Abstract
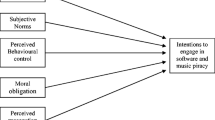
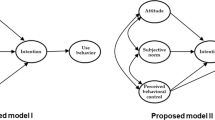
Since digital piracy has posed a significant threat to the development of the software industry and the growth of the digital media industry, it has, for the last decade, held considerable interest for researchers and practitioners. This article will propose an integrated model that combines the theory of planned behavior (TPB) and ethics theory, the two theories that are most often used in digital piracy studies. Data were obtained from university students in China, and the model was examined using the structural equation model (SEM). The results show that moral obligation and justice, derived from ethics theories and TPB variables, such as attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control, influence the behavioral intentions of individuals to commit digital piracy. The attitude of individuals toward digital piracy is also found to be influenced by perceived benefits, perceived risk, and habit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzen, I.: 1991, “The theory of planned behavior,” Organizational Behavior Human Decision Process 50 (2), 179-211.
Al-Jabri, I. and A. Abdul-Gader: 1997, “Software copyright infringements: An exploratory study of the effects of individual and peer beliefs,” Omega 25 (3), 335-343.
Al-Rafee, S. and T.P. Cronan: 2006, “Digital. Piracy: Factors that Influence Attitude Toward. Behaviour,” Journal of Business Ethics 63 (3), 237-259.
Bagozzi, R.P. and Y. Yi: 1988, “On the Evaluation of Structural Equation Models,” Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 16 (1), 74 ∼ 94.
Chen, Y., R. Shang, A. Lin: 2008, “The intention to download music files in a P2P environment: Consumption value, fashion, and ethical decision perspectives,” Electronic Commerce Research and Applications 7 (4), 411–422.
Chin WW (1998) Issues and Opinion on Structural Equation Modeling. MIS Quarterly 22(1):vii–xvi.
Chiou, J., C. Huang, and H. Lee: 2005, “The Antecedents of Music Piracy Attitudes and Intentions,” Journal of Business Ethics 57 (2), 161-174.
Christensen, A.L. and M.M. Eining: 1991, “Factors Influencing Software Piracy: Implications for Accountants,” Journal of Information Systems 13 (4), 49-60.
Cronan, T.P. and S. Al-Rafee: 2008, “Factors that Influence the Intention to Pirate Software and Media,” Journal of Business Ethics 78 (4), 527-545.
d’Astous, A. and D. Montpetit: 2005, “Music Piracy on the Web – How Effective Are Anti-Piracy Arguments? Evidence From the Theory of Planned Behaviour,” Journal of Consumer Policy 28, 289-310.
Fishbein, M. and I. Ajzen: 1975, Belief, Attitude, Intention, and Behavior: An Introduction to Theory and Research. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Fornell, C. and D.F. Larcker: 1981, “Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error,” Journal of Marketing Research 18 (1), 39-50.
Gefen, D. and D.W. Straub: 2005, “A Practical Guide To Factorial Validity Using PLS-Graph: Tutorial And Annotated Example,” Communications of the AIS 16 (1), 91-109.
Glass, S.R. and A.W. Wood: 1996, “Situational determinants of software piracy: an equity theory perspective,” Journal of Business Ethics 15 (11), 1189-1198.
Goles, T., B. Jayatilaka, B. George, L. Parsons, V. Chambers, D. Taylor, and R. Brune: 2008, “Softlifting: Exploring Determinants of Attitude,” Journal of Business Ethics 77 (4), 481-499.
Gopal, R.D. and G.L. Sanders: 1998, “International Software Piracy Analysis of Key Issues and Impacts,” Information Systems Research 9 (4), 380-397.
Haines, R. and D. Haines: 2007, Fairness, Guilt, and Perceived Importance as Antecedents of Intellectual Property Piracy Intentions. Proceedings of the 28nd International Conference on Information Systems.
Haines R. and L.N.K. Leonard: 2007, “Situational influences on ethical decision-making in an IT context,” Information and Management, 44 (3), 313-320.
Hofstede, G.: 2001, Culture’s consequences: Comparing values, behaviors, institutions and organizations across nations (2nd ed.). Sage Publications Thousand Oaks.
Hunt, S.D. and S. Vitell: 1986, “A General Theory of Marketing Ethics,” Journal of Macromarketing 6(5), 5-16.
Kohlberg, L.: 1969, Stages in the development of moral thought and action. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Kwong, T. and M. Lee: 2002, Behavioral intention model for the exchange mode internet music piracy. Proceedings of the 35th Hawaii International Conference on System Science.
LaRose, R., Y. J. Lai, R. Lange, B. Love and Y. Wu: 2005, ‘Sharing or Piracy? An Exploration of Downloading Behavior’, Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication 11(1), article 1. http://jcmc.indiana.edu/vol11/issue1/larose.html.
Limayem, M., M. Khalifa, and W. W. Chin: 2004, “Factors Motivating Software Piracy: A Longitudinal Study,” IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management 51 (1), 414-425.
Lin, T. C., M. H. Hsu, F. Y. Kuo and P. C. Sun: 1999, An Intention Model-Based Study of Software Piracy. Proceedings of the 32nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences.
Loch, K.D. and S. Conger: 1996, “Evaluating ethical decision making and computer use,” Communications of the ACM 39 (7), 74–83.
Moores, T.T. and J. Chang: 2006, “Ethical decision-making in software piracy: Initial development and test of a four-component model,” MIS Quarterly 30 (1), 167-180.
Pavlou, P.A., H. Liang, and Y. Xue: 2007, “Understanding and Mitigating. Uncertainty in Online Exchange Relationships: a Principal-Agent. Perspective,” MIS Quarterly, 31(1), 105-136.
Peace, G., D. Galletta, and L. Thong: 2003, “Software Piracy in the Workplace: A Model and Empirical Test,” Journal of. Management Information Systems 20 (1), 153-177.
Rawls, J.: 1971, A Theory of Justice. Harvard University Press.
Reidenbach, R.E. and D.P. Robin: 1988, “Some initial steps toward improving the measurement of ethical evaluations of marketing activities,” Journal of Business Ethics 7 (11), 871-879.
Reidenbach, R.E. and D.P. Robin: 1990, “Toward the Development of a Multidimensional Scale for Improving Evaluations of Business Ethics,” Journal of Business Ethics, 9 (8), 639-653.
Rest, J. R.: 1986, Moral development: Advances in research and theory. New York: Praeger.
Shang, R. A., Y.C. Chen, and P.C. Chen: 2008, “Ethical Decisions About Sharing Music Files in the P2P Environment,” Journal of Business Ethics 80 (2), 349-365.
Simpson, P.M., D. Banerjee, and C.L. Simpson, Jr.: 1994, “Softlifting: A Model of Motivating Factors,” Journal of Business Ethics 13 (6), 431-438.
Tan B.: 2002, “Understanding consumer ethical decision making with respect to purchase of pirated software,” Journal of Consumer Marketing 19 (2), 96-111.
Taylor, S. and P.A. Todd: 1995, “Understanding information technology usage: a test of competing models,” Information Systems Research 6 (2), 144-176.
Thong, T.L. and C.S. Yap: 1998, “Testing an ethical decision-making theory: The case of softlifting,” Journal of Management Information Systems 15 (1), 213-215.
Triandis HC (1979) Values, Attitudes, and Interpersonal Behavior. In: Howe H, Page M (eds) Nebraska Symposium on Motivation. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln.
Wagner, S. and G.L. Sanders: 2001, “Considerations in ethical decision-making and software piracy,” Journal of Business Ethics 29 (1/2), 161-167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, C. Theory of Planned Behavior and Ethics Theory in Digital Piracy: An Integrated Model. J Bus Ethics 100, 405–417 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0687-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0687-7