Abstract
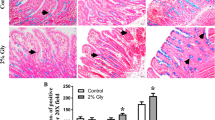
Lactoferrin is part of the immune system and multiple tissues including the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, liver, and lung contain receptors for lactoferrin. Lactoferrin has many functions, including antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and iron binding. Additionally, lactoferrin inhibits the migration of eosinophils, which are constitutively present in the GI tract, and increase during inflammation. Lactoferrin suppresses eosinophil infiltration into the lungs and eosinophil migration in -vitro. Healthy pigs have a large population of eosinophils in their small intestine and like humans, pigs have small intestinal lactoferrin receptors (LFR); thus, pigs were chosen to investigate the effects of consumption of milk containing recombinant human lactoferrin (rhLF-milk) on small intestinal eosinophils and expression of eosinophilic cytokines. In addition, LFR localization was analyzed in duodenum and circulating eosinophils to determine if the LFR could play a role in lactoferrin’s ability to inhibit eosinophil migration. In the duodenum there were significantly fewer eosinophils/unit area in pigs fed rhLF-milk compared to pigs fed control milk (p = 0.025); this was not seen in the ileum (p = 0.669). In the duodenum, no differences were observed in expression of the LFR, or any eosinophil migratory cytokines, and the amount of LFR protein was not different (p = 0.386). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) showed that within the duodenum the LFR localized on the brush border of villi, crypts, and within the lamina propria. Circulating eosinophils also contained LFRs, which may be a mechanism allowing lactoferrin to directly inhibit eosinophil migration.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baveye S, Elass E, Fernig DG, Blanquart C, Mazurier J, Legrand D (2000) Human lactoferrin interacts with soluble CD14 and inhibits expression of endothelial adhesion molecules, E-selectin and ICAM-1, induced by the CD14-lipopolysaccharide complex. Infect Immun 68:6519–6525
Bi BY, Leveugle B, Liu JL, Collard A, Coppe P, Roche AC, Nillesse N, Capron M, Spik G, Mazurier J (1994) Immunolocalization of the lactotransferrin receptor on the human T lymphoblastic cell line jurkat. Eur J Cell Biol 65:164–171
Bournazou I, Mackenzie KJ, Duffin R, Rossi AG, Gregory CD (2010) Inhibition of eosinophil migration by lactoferrin. Immunol Cell Biol 88:220–223
Brundige DR, Maga EA, Klasing KC, Murray JD (2008) Lysozyme transgenic goats’ milk influences gastrointestinal morphology in young pigs. J Nutr 138:921–926
Cooper CA, Brundige DR, Reh WA, Maga EA, Murray JD (2011) Lysozyme transgenic goats’ milk positively impacts intestinal cytokine expression and morphology. Transgenic Res 20:1235–1243
Cooper CA, Nelson KM, Maga EA, Murray JD (2012) Consumption of transgenic cows’ milk containing human lactoferrin results in beneficial changes in the gastrointestinal tract and systemic health of young pigs. Transgenic Res 22:571–578
Crouch SP, Slater KJ, Fletcher J (1992) Regulation of cytokine release from mononuclear cells by the iron-binding protein lactoferrin. Blood 80:235–240
Curran CS, Bertics PJ (2012) Lactoferrin regulates an axis involving CD11b and CD49d integrins and the chemokines MIP-1α and MCP-1 in GM-CSF-treated human primary eosinophils. J Interferon Cytokine Res 32:450–461
Dhennin-Duthille I, Masson M, Damiens E, Fillebeen C, Spik G, Mazurier J (2000) Lactoferrin upregulates the expression of CD4 antigen through the stimulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase in the human lymphoblastic T Jurkat cell line. J Cell Biochem 79:583–593
Elfinger M, Maucksch C, Rudolph C (2007) Characterization of lactoferrin as a targeting ligand for non-viral gene delivery to airway epithelial cells. Biomaterials 28:3448–3455
Harada E, Itoh Y, Sitizyo K, Takeuchi T, Araki Y, Kitagawa H (1999) Characteristic transport of lactoferrin from the intestinal lumen into the bile via the blood in piglets. Comp Biochem Physiol A: Mol Integr Physiol 124:321–327
Kanyshkova TG, Buneva VN, Nevinsky GA (2001) Lactoferrin and its biological functions. Biochemistry (Mosc) 66:1–7
Katsanos KH, Zinovieva E, Lambri E, Tsianos EV (2011) Eosinophilic-Crohn overlap colitis and review of the literature. J Crohns Colitis 5:256–261
Liao Y, Lopez V, Shafizadeh TB, Halsted CH, Lönnerdal B (2007) Cloning of a pig homologue of the human lactoferrin receptor: expression and localization during intestinal maturation in piglets. Comp Biochem Physiol A: Mol Integr Physiol 148:584–590
Maltby S, Wohlfarth C, Gold M, Zbytnuik L, Hughes MR, McNagny KM (2010) CD34 is required for infiltration of eosinophils into the colon and pathology associated with DSS-induced ulcerative colitis. Am J Pathol 177:1244–1254
Masterson JC, McNamee EN, Jedlicka P, Fillon S, Ruybal J, Hosford L, Rivera-Nieves J, Lee JJ, Furuta GT (2011) CCR3 blockade attenuates eosinophilic ileitis and associated remodeling. Am J Pathol 179:2302–2314
Nebermann L, Döhler JR, Perlick L (2001) Treatment of enterogenic endotoxinemia with lactoferrin in rats. Langenbecks Arch Surg 386:146–149
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:36
Samoszuk M (2006) Isolation of human eosinophils from peripheral blood using hypotonic lysis and centrifugation. Am J Hematol 81:552–553
Suzuki YA, Lopez V, Lönnerdal B (2005) Mammalian lactoferrin receptors: structure and function. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2560–2575
Svensson-Frej M (2011) Immunobiology of intestinal eosinophils - a dogma in the changing? J Innate Immun 3:565–576
Tsukahara T, Inoue R, Nakanishi N, Nakayama K, Matsubara N, Ushida K (2007) Evaluation of the low dose level of a heat-killed and dried cell preparation of Enterococcus faecalis to prevent porcine edema disease using experimental infection model with enterotoxcemic Escherichia coli in weaning pigs. J Vet Med Sci 69:103–109
Tung YT, Chen HL, Yen CC, Lee PY, Tsai HC, Lin MF, Chen CM (2013) Bovine lactoferrin inhibits lung cancer growth through suppression of both inflammation and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Dairy Sci 96:2095–2106
van der Does AM, Joosten SA, Vroomans E, Bogaards SJ, van Meijgaarden KE, Ottenhoff TH, van Dissel JT, Nibbering PH (2012) The antimicrobial peptide hLF1-11 drives monocyte-dendritic cell differentiation toward dendritic cells that promote antifungal responses and enhance Th17 polarization. J Innate Immun 4:284–292
Wakabayashi H, Koji Yamauchi K, Takase M (2006) Lactoferrin research, technology and applications. Int Dairy J 16:1241–1251
Wedemeyer J, Vosskuhl K (2008) Role of gastrointestinal eosinophils in inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal tumours. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 22:537–549
Winther L, Moseholm L, Reimert CM, Stahl-Skov P, Kaergaard-Poulsen L (1999) Basophil histamine release, IgE, eosinophil counts, ECP, and EPX are related to the severity of symptoms in seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy 54:436–445
Zimecki M, Artym J, Kocięba M, Kaleta-Kuratewicz K, Kruzel ML (2012) Lactoferrin restrains allergen-induced pleurisy in mice. Inflamm Res 61:1247–1255
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Pharming Group NV for providing the recombinant human lactoferrin milk and Doug Gisi and the UC-Davis Dairy Barn staff for providing control milk. We also thank Kent Parker and the UC-Davis Swine facility staff for assistance with pig rearing. We thank Danielle and Miranda George for help examining the histological slides, Samantha Lotti for help processing intestinal samples for qRT-PCR, Dr.Barbara Nitta-Oda for assistance with immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry, and Sean Owens (DVM) for his insight into porcine histopathology. This work was supported by a Jastro-Shields grant from the University of California, Davis.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, C., Nonnecke, E., Lönnerdal, B. et al. The lactoferrin receptor may mediate the reduction of eosinophils in the duodenum of pigs consuming milk containing recombinant human lactoferrin. Biometals 27, 1031–1038 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9778-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9778-8