Abstract
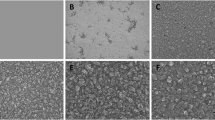
Surfaces of materials that promote cell adhesion, proliferation, and growth are critical for new generation of implantable biomedical devices. These films should be able to coat complex geometrical shapes very conformally, with smooth surfaces to produce hermetic bioinert protective coatings, or to provide surfaces for cell grafting through appropriate functionalization. Upon performing a survey of desirable properties such as chemical inertness, low friction coefficient, high wear resistance, and a high Young’s modulus, diamond films emerge as very attractive candidates for coatings for biomedical devices. A promising novel material is ultrananocrystalline diamond (UNCD®) in thin film form, since UNCD possesses the desirable properties of diamond and can be deposited as a very smooth, conformal coating using chemical vapor deposition. In this paper, we compared cell adhesion, proliferation, and growth on UNCD films, silicon, and platinum films substrates using different cell lines. Our results showed that UNCD films exhibited superior characteristics including cell number, total cell area, and cell spreading. The results could be attributed to the nanostructured nature or a combination of nanostructure/surface chemistry of UNCD, which provides a high surface energy, hence promoting adhesion between the receptors on the cell surface and the UNCD films.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.D. Abramoff, P.J. Magelhaes, S.J. Ram, Biophoton. Int. 11, 36 (2004)
O. Auciello, A.R. Krauss, D.M. Gruen, H.G. Busmann, E.M. Meyer, J. Tucek, A. Sumant, A. Jayatissa, N. Moldovan, D.C. Mancini, M.N. Gardos, MRS Symposium Proceedings 605, 73 (2000)
O. Auciello, J. Birrell, J.A. Carlisle, J.E. Gerbi, X. Xiao, B. Peng, H.D. Espinosa, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16, 539 (2004)
J.A. Carlisle, O. Auciello, Interface 12, 28 (2003)
F. Chiellini, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 21, 257 (2006)
R.A. Freitas Jr., Nanomedicine, Volume IIA: Biocompatibility, (Landes Bioscience, Georgetown, 2003), p 183, 185
M.N. Gardos, Surf. Coat. Technol. 113, 183 (1999)
L.A. Greene, A.S. Tischler, Adv. Cell. Neurobiol. 3, 373 (1982)
D.M. Gruen, S. Liu, A.R. Krauss, X. Pan, J. Appl. Phys. 75, 1758 (1994a)
D.M. Gruen, S. Liu, Krauss, A.R. Krauss, J. Luo, X. Pan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 64, 1502 (1994b)
D.M. Gruen, D.G. Zuiker, A.R. Krauss, X. Pan, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 13, 1628 (1995)
C. de Haro, R. Mas, G. Abadal, J. Muñoz, F. Perez-Murano, C. Domiñguez, Biomaterials 23, 4515 (2002)
I. Horcas, R. Fernández, J.M. Gómez-Rodríguez, J. Colchero, J. Gómez-Herrero, A.M. Baro, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 0137051 (2007)
S. Jiao, A. Sumant, M.A. Kirk, D.M. Gruen, A.R. Krauss, O. Auciello, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 118 (2001)
C.J. Kirkpatrick, F. Bittinger, M. Wagner, H. Köhler, T.G. van Kooten, C.L. Klein, M. Otto, J. Eng. Med. 212, 75 (1998)
H.J. Steffen, J. Schmidt, A.G. Elipe, Surf. Int. Anal. 29, 386 (2000)
X. Xiao, J. Wang, J.A. Carlisle, B. Mech, R. Greenberg, R. Freda, M.S. Humayun, J. Weiland, O. Auciello, J. Biomed. Mater. 77B2, 273 (2006)
W. Yang, O. Auciello, J.E. Butler, W. Cai, J.A. Carlisle, J.E. Gerbi, D.M. Gruen, T. Knickerbocker, T. Lasseter, J.N. Russell, L.M. Smith, R.J. Hamers, Nat. Mater. 1, 253 (2002)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. Broyles and Prof. Shi for the providing the different cell lines, and Ms. Laleh Rabieirad of Purdue University for help with the platinum/titanium sputtering. We would like to thank Dr. Hongjun Zeng of Nanotechnology Core Facility of University of Illinois, Chicago for performing the PECVD of the silicon dioxide on the UNCD substrate. We would like to thank INAC program at Purdue for providing the funding to support this study. ANL researchers acknowledge support from the US Department of Energy, BES-Materials Sciences, under Contract DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajaj, P., Akin, D., Gupta, A. et al. Ultrananocrystalline diamond film as an optimal cell interface for biomedical applications. Biomed Microdevices 9, 787–794 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9090-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9090-2