Abstract
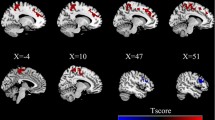
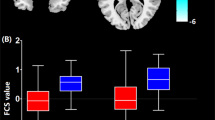
Neuroimaging studies have demonstrated that psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) are characterized by unstable cognitive-emotional and motor system, which is engaged in hyperactivity of limbic regions and sensorimotor area. The insula, which is a part of the limbic system, includes various subregions with some distinct connectivity patterns separately. However, whether these insular subregions show different connectivity patterns respectively in PNES remains largely unknown. We aimed to investigate the functional connectivity (FC) of insular subregions in PNES and extend the understanding of the complex pathophysiological mechanisms of this disease. A resting-state FC based on the insular subregions were conducted in 18 patients and 20 healthy controls. We examined the differences in FC values between PNES patients and controls using two sample t test. Our results showed patients had significantly stronger FC between insular subregions and sensorimotor network, lingual gyrus, superior parietal gyrus and putamen, which suggested a hyperlink pattern of insular subregions involved in abnormal emotion regulation, cognitive processes and motor function in PNES. Pearson correlation analysis between the mean FC values within abnormal regions and the frequency of PNES further indicated PNES exhibited abnormal functional organization whose stressful emotion of patients have great direct influence on their motor functions. The differentially impaired functional connectivity patterns of insular subregions might provide new insights into the complex neurological mechanism of PNES.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander GE, Crutcher MD (1990) Preparation for movement: neural representations of intended direction in three motor areas of the monkey. J Neurophysiol 64(1):133–150
Bakvis P, Spinhoven P, Zitman FG, Roelofs K (2011) Automatic avoidance tendencies in patients with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. Seizure 20(8):628–634. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2011.06.006
Baslet G (2011) Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures: a model of their pathogenic mechanism. Seizure 20(1):1–13. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2010.10.032
Baslet G (2012) Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: a treatment review. What have we learned since the beginning of the millennium? Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 8:585–598. doi:10.2147/NDT.S32301
Benbadis SR, Siegrist K, Tatum WO, Heriaud L, Anthony K (2004) Short-term outpatient EEG video with induction in the diagnosis of psychogenic seizures. Neurology 63(9):1728–1730
Bettus G, Guedj E, Joyeux F, Confort-Gouny S, Soulier E, Laguitton V, Cozzone PJ, Chauvel P, Ranjeva JP, Bartolomei F, Guye M (2009) Decreased basal fMRI functional connectivity in epileptogenic networks and contralateral compensatory mechanisms. Hum Brain Mapp 30(5):1580–1591. doi:10.1002/hbm.20625
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34(4):537–541
Burgmer M, Konrad C, Jansen A, Kugel H, Sommer J, Heindel W, Ringelstein EB, Heuft G, Knecht S (2006) Abnormal brain activation during movement observation in patients with conversion paralysis. Neuroimage 29(4):1336–1343. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.08.033
Cauda F, D’Agata F, Sacco K, Duca S, Geminiani G, Vercelli A (2011) Functional connectivity of the insula in the resting brain. Neuroimage 55(1):8–23. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.049
Cerliani L, Thomas RM, Jbabdi S, Siero JC, Nanetti L, Crippa A, Gazzola V, D’Arceuil H, Keysers C (2012) Probabilistic tractography recovers a rostrocaudal trajectory of connectivity variability in the human insular cortex. Hum Brain Mapp 33(9):2005–2034. doi:10.1002/hbm.21338
Cloutman LL, Binney RJ, Drakesmith M, Parker GJ, Lambon Ralph MA (2012) The variation of function across the human insula mirrors its patterns of structural connectivity: evidence from in vivo probabilistic tractography. Neuroimage 59(4):3514–3521. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.016
Craig AD (2009) How do you feel—now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(1):59–70. doi:10.1038/nrn2555
de Lange FP, Roelofs K, Toni I (2007) Increased self-monitoring during imagined movements in conversion paralysis. Neuropsychologia 45(9):2051–2058. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.02.002
Deen B, Pitskel NB, Pelphrey KA (2011) Three systems of insular functional connectivity identified with cluster analysis. Cereb Cortex 21(7):1498–1506. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq186
Devinsky O, Gazzola D, LaFrance WC Jr (2011) Differentiating between nonepileptic and epileptic seizures. Nat Rev Neurol 7(4):210–220. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2011.24
Ding JR, An D, Liao W, Li J, Wu GR, Xu Q, Long Z, Gong Q, Zhou D, Sporns O, Chen H (2013) Altered functional and structural connectivity networks in psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. PLoS One 8(5):e63850. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063850
Dosenbach NU, Fair DA, Miezin FM, Cohen AL, Wenger KK, Dosenbach RA, Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Raichle ME, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2007) Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task control in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(26):11073–11078. doi:10.1073/pnas.0704320104
Dupont S, Bouilleret V, Hasboun D, Semah F, Baulac M (2003) Functional anatomy of the insula: new insights from imaging. Surg Radiol Anat 25(2):113–119. doi:10.1007/s00276-003-0103-4
Fair DA, Cohen AL, Dosenbach NU, Church JA, Miezin FM, Barch DM, Raichle ME, Petersen SE, Schlaggar BL (2008) The maturing architecture of the brain’s default network. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(10):4028–4032. doi:10.1073/pnas.0800376105
Fogassi L, Ferrari PF, Gesierich B, Rozzi S, Chersi F, Rizzolatti G (2005) Parietal lobe: from action organization to intention understanding. Science 308(5722):662–667. doi:10.1126/science.1106138
Fox MD, Zhang D, Snyder AZ, Raichle ME (2009) The global signal and observed anticorrelated resting state brain networks. J Neurophysiol 101(6):3270–3283. doi:10.1152/jn.90777.2008
Greicius MD, Supekar K, Menon V, Dougherty RF (2009) Resting-state functional connectivity reflects structural connectivity in the default mode network. Cereb Cortex 19(1):72–78. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn059
Griffiths PD, Perry RH, Crossman AR (1994) A detailed anatomical analysis of neurotransmitter receptors in the putamen and caudate in Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 169(1–2):68–72
Guo WB, Liu F, Xue ZM, Yu Y, Ma CQ, Tan CL, Sun XL, Chen JD, Liu ZN, Xiao CQ, Chen HF, Zhao JP (2011) Abnormal neural activities in first-episode, treatment-naive, short-illness-duration, and treatment-response patients with major depressive disorder: a resting-state fMRI study. J Affect Disord 135(1–3):326–331. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2011.06.048
Guo W, Liu F, Liu J, Yu L, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Xiao C, Zhai J, Zhao J (2014) Abnormal causal connectivity by structural deficits in first-episode, drug-naive schizophrenia at rest. Schizophr Bull. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbu126
Guz H, Doganay Z, Ozkan A, Colak E, Tomac A, Sarisoy G (2004) Conversion and somatization disorders: dissociative symptoms and other characteristics. J Psychosom Res 56(3):287–291. doi:10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00069-2
Hoptman MJ, Zuo XN, D’Angelo D, Mauro CJ, Butler PD, Milham MP, Javitt DC (2012) Decreased interhemispheric coordination in schizophrenia: a resting state fMRI study. Schizophr Res 141(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2012.07.027
Kapur N, Friston KJ, Young A, Frith CD, Frackowiak RS (1995) Activation of human hippocampal formation during memory for faces: a PET study. Cortex 31(1):99–108
Krumholz A, Niedermeyer E (1983) Psychogenic seizures: a clinical study with follow-up data. Neurology 33(4):498–502
Kurth F, Eickhoff SB, Schleicher A, Hoemke L, Zilles K, Amunts K (2010a) Cytoarchitecture and probabilistic maps of the human posterior insular cortex. Cereb Cortex 20(6):1448–1461. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp208
Kurth F, Zilles K, Fox PT, Laird AR, Eickhoff SB (2010b) A link between the systems: functional differentiation and integration within the human insula revealed by meta-analysis. Brain Struct Funct 214(5–6):519–534. doi:10.1007/s00429-010-0255-z
Landgrebe M, Barta W, Rosengarth K, Frick U, Hauser S, Langguth B, Rutschmann R, Greenlee MW, Hajak G, Eichhammer P (2008) Neuronal correlates of symptom formation in functional somatic syndromes: a fMRI study. Neuroimage 41(4):1336–1344. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.04.171
Lesser RP (2003) Treatment and outcome of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsy Curr 3(6):198–200. doi:10.1046/j.1535-7597.2003.03601.x
Liao W, Zhang Z, Pan Z, Mantini D, Ding J, Duan X, Luo C, Wang Z, Tan Q, Lu G, Chen H (2011) Default mode network abnormalities in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: a study combining fMRI and DTI. Hum Brain Mapp 32(6):883–895. doi:10.1002/hbm.21076
Liu F, Guo W, Fouche JP, Wang Y, Wang W, Ding J, Zeng L, Qiu C, Gong Q, Zhang W, Chen H (2013a) Multivariate classification of social anxiety disorder using whole brain functional connectivity. Brain Struct Funct. doi:10.1007/s00429-013-0641-4
Liu F, Guo W, Liu L, Long Z, Ma C, Xue Z, Wang Y, Li J, Hu M, Zhang J, Du H, Zeng L, Liu Z, Wooderson SC, Tan C, Zhao J, Chen H (2013b) Abnormal amplitude low-frequency oscillations in medication-naive, first-episode patients with major depressive disorder: a resting-state fMRI study. J Affect Disord 146(3):401–406. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2012.10.001
Liu F, Hu M, Wang S, Guo W, Zhao J, Li J, Xun G, Long Z, Zhang J, Wang Y, Zeng L, Gao Q, Wooderson SC, Chen J, Chen H (2012) Abnormal regional spontaneous neural activity in first-episode, treatment-naive patients with late-life depression: a resting-state fMRI study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 39(2):326–331
Liu F, Xie B, Wang Y, Guo W, Fouche JP, Long Z, Wang W, Chen H, Li M, Duan X, Zhang J, Qiu M (2014) Characterization of post-traumatic stress disorder using resting-state fMRI with a multi-level parametric classification approach. Brain Topogr. doi:10.1007/s10548-014-0386-2
Long Z, Duan X, Wang Y, Liu F, Zeng L, Zhao JP, Chen H (2014) Disrupted structural connectivity network in treatment-naive depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 56C, 18–26. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.07.007
Magaudda A, Gugliotta SC, Tallarico R, Buccheri T, Alfa R, Lagana A (2011) Identification of three distinct groups of patients with both epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsy Behav 22(2):318–323. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2011.07.005
Montoya A, Price BH, Lepage M (2006) Neural correlates of ‘functional’ symptoms in neurology. Funct Neurol 21(4):193–197
Nanetti L, Cerliani L, Gazzola V, Renken R, Keysers C (2009) Group analyses of connectivity-based cortical parcellation using repeated k-means clustering. Neuroimage 47(4):1666–1677. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.06.014
Peng ZW, Xu T, He QH, Shi CZ, Wei Z, Miao GD, Jing J, Lim KO, Zuo XN, Chan RC (2014) Default network connectivity as a vulnerability marker for obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychol Med 44(7):1475–1484. doi:10.1017/S0033291713002250
Picard N, Strick PL (2003) Activation of the supplementary motor area (SMA) during performance of visually guided movements. Cereb Cortex 13(9):977–986
Reuber M (2008) Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: answers and questions. Epilepsy Behav 12(4):622–635. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2007.11.006
Reuber M, House AO, Pukrop R, Bauer J, Elger CE (2003) Somatization, dissociation and general psychopathology in patients with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. Epilepsy Res 57(2–3):159–167. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2003.11.004
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN, Wang R, Dai G, D’Arceuil HE, de Crespigny AJ, Wedeen VJ (2007) Association fibre pathways of the brain: parallel observations from diffusion spectrum imaging and autoradiography. Brain 130(Pt 3):630–653. doi:10.1093/brain/awl359
Stone J, Zeman A, Simonotto E, Meyer M, Azuma R, Flett S, Sharpe M (2007) FMRI in patients with motor conversion symptoms and controls with simulated weakness. Psychosom Med 69(9):961–969. doi:10.1097/PSY.0b013e31815b6c14
Ture U, Yasargil DC, Al-Mefty O, Yasargil MG (1999) Topographic anatomy of the insular region. J Neurosurg 90(4):720–733
Uliaszek AA, Prensky E, Baslet G (2012) Emotion regulation profiles in psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. Epilepsy Behav 23(3):364–369. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.01.009
van der Kruijs SJ, Bodde NM, Vaessen MJ, Lazeron RH, Vonck K, Boon P, Hofman PA, Backes WH, Aldenkamp AP, Jansen JF (2012) Functional connectivity of dissociation in patients with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 83(3):239–247. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2011-300776
van der Kruijs SJ, Jagannathan SR, Bodde NM, Besseling RM, Lazeron RH, Vonck KE, Boon PA, Cluitmans PJ, Hofman PA, Backes WH, Aldenkamp AP, Jansen JF (2014) Resting-state networks and dissociation in psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. J Psychiatr Res 54:126–133. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.03.010
Voon V, Brezing C, Gallea C, Ameli R, Roelofs K, LaFrance WC Jr, Hallett M (2010a) Emotional stimuli and motor conversion disorder. Brain 133(Pt 5):1526–1536. doi:10.1093/brain/awq054
Voon V, Gallea C, Hattori N, Bruno M, Ekanayake V, Hallett M (2010b) The involuntary nature of conversion disorder. Neurology 74(3):223–228. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ca00e9
Vuilleumier P, Chicherio C, Assal F, Schwartz S, Slosman D, Landis T (2001) Functional neuroanatomical correlates of hysterical sensorimotor loss. Brain 124(Pt 6):1077–1090
Waites AB, Briellmann RS, Saling MM, Abbott DF, Jackson GD (2006) Functional connectivity networks are disrupted in left temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 59(2):335–343. doi:10.1002/ana.20733
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by 973 Project 2012CB517901, and by the Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant Nos. 61035006, 61125304, and by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China 20120185110028. The authors have no financial relationships to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Liu, K., Ma, X. et al. Altered Functional Connectivity Patterns of the Insular Subregions in Psychogenic Nonepileptic Seizures. Brain Topogr 28, 636–645 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-014-0413-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-014-0413-3