Abstract
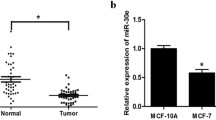
Metastasis remains a main cause of mortality from breast cancer and an unresolved issue. The purpose of this study is to investigate the role of miR-302a in the development of breast cancer metastasis mediated by CXCR4, a critical regulator of metastasis, and to identify miR-302a as an effective therapeutic agent for therapy and prevention of breast cancer metastasis. Our studies show that miR-302a expression levels were downregulated in metastatic breast cancer cells and tumor tissues. Additionally, the expression levels of miR-302a were inversely correlated with CXCR4 levels. More promisingly, miR-302a inhibited the invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo and reduced the expression of CXCR4. Our findings demonstrated that the repression of miR-302a levels contributes to breast cancer metastasis and restoration of miR-302a baseline expression inhibits the invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells. These data suggest that miR-302a mimics are potential therapeutic agents for breast cancer metastasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 October 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-022-06779-x
Abbreviations
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- CXCR4:
-
CXC chemokine receptor 4
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SDF-1:
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
References
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O (2000) Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 12(2):121–127
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, Barrera JL, Mohar A, Verastegui E, Zlotnik A (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410(6824):50–56
Geminder H, Sagi-Assif O, Goldberg L, Meshel T, Rechavi G, Witz IP, Ben-Baruch A (2001) A possible role for CXCR4 and its ligand, the CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1, in the development of bone marrow metastases in neuroblastoma. J Immunol 167(8):4747–4757
Taichman RS, Cooper C, Keller ET, Pienta KJ, Taichman NS, McCauley LK (2002) Use of the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 pathway in prostate cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Res 62(6):1832–1837
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan M, Zhou X, Xia W, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D, Hung MC (2004) Upregulation of CXCR4 is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 6(5):459–469
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman M, William L, Shim H (2005) Silencing of CXCR4 blocks breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 65:967–971
Liang Z, Wu T, Lou H, Yu X, Taichman RS, Lau SK, Nie S, Umbreit J, Shim H (2004) Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by selective synthetic polypeptide against CXCR4. Cancer Res 64(12):4302–4308
Yoon Y, Liang Z, Zhang X, Choe M, Zhu A, Cho HT, Shin DM, Goodman MM, Chen ZG, Shim H (2007) CXC chemokine receptor-4 antagonist blocks both growth of primary tumor and metastasis of head and neck cancer in xenograft mouse models. Cancer Res 67(15):7518–7524
Gontero P, Banisadr S, Frea B, Brausi M (2004) Metastasis markers in bladder cancer: a review of the literature and clinical considerations. Eur Urol 46(3):296–311
Turner HE, Harris AL, Melmed S, Wass JA (2003) Angiogenesis in endocrine tumors. Endocr Rev 24(5):600–632
Liang Z, Brooks J, Willard M, Liang K, Yoon Y, Kang S, Shim H (2007) CXCR4/CXCL12 axis promotes VEGF-mediated tumor angiogenesis through Akt signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359(3):716–722
Hao L, Zhang C, Qiu Y, Wang L, Luo Y, Jin M, Zhang Y, Guo TB, Matsushima K, Zhang Y (2007) Recombination of CXCR4, VEGF, and MMP-9 predicting lymph node metastasis in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 253(1):34–42
Croce CM, Calin GA (2005) miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 122(1):6–7
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Slack FJ, Weidhaas JB (2006) MicroRNAs as a potential magic bullet in cancer. Future Oncol 2(1):73–82
Jiang J, Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Schmittgen TD (2005) Real-time expression profiling of microRNA precursors in human cancer cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res 33(17):5394–5403
Stadler B, Ivanovska I, Mehta K, Song S, Nelson A, Tan Y, Mathieu J, Darby C, Blau CA, Ware C, Peters G, Miller DG, Shen L, Cleary MA, Ruohola-Baker H (2010) Characterization of microRNAs involved in embryonic stem cell states. Stem cells Dev 19(7):935–950
Cai N, Wang YD, Zheng PS (2013) The microRNA-302-367 cluster suppresses the proliferation of cervical carcinoma cells through the novel target AKT1. RNA 19(1):85–95
Koga C, Kobayashi S, Nagano H, Tomimaru Y, Hama N, Wada H, Kawamoto K, Eguchi H, Konno M, Ishii H, Umeshita K, Doki Y, Mori M (2014) Reprogramming Using microRNA-302 Improves Drug Sensitivity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Ann Surg Oncol.
Liang Z, Ahn J, Guo D, Votaw JR, Shim H (2013) MicroRNA-302 replacement therapy sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation. Pharm Res 30(4):1008–1016
Liang Z, Wu H, Xia J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Huang K, Wagar N, Yoon Y, Cho HT, Scala S, Shim H (2010) Involvement of miR-326 in chemotherapy resistance of breast cancer through modulating expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1. Biochem Pharmacol 79(6):817–824
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Shim H, Lau SK, Devi S, Yoon Y, Cho HT, Liang Z (2006) Lower expression of CXCR4 in lymph node metastases than in primary breast cancers: potential regulation by ligand-dependent degradation and HIF-1alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(1):252–258
Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, Bartolini S, Ceresoli GL, Bemis L, Haney J, Witta S, Danenberg K, Domenichini I, Ludovini V, Magrini E, Gregorc V, Doglioni C, Sidoni A, Tonato M, Franklin WA, Crino L, Bunn PA Jr, Varella-Garcia M (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 97(9):643–655
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449(7163):682–688
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh P, Muth D, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reinhardt F, Onder TT, Valastyan S, Westermann F, Speleman F, Vandesompele J, Weinberg RA (2010) miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 12(3):247–256
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL, Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D, Luker GD (2004) CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 64(23):8604–8612
Fareh M, Turchi L, Virolle V, Debruyne D, Almairac F, de-la-Forest Divonne S, Paquis P, Preynat-Seauve O, Krause KH, Chneiweiss H, Virolle T (2012) The miR 302-367 cluster drastically affects self-renewal and infiltration properties of glioma-initiating cells through CXCR4 repression and consequent disruption of the SHH-GLI-NANOG network. Cell Death Differ 19(2):232–244
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ (2006) miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Database issue):D140–D144
Cruz-Rivera E, Paul VJ (2007) Chemical deterrence of a cyanobacterial metabolite against generalized and specialized grazers. J Chem Ecol 33(1):213–217
Lipchina I, Studer L, Betel D (2012) The expanding role of miR-302-367 in pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell Cycle 11(8):1517–1523
Lin SL, Chang DC, Chang-Lin S, Lin CH, Wu DT, Chen DT, Ying SY (2008) Mir-302 reprograms human skin cancer cells into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. RNA 14(10):2115–2124
Stenvang J, Silahtaroglu AN, Lindow M, Elmen J, Kauppinen S (2008) The utility of LNA in microRNA-based cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol 18(2):89–102
Love TM, Moffett HF, Novina CD (2008) Not miR-ly small RNAs: big potential for microRNAs in therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121(2):309–319
Gaur A, Jewell DA, Liang Y, Ridzon D, Moore JH, Chen C, Ambros VR, Israel MA (2007) Characterization of microRNA expression levels and their biological correlates in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 67(6):2456–2468
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435(7043):834–838
Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR, Jacks T (2007) Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet 39(5):673–677
Doench JG, Sharp PA (2004) Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev 18(5):504–511
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120(1):15–20
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19(1):92–105
Barroso-del Jesus A, Lucena-Aguilar G, Menendez P (2009) The miR-302-367 cluster as a potential stemness regulator in ESCs. Cell Cycle 8(3):394–398
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Program Concept Award (BC052118) to ZL as well as a Research Grant from NIH NCI (1R01CA165306) to HS. The authors thank Jessica Paulishen for proof-reading.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Z., Bian, X. & Shim, H. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis with microRNA-302a by downregulation of CXCR4 expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 146, 535–542 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3053-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3053-0