Abstract
Objective
To examine associations between recently identified common type 2 diabetes (T2D) susceptibility genetic variants and pancreatic cancer risk.
Methods
Using data on individuals of European ancestry from the Cancer Genetic Markers of Susceptibility PanScan-I study (1,763 pancreatic cancer cases and 1,802 controls), we tested associations for 37 T2D susceptibility variants with pancreatic cancer risk. Associations with pancreatic cancer were also tested for three composite T2D susceptibility measures, incorporating data on all 37 variants, and for ten additional variants related to T2D-related phenotypes, including fasting glucose and beta-cell function.
Results
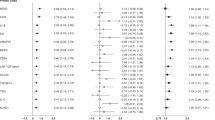
Of the 37 T2D risk alleles, two showed nominally significant positive associations with pancreatic cancer risk (FTO rs8050136 per-allele OR = 1.12; CI: 1.02–1.23; MTNR1B rs1387153 OR = 1.11; CI: 1.00–1.23) and one showed an inverse association (BCL11A rs243021 OR = 0.88; CI: 0.80–0.97). The composite T2D susceptibility measures were not associated with pancreatic cancer. The glucose-raising allele of MADD rs11039149 was associated with increased risk of pancreatic cancer (OR = 1.14; CI: 1.03–1.27).
Conclusions
Overall, these results do not provide strong evidence that common variants underling T2D or related phenotypes also affect pancreatic cancer risk; however, associations for FTO, MTNR1B, BCL11A, and MADD variants warrant further investigation in larger studies. Hypothesis-driven analyses of existing genome-wide genetic data can be cost-efficient and promising approaches for investigating genetic susceptibility to complex diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huxley R, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Barzi F, Woodward M (2005) Type-II diabetes and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of 36 studies. Br J Cancer 92:2076–2083
Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Graubard BI, Chari S et al (2005) Insulin, glucose, insulin resistance, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers. JAMA 294:2872–2878
Jee SH, Ohrr H, Sull JW, Yun JE, Ji M, Samet JM (2005) Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. Jama 293:194–202
Pisani P (2008) Hyper-insulinaemia and cancer, meta-analyses of epidemiological studies. Arch Physiol Biochem 114:63–70
Ben Q, Cai Q, Li Z et al (2011) The relationship between new-onset diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer risk: a case-control study. Eur J Cancer 47:248–254
Gupta S, Vittinghoff E, Bertenthal D et al (2006) New-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:1366–1372 (quiz 1301)
Hassan MM, Bondy ML, Wolff RA et al (2007) Risk factors for pancreatic cancer: case-control study. Am J Gastroenterol 102:2696–2707
Li D, Tang H, Hassan MM, Holly EA, Bracci PM, Silverman DT (2011) Diabetes and risk of pancreatic cancer: a pooled analysis of three large case-control studies. Cancer Causes Control 22:189–197
Rousseau MC, Parent ME, Pollak MN, Siemiatycki J (2006) Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk in a population-based case-control study among men from Montreal, Canada. Int J Cancer 118:2105–2109
Wang F, Gupta S, Holly EA (2006) Diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer in a population-based case-control study in the San Francisco Bay Area, California. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15:1458–1463
Li D, Abbruzzese JL (2010) New strategies in pancreatic cancer: emerging epidemiologic and therapeutic concepts. Clin Cancer Res 16:4313–4318
Bouatia-Naji N, Bonnefond A, Cavalcanti-Proenca C et al (2009) A variant near MTNR1B is associated with increased fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes risk. Nat Genet 41:89–94
Lyssenko V, Nagorny CL, Erdos MR et al (2009) Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion. Nat Genet 41:82–88
Rung J, Cauchi S, Albrechtsen A et al (2009) Genetic variant near IRS1 is associated with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. Nat Genet 41:1110–1115
Saxena R, Voight BF, Lyssenko V et al (2007) Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science 316:1331–1336
Scott LJ, Mohlke KL, Bonnycastle LL et al (2007) A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science 316:1341–1345
Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J et al (2007) A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 445:881–885
Unoki H, Takahashi A, Kawaguchi T et al (2008) SNPs in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations. Nat Genet 40:1098–1102
Yasuda K, Miyake K, Horikawa Y et al (2008) Variants in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet 40:1092–1097
Zeggini E, Scott LJ, Saxena R et al (2008) Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 40:638–645
Dupuis J, Langenberg C, Prokopenko I et al (2010) New genetic loci implicated in fasting glucose homeostasis and their impact on type 2 diabetes risk. Nat Genet 42:105–116
Saxena R, Hivert MF, Langenberg C et al (2010) Genetic variation in GIPR influences the glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose challenge. Nat Genet 42:142–148
Voight BF, Scott LJ, Steinthorsdottir V et al (2010) Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat Genet 42:579–589
Prokopenko I, Langenberg C, Florez JC et al (2009) Variants in MTNR1B influence fasting glucose levels. Nat Genet 41:77–81
Amundadottir L, Kraft P, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the ABO locus associated with susceptibility to pancreatic cancer. Nat Genet 41:986–990
Petersen GM, Amundadottir L, Fuchs CS et al (2010) A genome-wide association study identifies pancreatic cancer susceptibility loci on chromosomes 13q22.1, 1q32.1 and 5p15.33. Nat Genet 42:224–228
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38:904–909
Lawrence R, Day-Williams AG, Mott R, Broxholme J, Cardon LR, Zeggini E (2009) GLIDERS–a web-based search engine for genome-wide linkage disequilibrium between HapMap SNPs. BMC Bioinf 10:367
Pierce BL, Ahsan H (2010) Genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes is associated with reduced prostate cancer risk. Hum Hered 69:193–201
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN et al (2007) A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science 316:889–894
Arslan AA, Helzlsouer KJ, Kooperberg C et al (2010) Anthropometric measures, body mass index, and pancreatic cancer: a pooled analysis from the Pancreatic Cancer Cohort Consortium (PanScan). Arch Intern Med 170:791–802
Fesinmeyer MD, Stanford JL, Brentnall TA et al (2009) Association between the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma Pro12Ala variant and haplotype and pancreatic cancer in a high-risk cohort of smokers: a pilot study. Pancreas 38:631–637
Fong PY, Fesinmeyer MD, White E et al (2010) Association of diabetes susceptibility gene calpain-10 with pancreatic cancer among smokers. J Gastrointest Cancer 41:203–208
Cowie CC, Rust KF, Ford ES et al (2009) Full accounting of diabetes and pre-diabetes in the US population in 1988–1994 and 2005–2006. Diabetes Care 32:287–294
Skol AD, Scott LJ, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M (2006) Joint analysis is more efficient than replication-based analysis for two-stage genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38:209–213
Yun JE, Jo I, Park J et al (2006) Cigarette smoking, elevated fasting serum glucose, and risk of pancreatic cancer in Korean men. Int J Cancer 119:208–212
Douglas JB, Silverman DT, Pollak MN, Tao Y, Soliman AS, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ (2010) Serum IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-3, and IGF-I/IGFBP-3 molar ratio and risk of pancreatic cancer in the prostate, lung, Colorectal, and ovarian cancer screening trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 19:2298–2306
Wolpin BM, Michaud DS, Giovannucci EL et al (2007) Circulating insulin-like growth factor axis and the risk of pancreatic cancer in four prospective cohorts. Br J Cancer 97:98–104
Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Limburg P, Pollak M, Taylor PR, Virtamo J, Albanes D (2004) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-binding protein-3, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:438–444
Kong A, Steinthorsdottir V, Masson G et al (2009) Parental origin of sequence variants associated with complex diseases. Nature 462:868–874
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Department of Defense grant W81XWH-10-1-0499 (to BLP) and NIH grants CA122171 and CA102484 (to HA). The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierce, B.L., Austin, M.A. & Ahsan, H. Association study of type 2 diabetes genetic susceptibility variants and risk of pancreatic cancer: an analysis of PanScan-I data. Cancer Causes Control 22, 877–883 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9760-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9760-5