Abstract
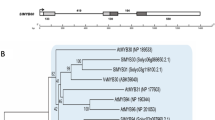
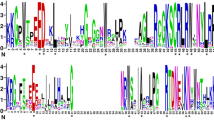
VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3 (VIN3) is a chromatin remodelling protein that is induced by low temperatures and is required for the vernalization response in Arabidopsis thaliana. VIN3 is one of the polycomb group (PcG) proteins, which mediates epigenetic repression of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) in A. thaliana. Here, we present cloning, characterization, and expression of a putative SlVIN3 gene in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by isolating cDNA clones corresponding to SlVIN3 gene using primers designed based on conserved sequences between PcG genes in A. thaliana and tomato. The SlVIN3 cDNAs were cloned into a pBS plasmid and sequenced. Both 5′ and 3′ RACE were generated and sequenced. The flcDNA of 2 823 bp length for the SlVIN3 gene was composed of 5’UTR (336 bp), ORF (2 217 bp), and 3’UTR (270 bp). The translated ORF encoded a polypeptide of 739 amino acids. Alignment of deduced amino acids indicates that there are highly conserved regions between tomato SlVIN3 predicted protein and plant VIN3 gene family members. Both unrooted phylogenetic trees constructed using the maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood methods indicate that there is a close relationship between SlVIN3 predicted protein and VIN3 protein of Vitis vinifera. The expression of SlVIN3 gene remained high during floral organ differentiation and growth and decreased when the fruit started to develop.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAC:
-
bacterial artificial chromosomes
- EST:
-
expressed sequence tag
- FLC:
-
flowering locus C
- FlcDNA:
-
full length cDNA
- FN3:
-
fibronectin type 3 domain
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
- PcG:
-
polycomb group
- PHD:
-
plant homeodomain
- RT-qPCR:
-
real time quantitative PCR
- SGN:
-
Solanaceae genomics network database
- SlVIN3 :
-
Solanum lycopersicum vernalization insensitive 3
- UTR:
-
untranslated region
- VID:
-
VIN3-interacting domain
- VIL:
-
vernalization insensitive like
- VIN 3:
-
VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3
- VRN:
-
vernalization
References
Bond, D.M., Dennis, E.S., Pogson, B.J., Finnegan, E.J.: Histone acetylation, VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3, FLOWERING LOCUS C, and the vernalization response. — Mol. Plants 2: 724–737, 2009a.
Bond, D.M., Wilson, I.W., Dennis, E.S., Pogson, B.J., Finnegan, E.J.: VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3 (VIN3) is required for the response of Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings exposed to low oxygen conditions. — Plant J. 59: 576–587, 2009b.
Chomczynski, P., Mackey, K.: Modification of the TRIZOL reagent procedure for isolation of RNA from polysaccharide-and proteoglycan-rich sources. — Biotechniques 19: 942–945, 1995.
Chouard, P.: Vernalization and its relations to dormancy. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 11: 191–238, 1960.
Dennis, E.S., Peacock, W.J.: Vernalization in cereals. — J. Biol. 8: 57, 2009.
Eck, R.V., Dayhoff, M.O.: Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure. — National Biomedical Research Foundation, Silver Spring 1966.
Felsenstein, J., Churchill, G.A.: A hidden Markov model approach to variation among sites in rate of evolution. — Mol. Biol. Evol. 13: 93–104, 1996.
Finnegan, E.J., Dennis, E.S.: Vernalization-induced trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 at FLC is not maintained in mitotically quiescent cells. — Curr. Biol. 17: 1978–1983, 2007.
Finnegan, E.J., Bond, D.M., Buzas, D.M., Goodrich, J., Helliwell, C.A., Tamada, Y., Yun, J., Amasino, R.M., Dennis, E.S.: Polycomb proteins regulate the quantitative induction of VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3 in response to low temperatures. — Plant J. cell. mol. Biol. 65: 382–391, 2011.
Finnegan, J.E., Kovac, K.A., Jaligot, E., Sheldon, C.C., Peacock, W.J., Dennis, E.S.: The downregulation of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) expression in plants with low levels of DNA methylation and by vernalization occurs by distinct mechanisms. — Plant J. 44: 420–432, 2005.
Fitch, W.M.: Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specified tree topology. — Syst. Zool. 20: 406–416, 1971.
Froger, A., Hall, J.E.: Transformation of plasmid DNA into E. coli using the heat shock method. — J. Vis. Exp. 6: 253, 2007.
Fu, D., Dunbar, M., Dubcovsky, J.: Wheat VIN3-like PHD finger genes are up-regulated by vernalization. — Mol. Genet. Genomics 277: 301–313, 2007.
Greb, T., Mylne, J.S., Crevillen, P., Geraldo, N., An, H., Gendall, A.R., Dean, C.: The PHD finger protein VRN5 functions in the epigenetic silencing of Arabidopsis thaliana FLC. — Curr. Biol. 17: 73–78, 2007.
Hennig, L., Derkacheva, M.: Diversity of polycomb group complexes in plants: same rules, different players? — Trends Genet. 25: 414–423, 2009.
Kim, D., Sung, S.: Coordination of the vernalization response through a VIN3 and FLC gene family regulatory network in Arabidopsis. — Plant Cell 25: 454–469, 2013.
Kim, D., Sung, S.: The plant homeo domain finger protein, VIN3-LIKE 2, is necessary for photoperiod-mediated epigenetic regulation of the floral repressor, MAF5. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 107: 17029–17034, 2010.
Knapp, S.: Floral diversity and evolution in the Solanaceae. — In: Cronk, Q.C.B, Bateman, R.M., Hawkins, J.A. (ed.): Developmental Genetics and Plant Evolution. Pp. 267–297. Taylor and Francis, London 2002.
Letunic, I., Doerks, T., Bork, P.: SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. — Nucl. Acids Res. 40: 302–305, 2012.
Livak, K.J., Schmittgen, T.D.: Analysis of relative gene expression using real time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. — Methods 25: 402–408, 2001.
Mellor, J.: It takes a PHD to read the histone code. — Cell 126: 22–24, 2006.
Michaels, S.D.: Flowering time regulation produces much fruit. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12: 75–80, 2009.
Michaels, S.D., Amasino, R.M.: FLOWERING LOCUS C encodes a novel MADS domain protein that acts as a repressor of flowering. — Plant Cell 11: 949–956, 1999.
Oliver, S.N., Finnegan, E.J., Dennis, E.S., Peacock, W.J., Trevaskis, B.: Vernalization-induced flowering in cereals is associated with changes in histone methylation at the VERNALIZATION1 gene. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 106: 8386–91, 2009.
Pankov, R., Yamada, K.M.: Fibronectin at a glance. — J. Cell Sci. 115: 3861–3863, 2002.
Potts, J.R., Campbell, I.D.: Fibronectin structure and assembly. — Curr. Opin. cell. Biol. 6: 648–655, 1994.
Ratcliffe, O.J., Kumimoto, R.W., Wong, B.J., Riechmann, J.L.: Analysis of the Arabidopsis MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING gene family: MAF2 prevents vernalization by short periods of cold. — Plant Cell 15: 1159–1169, 2003.
Sambrook, J., Russell, D.W.: Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. 3rd Ed. — Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor 2001.
Sanchez, R., Zhou, M.M.: The PHD finger: a versatile epigenome reader. — Trends biochem. Sci. 36: 364–372, 2011.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S., Coulson, A.R.: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 74: 5463–5467, 1977.
Schubert, D., Primavesi, L., Bishopp, A., Roberts, G., Doonan, J., Jenuwein, T., Goodrich, J.: Silencing by plant Polycombgroup genes requires dispersed trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27. — EMBO J. 25: 4638–4649, 2006.
Schubert, D., Clarenz, O., Goodrich, J.: Epigenetic control of plant development by Polycomb-group proteins. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 8: 553–561, 2005.
Schultz, J., Milpetz, F., Bork, P., Ponting, C.P.: SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 5857–5864, 1998.
Sheldon, C., Burn, E., Perez, P., Metzger, J., Edwards, A., Peacock, J., Dennis, S.: The FLF MADS box gene: a repressor of flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana regulated by vernalization and methylation. — Plant Cell 11: 445–458, 1999.
Sung, S., Amasino, R.M.: Vernalization in Arabidopsis thaliana is mediated by the PHD finger protein VIN3. — Nature 427: 159–164, 2004.
Sung, S., Schmitz, R.J., Amasino, R.M.: A PHD finger protein involved in both the vernalization and photoperiod pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Genes Dev. 20: 3244–3248, 2006.
Sung, S., Schmitz, R., Amasino, R.M.: The Role of VIN3-LIKE genes in environmentally induced epigenetic regulation of flowering. — Plant Signal. Behav. 2: 127–128, 2007.
Thompson, J.D., Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., Higgins, D.G.: The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. — Nucl. Acids Res. 25: 4876–4882, 1997.
Werner, J.D., Borevitz, J.O., Warthmann, N., Trainer, G.T., Ecker, J.R., Chory, J., Weigel, D.: Quantitative trait locus mapping and DNA array hybridization identify an FLM deletion as a cause for natural flowering-time variation. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 102: 2460–2465, 2005.
Wysocka, J., Swigut, T., Xiao, H., Milne, T., Kwon, S., Landry, J., Kauer, M., Tackett, A., Chait, B., Badenhorst, P., Wu, C., Allis, D.: A PHD finger of NURF couples histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation with chromatin remodelling. — Nature 442: 86–90, 2006.
Zhao, S.Q., Hu, J., Guo, L.B., Qian, Q., Xue, H.W.: Rice leaf inclination2, a VIN3-like protein, regulates leaf angle through modulating cell division of the collar. — Cell Res. 20: 935–947, 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: The authors are greatly indebted to Dr. K. Abo-Khabar, the director of the Biomolecular Research Department in King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre in Riyadh, and other staff members for giving the opportunity to work in the laboratory and for technical assistance with cDNA sequencing. This work was supported by a grant from the Center of Excellence in Biotechnology Research in King Saud University (No. CEBR-GSRP 01/2010).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almutairi, Z.M., Sadder, M.T. Cloning and expression profiling polycomb gene VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3 in tomato. Biol Plant 58, 419–426 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0421-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0421-x