Abstract
Introduction
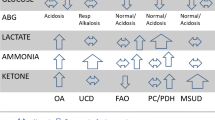
Ketone formation is a normal response when hypoglycemia occurs. Since the majority of children with recurrent hypoglycemia cannot be diagnosed with a known endocrine or metabolic disorder on a critical sample, ketotic hypoglycemia has been described as the most common cause of low blood glucose concentrations in children. Critical samples, however, will miss the ketotic forms of glycogen storage disease (GSD), which present with elevated ketones, hypoglycemia, and normal hormonal concentrations.
Results
A total of 164 children (96 boys, 68 girls) were enrolled in the study. Prediction of pathogenicity of DNA changes using computer modeling confirmed pathology in 20 individuals [four GSD 0, two GSD VI, 12 GSD IX alpha, one GSD IX beta, one GSD IX gamma] (12 %). Boys were most likely to have changes in the PHKA2 gene, consistent with GSD IX alpha, an X-linked disorder.
Conclusions
Mutations in genes involved in glycogen synthesis and degradation were commonly found in children with idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia. GSD IX is likely an unappreciated cause of ketotic hypoglycemia in children, while GSD 0 and VI are relatively uncommon. GSD IX alpha should particularly be considered in boys with unexplained hypoglycemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GSD:
-
glycogen storage disease
- KH:
-
ketotic hypoglycemia
References
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L et al (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7(4):248–249
Bachrach BE, Weinstein DA, Orho-Melander M, Burgess A, Wolfsdorf JI (2002) Glycogen synthase deficiency (glycogen storage disease type 0) presenting with hyperglycemia and glucosuria: report of three new mutations. J Pediatr 140:781–783
Bashan N, Potashnik R, Ehrlich T, Moses SW (1987) Phosphorylase kinase in leukocytes and erythrocytes of a patient with glycogen storage disease type IX. J Inherit Metab Dis 10(2):119–127
Bodamer OA, Hussein K, Morris AA et al (2006) Glucose and leucine kinetics in idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia. Arch Dis Child 91:483–486
Daly LP, Osterhoudt KC, Weinzimer SA (2003) Presenting features of idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia. J Emerg Med 25:39–43
Davit-Spraul A, Piraud M, Dobbelaere D et al (2011) Liver glycogen storage diseases due to phosphorylase system deficiencies: diagnosis thanks to non invasive blood enzymatic and molecular studies. Mol Genet Metab 104(1–2):137–143
Grunt JA, McGarry ME, McCollum AT, Gould JB (1970) Studies of children with ketotic hypoglycemia. Yale J Biol Med 42:420–438
Haymond MW, Karl IE, Pagliara AS (1974) Ketotic hypoglycemia: an amino acid substrate limited disorder. J Endocrinol Metab 38:521–530
Huidekoper HH, Duran M, Turkenburg M, Ackermans MT, Sauerwein HP, Wijburg FA (2008) Fasting adaptation in idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia: a mismatch between glucose production and demand. Eur J Pediatr 167:859–865
Kogut MD, Blaskovics M, Donnell GN (1969) Idiopathic hypoglycemia: a study of twenty-six children. J Pediatr 74:853–871
Morris AA, Leonard JV (1997) Early recognition of metabolic decompensation. Arch Dis Child 76(6):555–556
Nessa A, Kumaran A, Kirk R, Dalton A, Ismail D, Hussain K (2012) Mutation al analysis of the GYS2 gene in patients diagnosed with ketotic hypoglycaemia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 25(9–10):963–967
Ng PC, Henikoff S (2001) Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions. Genome Res 11(5):863–874
Paesold-Burda P, Baumgartner MR, Santer R, Bosshard NU, Steinmann B (2007) Elevated serum biotinidase activity in hepatic glycogen storage disorders—a convenient biomarker. J Inherit Metab Dis 30(6):896–902
Pagliara AS, Karl IE, De Vivo DC, Feigin RD, Kipnis DM (1972) Hypoalaninemia: a concomitant of ketotic hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest 51:1440–1449
Pollack ES, Pollack CV Jr (1993) Ketotic hypoglycemia: a case report. J Emerg Med 11:531–534
Schwarz JM, Rödelsperger C, Schuelke M, Seelow D (2010) Mutationtaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat Methods 7(8):575–576
Tsilianidis LA, Fiske LM, Siegel S et al (2013) Aggressive therapy improves cirrhosis in glycogen storage disease type IX. Mol Genet Metab 109(2):179–182
Weinstein DA, Wolfsdorf JI (2002) Glycogen storage diseases—a primer for clinicians. Endocrinologist 12:531–538
Weinstein DA, Correia CE, Saunders AC, Wolfsdorf JI (2006) Hepatic glycogen synthase deficiency: an under-recognized cause of ketotic hypoglycemia. Mol Genet Metab 87:284–288
Wolfsdorf JI, Weinstein DA (2003) Glycogen storage diseases—genetics and management. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 4:95–102
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by philanthropic support provided by the following funds managed through the University of Florida Office of Development: Scott Miller GSD Program Fund, Matthew Ehrman Fund for GSD Research, Ralph and Alice Brown GSD Type VI Research Fund, Matthew’s GSD Type IX Fund, and the Sturtz GSD Research Fund. We thank patients and families for their participation, along with the many physicians named in “Appendix 1”, who provided samples for the investigations. The authors also thank Andie Jacinto, Iris Ferrecchia, Tayoot Chengsupanimit, and Megan Curry for their help with proofreading, table preparation, and assisting with the reference section.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Olaf Bodamer
Laurie M. Brown and Michelle M. Corrado are co-principal investigators
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, L.M., Corrado, M.M., van der Ende, R.M. et al. Evaluation of glycogen storage disease as a cause of ketotic hypoglycemia in children. J Inherit Metab Dis 38, 489–493 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-014-9744-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-014-9744-1