Abstract
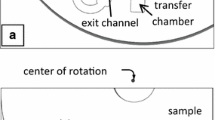
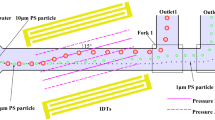
Centrifugal microfluidics has been recognized as a promising pumping method in microfluidics because of its simplicity, easiness of automation, and parallel processing. However, the patterning of stripe flow in centrifugal microfluidics is challenging because a fluid is significantly affected by the Coriolis force, which produces an intrinsic secondary flow. This paper reports a technical and design strategy for centrifugal microfluidics called “density-gradient-assisted centrifugal microfluidics.” The flow behavior is observed with the presence of a density gradient and without a density gradient in two concentrically traveling phase flows. As a result, clear stripe flow pattern is observed with a density difference of 0.05 g/cm3 between water and a percoll solution at a flow rate of 11.8 μl/s (7 ml/10 min) and spinning speed of 3000 rpm. In contrast, without a density gradient, it is necessary to reduce the flow rate and spinning speed to 0.1 μl/s and 1000 rpm, respectively. This paper also presents the use of a density gradient to assist in focusing resin (polystyrene) particles on the boundary of a stripe flow pattern that consists of water and percoll with different densities. Moreover, the density-based separation and sorting of particles in a mixed particle suspension is demonstrated. Polystyrene is selectively focused on the boundary, but silica particles are separated from the focused trajectory due to a difference in density. The separated particles are continuously sorted into different reservoirs with polystyrene and silica separation efficiencies of 96.5% and 98.5%, respectively. The pumping, stripe flow pattern formation, particle concentration, and sorting are simultaneously realized by applying a density gradient and centrifugal force. Therefore, this principle can realize a very simple technique for label-free particle separation by just spinning a disk device and can be applied in other applications by the use of the density-gradient assistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.A.S. Bhagat, S.S. Kuntaegowdanahalli, I. Papautsky, Lab Chip 8, 1906–1914 (2008)
T.F. Didara, M. Tabrizian, Lab Chip 12, 4363–4371 (2012)
J. Ducrée, T. Brenner, S. Haeberle, T. Glatzel, R. Zengerle, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2, 78–84 (2006a)
J. Ducrée, S. Haeberle, T. Brenner, T. Glatzel, R. Zengerle, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2, 97–105 (2006b)
D.C. Duffy, J.C. McDonald, O.J.A. Schueller, G.M. Whitesides, Anal. Chem. 70, 4974–4984 (1998)
D.C. Duffy, H.L. Gillis, J. Lin, N.F. Sheppard Jr., G.J. Kellogg, Anal. Chem. 71, 4669–4678 (1999)
W.H. Grover, A.K. Bryan, M. Diez-Silva, S. Suresh, J.M. Higgins, S.R. Manalis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 10992–10996 (2011)
M. Grumann, T. Brenner, C. Beer, R. Zengerle, J. Ducrée, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, 025101 (2005)
S. Hardt, T. Hahn, Lab Chip 12, 434–442 (2012)
D. Huh, J.H. Bahng, Y. Ling, H.-H. Wei, O.D. Kripfgans, J.B. Fowlkes, J.B. Grotberg, S. Takayama, Anal. Chem. 79, 1369–1376 (2007)
T. Kawai, N. Naruishi, H. Nagai, Y. Tanaka, Y. Hagihara, Y. Yoshida, Anal. Chem. 85, 6587–6592 (2013)
T. Kobayashi, T. Funamoto, M. Hosaka, S. Konishi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 077001 (2010)
S. Lay, S. Wang, J. Luo, L.J. Lee, S.T. Yang, M.J. Madou, Anal. Chem. 76, 1832–1838 (2004)
Y. Lu, Y. Xia, G. Luo, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 10, 1079–1086 (2011)
D. Mark, F. Stetten, R. Zengerle, Lab Chip 12, 2464–2468 (2012)
T. Morijiri, S. Sunahiro, M. Senaha, M. Yamada, M. Seki, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 11, 105–110 (2011)
T.V. Nguyen, P.N. Duncan, S. Ahrar, E.E. Hui, Lab Chip 12, 3991–3994 (2012)
N. Pamme, Lab Chip 7, 1644–1659 (2007)
H. Pertoft, J. Biochem, Biosys. Methods 44, 1–30 (2000)
R. Safavieh, D. Juncker, Lab Chip 13, 4180–4189 (2013)
M. Tokeshi, T. Minagawa, K. Uchiyama, A. Hibara, K. Sato, H. Hisamoto, T. Kitamori, Anal. Chem. 74, 1565–1571 (2002)
M. Tsukamoto, S. Taira, S. Yamamura, Y. Morita, N. Nagatani, Y. Takamura, E. Tamiya, Analyst 134, 1994–1998 (2009)
Y. Ukita, Y. Takamura, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 15, 829–837 (2013)
Y. Ukita, Y. Takamura, Microfluid. Nanofluid. (under review) 2017
Y. Ukita, S. Kondo, T. Azeta, M. Ishizawa, C. Kataoka, M. Takeo, Y. Utsumi, Sensors Actuators B, 2012, 166-167, 898–906.
T. Wang, S. Oehrlein, M.M. Somoza, J.R.S. Perez, R. Kershner, F. Cerrina, Lab Chip 11, 1629–1637 (2011)
D.A. Wolff, H. Pertoft, 579-585. J. Cell Biol., 55 (1972)
X. Xuan, J. Zhu, C. Church, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 9, 1–16 (2010)
M. Yamada, M. Nakashima, M. Seki, Anal. Chem. 76, 5465–5471 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 513 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ukita, Y., Oguro, T. & Takamura, Y. Density-gradient-assisted centrifugal microfluidics: an approach to continuous-mode particle separation. Biomed Microdevices 19, 24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0158-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0158-3