J Cardiol 108(1):92–98
Koos R, Altiok E, Mahnken AH, Neizel M, Dohmen G, Marx N et al (2012) Evaluation of aortic root for definition of prosthesis size by magnetic resonance imaging and cardiac computed tomography: implications for transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Int J Cardiol. 158(3):353–358
Ruile P, Blanke P, Krauss T, Dorfs S, Jung B, Jander N et al (2015) Pre-procedural assessment of aortic annulus dimensions for transcatheter aortic valve replacement: comparison of a non-contrast 3D MRA protocol with contrast-enhanced cardiac dual-source CT angiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging [Epub ahead of print]
Bernhardt P, Rodewald C, Seeger J, Gonska B, Buckert D, Radermacher M et al. (2015) Non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography is equal to contrast-enhanced multislice computed tomography for correct aortic sizing before transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Clin Res Cardiol 105(3):273–278
Smíd M, Ferda J, Baxa J, Cech J, Hájek T, Kreuzberg B et al (2010) Aortic annulus and ascending aorta: comparison of preoperative and periooperative measurement in patients with aortic stenosis. Eur J Radiol 74(1):152–155
Piazza N, de Jaegere P, Schultz C, Becker AE, Serruys PW, Anderson RH (2008) Anatomy of the aortic valvar complex and its implications for transcatheter implantation of the aortic valve. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 1(1):74–81
Kasel AM, Cassese S, Bleiziffer S, Amaki M, Hahn RT, Kastrati A et al (2013) Standardized imaging for aortic annular sizing: implications for transcatheter valve selection. J Am Coll Cardiol Cardiovasc Imaging 6(2):249–262
Potthast S, Mitsumori L, Stanescu LA, Richardson ML, Branch K, Dubinsky TJ et al (2010) Measuring aortic diameter with different MR techniques: comparison of three-dimensional (3D) navigated steady-state free-precession (SSFP), 3D contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA), 2D T2 black blood, and 2D cine SSFP. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(1):177–184
Suchá D, Tuncay V, Prakken NHJ, Leiner T, van Ooijen PMA, Oudkerk M et al (2015) Does the aortic annulus undergo conformational change throughout the cardiac cycle? A systematic review. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16(12):1307–1317
Leber AW, Eichinger W, Rieber J, Lieber M, Schleger S, Ebersberger U et al (2013) MSCT guided sizing of the Edwards Sapien XT TAVI device: impact of different degrees of oversizing on clinical outcome. Int J Cardiol 168(3):2658–2664
Karambatsakidou A, Omar A, Chehrazi B, Rück A, Scherp Nilsson J, Fransson A (2016) Skin dose, effective dose and related risk in transcatheter aortic valve implantation (tavi) procedures: is the cancer risk acceptable for younger patients? Radiat Prot Dosimetry [Epub ahead of print]
Wong S, Spina R, Toemoe S, Dhital K (2016) Is cardiac magnetic resonance imaging as accurate as echocardiography in the assessment of aortic valve stenosis? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 22(4):480–486
Flett AS, Sado DM, Quarta G, Mirabel M, Pellerin D, Herrey AS et al (2012) Diffuse myocardial fibrosis in severe aortic stenosis: an equilibrium contrast cardiovascular magnetic resonance study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 13(10):819–826
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the collaboration and support of Gaita F., Gandini G., Davini O., Righi D., Attisani M., Berzovini C., Capriolo M., Comoglio C., Frea S., Marchetto G., Marchisio F., Rusciano A., Salmè G. and Secinaro A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faletti, R., Gatti, M., Salizzoni, S. et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance as a reliable alternative to cardiovascular computed tomography and transesophageal echocardiography for aortic annulus valve sizing. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 32, 1255–1263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-0899-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-0899-8