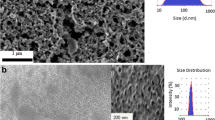
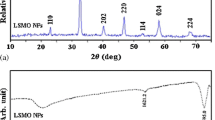
Abstract
This paper presents the development of magnetic lipid nanoparticles that could serve as controlled delivery vehicles for releasing encapsulated drugs in a desired manner. The nanoparticles are composed of multiple drugs in lipid matrices, which are solid at body temperature and melt around 45°C to 55°C. In addition, super-paramagnetic γ-Fe2O3 particles with sizes ranging from 5 to 25 nm are surface modified and dispersed uniformly in the lipid nanoparticles. In the prototype demonstration, lipid nanoparticles with average sizes between 100 and 180 nm were fabricated by high-pressure homogenization at elevated temperatures. When exposed to an alternating magnetic field of 60 kA/m at 25 kHz, a solution containing 2 g/L encapsulated γ-Fe2O3 particles showed a temperature increase from 37°C to 50°C in 20 min. Meanwhile, the dissipated heat melted the surrounding lipid matrices and resulted in an accelerated release of the encapsulated drugs. Within 20 min, approximately 35% of the encapsulated drug molecules were released from the lipid nanoparticles through diffusion. As such, the presented lipid nanoparticles enable a new scheme that combines magnetic control of heating and drug delivery, which could greatly enhance the performance of encapsulated drugs.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.M. Allen, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 750 (2002)
T.M. Allen, P.R. Cullis, Science 303, 1818 (2004)
W. Andra, in Magnetism in Medicine: A Handbook, ed. by W., Andra, H., Nowak (Wiley-VCH, Berlin, 1998)
D.Y. Arifin, L.Y. Lee, C.H. Wang, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58, 1274 (2006)
M. Babincova, P. Cicmanec, V. Altanerova, C. Altaner, P. Babinec, Bioelectrochemistry 55, 17 (2002)
M. Babincova, V. Altanerova, C. Altaner, P. Cicmanec, P. Babinec, Med. Phys. 31, 2219 (2004)
L. Brannon-Peppas, J.O. Blanchette, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56, 1649 (2004)
D.C. Drummond, M. Zignani, J.C. Leroux, Prog. Lipid Res. 39, 409 (2000)
A.K. Gupta, M. Gupta, Biomaterials 26, 3995 (2005)
J.W. Hand, J.R. James, Physical Techniques in Clinical Hyperthermia (Wiley, New York, 1986)
J. Heller, Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 10, 253 (1993)
A. Jordan, R. Scholz, P. Wust, H. Fahling, R. Felix, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 201, 413 (1999)
R. Langer, Nature 392S, 5 (1998)
R.T. Liggins, H.M. Burt, Int. J. Pharm. 222, 19 (2001)
T.G. Mason, J.N. Wilking, K. Meleson, C.B. Chang, S.M. Graves, J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 18, R635 (2006)
W. Mehnert, K. Mader, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 47, 165 (2001)
S.M. Moghimi, A.C. Hunter, Trends Biotechnol. 18, 412 (2000)
S.M. Moghimi, A.C. Hunter, J.C. Murray, Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 283 (2001)
S.M. Moghimi, A.C. Hunter, J.C. Murray, FASEB J. 19, 311 (2005)
S. Mornet, S. Vasseur, F. Grasset, E. Duguet, J. Mater. Chem. 14, 2161 (2004)
P. Moroz, S.K. Jones, B.N. Gray, J. Surg. Oncol. 77, 259 (2001)
R.H. Muller, K. Mader, S. Gohla, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50, 161 (2000)
Q.A. Pankhurst, J. Connolly, S.K. Jones, J. Dobson, J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 36, R167 (2003)
K. Park, Controlled Drug Delivery: Challenges and Strategies (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1997)
L.W. Phipps, Nature 233, 617 (1971)
A.M. Ponce, Z. Vujaskovic, F. Yuan, D. Needham, M.W. Dewhirst, Int. J. Hyperthermia 22, 205 (2006)
P.H. Redfern, Drug Deliv. Syst. Sci. 2, 21 (2002)
R.E. Rosensweig, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 252, 370 (2002)
M. Sako, S. Hirota, Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 13, 1618 (1986)
C. Schwarz, W. Mehnert, J. Microencapsul. 16, 205 (1999)
S. Schultz, G. Wagner, K. Urban, J. Ulrich, Chem. Eng. Technol. 27, 361 (2004)
J. Siepmann, N. Faisant, J. Akiki, J. Richard, J.P. Benoit, J. Control. Release 96, 123 (2004)
J. Siepmann, K. Elkharraz, F. Siepmann, D. Klose, Biomacromolecules 6, 2312 (2005)
K.S. Soppimath, T.M. Aminabhavi, A.R. Kulkarni, W.E. Rudzinski, J. Control. Release 70, 1 (2001)
B.G. Stubbe, S.C. De Smedt, J. Demeester, Pharm. Res. 21, 1732 (2004)
K.S. Suslick, Science 247, 1439 (1990)
G.I. Taylor, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. 146, 501 (1934)
E. Viroonchatapan, H. Sato, M. Ueno, I. Adachi, J. Murata, I. Saiki, K. Tazawa, I. Horikoshi, J. Drug Target. 5, 379 (1998)
A. zur Muhlen, C. Schwarz, W. Mehnert, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 45, 149 (1998)
Acknowledgements
The demonstrated systems were fabricated in the ESS Microfabrication Lab at National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan. This work was supported in part by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Contract no. NSC 96-2221-E-007-116-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, MH., Su, YC. Iron-oxide embedded solid lipid nanoparticles for magnetically controlled heating and drug delivery. Biomed Microdevices 10, 785–793 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9192-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9192-5