Abstract
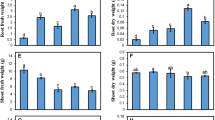
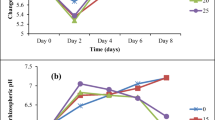
Hydroponics experiments were conducted to study the effects of sodium nitroprusside (SNP, a donor of NO) on lead toxicity in ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) seedlings. When the ryegrass seedlings were grown in a nutrient solution containing 500 μM Pb2+ for two weeks, the plant biomass as well as net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, chlorophyll and carotenoid content of leaves decreased. The Pb stress also induced the production of superoxide anion (O2 ·−) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), leading to malondialdehyde (MDA) accumulation. Furthermore, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) decreased in the Pb-treated seedlings, but the catalase (CAT) activity increased. Additionally, the content of Cu in shoots and the content of K, Mg, Fe, and Zn in both shoots and roots decreased, but the content of Ca in shoots and roots increased under the Pb stress. Moreover, Pb accumulated mostly in roots, whereas a small quantity was translocated to shoots. However, the addition of 50, 100, and 200 μM SNP into the solution containing Pb increased the chlorophyll content and net photosynthetic rate, reduced Pb-induced oxidative damages, improved antioxidant enzyme activities, and inhibited translocation of Pb from roots to shoots. In particular, 100 μM SNP had the best effect on promoting growth of the ryegrass seedlings under the Pb toxicity. However, the application of 400 μM SNP had no obvious alleviating effect on Pb toxicity in the ryegrass seedlings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
catalase
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- O2 ·− :
-
superoxide anion
- POD:
-
peroxidase
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SNP:
-
sodium nitroprusside
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
References
Ahamed, M., Javed Siddiqui, M.K.: Environmental lead toxicity and nutritional factors. — Clinical. Nutr. 26: 400–408, 2007.
Ali, N.A., Bernal, M.P., Ater, M.: Tolerance and bioaccumulation of copper in Phragmites australis and Zea mays. — Plant Soil 239: 103–111, 2002.
Alkhatib, R., Maruthavanan, J., Ghoshroy, S., Steiner, R., Sterling, T., Creamer, R.: Physiological and ultrastructural effects of lead on tobacco. — Biol. Plant. 56: 711–716, 2011.
Arienzo, M., Adamo, P., Cozzolino, V.: The potential of Lolium perenne for revegetation of contaminated soil from a metallurgical site. — Sci. total Environ. 319: 13–25, 2004.
Beligni, M.V., Lamattina, L.: Nitric oxide counteracts cytotoxic processes mediated by reactive oxygen species in plant tissues. — Planta 208: 337–344, 1999.
Burzynski, M.: The influence of lead and cadmium on the absorption and distribution of potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron in cucumber seedlings. — Acta Physiol. Plant. 9: 229–238, 1987.
Dong, Y.J., Xu, L.L., Wang, Q.H., Fan, Z.Y., Kong, J., Bai, X.Y.: Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on photosynthesis, antioxidative ability, and mineral element contents of perennial ryegrass under copper stress. — J. Plant. Interact. 1: 402–411, 2014.
Elstner, E.F., Heupel, A.: Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxyl ammonium-chloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. — Anal. Biochem. 70: 616–620, 1976.
Gopal, R., Rizvi, A.H.: Excess lead alters growth, metabolism and translocation of certain nutrients in radish. — Chemosphere 70: 1539–1544, 2008.
Heath, R.L., Packer, L.: Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. — Arch Biochem. Biophys. 125: 189–198, 1968.
Hermes, V.S., Dall’asta, P., Amaral, F.P., Anacleto, K.B., Arisi, A.C.M.: The regulation of transcription of genes related to oxidative stress and glutathione synthesis in Zea mays leaves by nitric oxide. — Biol. Plant. 57: 620–626, 2013.
Hannaway, D., Fransen, S., Cropper, J., Teel, M., Chaney, M., Griggs, T., Halse, R., Hart, J., Cheeke, P., Hansen, D., Klinger, R., Lane, W.: Perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). — A Pacific Northwest Extension Publication, PNW 503: 1–19, 1999.
Hsu, Y., Kao, C.: Cadmium toxicity is reduced by nitric oxide in rice leaves. — Plant Growth Regul. 42: 227–238, 2004.
Hu, K.D., Hu, L.Y., Li, Y.H., Zhang, F.Q., Zhang, H.: Protective roles of nitric oxide on germination and antioxidant metabolism in wheat seeds under copper stress. — Plant Growth Regul. 53: 173–183, 2007.
Islam, E., Liu, D., Li, T.Q., Yang, X.E., Jin, X.F., Mahmood, Q., Tian, S.K., Li, J.Y.: Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. — J. Hazard Mater. 154: 914–926, 2008.
Jiang, W.S., Liu, D.H.: Pb-induced cellular defense system in the root meristematic cells of Allium sativum L. — BMC Plant Biol. 10: 1–8, 2010.
Knudson, L.L., Tibbitts, T.W., Edwards, G.E.: Measurement of ozone injury by determination of leaf chlorophyll concentration. — Plant Physiol. 60: 606–608, 1977.
Kopittke, P.M., Asher, C.J., Blamey, F.P.C., Menzies, N.W.: Toxic effects of Pb2+ on the growth and mineral nutrition of signal grass (Brachiaria decumbens) and Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana). — Plant Soil 300: 127–136, 2007.
Kopyra, M., Gwozdz, E.A.: Nitric oxide stimulates seed germination and counteracts the inhibitory effect of heavy metals and salinity on root growth of Lupinus luteus. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 41: 1011–1017, 2003.
Lamattina, L., Garcia-Mata, C., Graziano, M., Pagnussat, G.: Nitric oxide: the versatility of an extensive signal molecule. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 54: 109–136, 2003.
Laspina, N.V., Groppa, M.D., Tomaro, M.L., Benavides, M.P.: Nitric oxide protects sunflower leaves against Cd-induced oxidative stress. — Plant Sci. 169: 323–330, 2005.
Liu, T., Liu, S., Guan, H., Ma, L., Chen, Z., Gu, H., Qu, L.J.: Transcriptional profiling of Arabidopsis seedlings in response to heavy metal lead. — Environ. exp. Bot. 67: 377–386, 2009.
Mihailovic, N., Drazic, G.: Incomplete alleviation of nickel toxicity in bean by nitric oxide supplementation. — Plant Soil Environ. 57: 396–401, 2011.
Mittler, R., Vanderauwera, S., Gollery, M., Breusegem, F.V.: Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. — Trends Plant Sci. 9: 490–498, 2004.
Nakano, Y., Asada, K.: Hydrogen peroxide scanvenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplast. — Plant Cell Physiol. 22: 867–880, 1981.
Nickel, R.S., Cunningham, B.A.: Improved peroxidase assay method using Ieuco 2,3,6-trichlcroindophenol and application to comparative measurements of peroxidase catalysis. — Anal. Biochem. 27: 292–299, 1969.
Orozco-Cardenas, M.L., Ryan, C.A.: Nitric oxide negatively modulates wound signaling in tomato plants. — Plant Physiol. 130: 487–493, 2002.
Pal, R., Banerjee, A., Kundu, R.: Responses of castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) to lead stress. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. 83: 643–650, 2013.
Palmgren, M.G., Harper, J.F.: Pumping with plant P-type ATPases. — J. exp. Bot. 50: 883–893, 1999.
Patra, H.L., Kar, M., Mishre, D.: Catalase activity in leaves and cotyledons during plant development and senescence. — Biochem. Pharmacol. 172: 385–390, 1978.
Phang, I.C., Leung, D.W.M., Taylor, H.H., Burritt, D.J.: The protective effect of sodium nitroprusside (SNP) treatment on Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings exposed to toxic level of Pb is not linked to avoidance of Pb uptake. — Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 74: 1310–1315, 2011a.
Phang, I.C., Leung, D.W.M., Taylor, H.H., Burritt, D.J.: Correlation of growth inhibition with accumulation of Pb in cell wall and changes in response to oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. — Plant Growth Regul. 64: 17–25, 2011b.
Reddy, A.M., Kumar, S.G., Jyonthsnakumari, G., Thimmanaik, S., Sudhakar, C.: Lead induced changes in antioxidant metabolism of horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.) and bengalgram (Cicer arietinum L.). — Chemosphere 60: 97–104, 2005.
Samardakiewicz, S., Woźny, A.: Cell division in Lemna minor roots treated with lead. — Aquat. Bot. 83: 289–295, 2005.
Saxena, I., Shekhawat, G.S.: Nitric oxide (NO) in alleviation of heavy metal induced phytotoxicity and its role in protein nitration. — Nitric Oxide 32: 13–20, 2013.
Stewart, R.C., Bewley, J.D.: Lipid peroxidation associated with accelerated aging of soybean axes. — Plant Physiol. 65: 245–248, 1980.
Tao, Y.M., Chen, Y.Z., Tan, T., Liu, X.C., Yang, D.L., Liang, S.C.: Comparison of antioxidant responses to cadmium and lead in Bruguiera gymnorrhiza seedlings. — Biol. Plant. 56: 149–152, 2012.
Tu, J., Shen, W.B., Xu, L.L.: Regulation of nitric oxide on the aging process of wheat leaves. — Acta. bot. sin. 45: 1055–1062, 2003.
Uchida, A., Jagendorf, A.T., Hibino, T., Takabe, T., Takabe, T.: Effects of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide on both salt and heat stress tolerance in rice. — Plant Sci. 163: 515–523, 2002.
Velikova, V., Yordanov, I., Edreva, A.: Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. Plant Sci. 151: 59–66, 2000.
Verma, S., Dubey, R.S.: Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. — Plant Sci. 164: 645–655, 2003.
Wang, Q.H., Liang, X., Dong, Y.J., Xu, L.L., Zhang, X.W., Hou, J., Fan, Z.Y.: Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on cadmium toxicity, element contents and antioxidative system in perennial ryegrass. — Plant Growth Regul. 69: 11–20, 2013a.
Wang, Q.H., Liang, X., Dong, Y.J., Xu, L.L., Zhang, X.W., Kong, J., Liu, S.: Effects of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on physiological characteristics of perennial ryegrass under cadmium stress. — J. Plant Growth Regul. 32: 721–731, 2013b.
Wink, D.A., Mitchell, J.B.: Chemical biology of nitric oxide: insights into regulatory, cytotoxic, and cytoprotective mechanisms of nitric oxide. — Free Radical Biol. Med. 25: 434–456, 1998.
Xiao, Q., Ru, Q.M., Wu, F.H., Huang, X., Pei, Z.M., Zheng, H.L.: Nitric oxide alleviates oxidative stress caused by lanthanum in rice leaves. — J. Rare Earths 25: 631–636, 2007.
Xiong, J., An, L.Y., Lu, H., Zhu, C.: Exogenous nitric oxide enhances cadmium tolerance of rice by increasing pectin and hemicellulose contents in root cell wall. — Planta 230: 755–765, 2009.
Xu, J., Wang, W.Y., Yin, H.X., Liu, X.J., Sun, H., Mi, Q.: Exogenous nitric oxide improves antioxidative capacity and reduces auxin degradation in roots of Medicago truncatula seedlings under cadmium stress. — Plant Soil 326: 321–330, 2010.
Yan, C.L., Hong, Y.T., Fu, S.Z., Fang, C.H., Lei, J.X., Shen, Q.: Effect of Cd, Pb stress on the activated oxygen scavenging system in tobacco leaves. — Chin. J. Geochem. 17: 372–378, 1998.
Zhang, Y., Han, X., Chen, X., Jin, H., Cui, X.: Exogenous nitric oxide on antioxidative system and ATPase activities from tomato seedlings under copper stress. — Scientia Hort. 123: 217–223, 2009.
Zhang, Z.Y., Wang, H.H., Wang, X.M., Bi, Y.R.: Nitric oxide enhances aluminum tolerance by affecting cell wall polysaccharides in rice roots. — Plant Cell Rep. 30: 1701–1711, 2011.
Zhou, Y.Q., Huang, S.Z., Yu, S.L., Gu, J.G., Zhao, J.Z., Han, Y.L., Fu, J.J.: The physiological response and sub-cellular localization of lead and cadmium in Iris pseudacorus L. — Ecotoxicology 19: 69–76, 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: The authors thank an English lecturer Mr. S. Craig (the Taishan University of China) and a lecturer X. Wang (the College of Foreign Languages, the Shandong Agricultural University) for their critical reading and revision of the manuscript. The authors also thank P. Yang (the College of Animal Science and Technology, the Shandong Agricultural University, China) for her supplying instruments and patient guidance. Special acknowledgements are given to the editors and reviewers. This research work was financially supported by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (ZR2013CM003) and a Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (J14LF08).
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X.Y., Dong, Y.J., Wang, Q.H. et al. Effects of lead and nitric oxide on photosynthesis, antioxidative ability, and mineral element content of perennial ryegrass. Biol Plant 59, 163–170 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0476-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0476-8