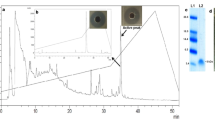
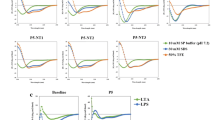
Abstract
The tri-hybrid peptide-LHP7 has the potent activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative as well as fungi, but its mechanism of action has remained elusive. The effluences of LHP7 on the Staphylococcus aureus cell membrane and targets of intracellular action were investigated. LHP7 exhibited an inhibitory effect on the S. aureus growth, similar to those achieved by plectasin, vancomycin and gramicidin. The membrane integrity studies confirmed that LHP7 disrupted the cell membrane, indicating a membrane permeabilizing killing action. A marginal decline in the intensity fluorescence indicated no significant depolarization of the membrane potential following LHP7 treatment. Furthermore, electron microscopy showed that cell shrinkage, cell wall thickening, cellular content leakage, and cell disruption were observed in the cells treated with LHP7. A gel retardation assay showed that LHP7 bound to the genomic DNA of S. aureus or plasmid DNA at a mass ratio of 2.5–10 (peptide/DNA). Circular dichroism indicated that LHP7 inserted into the groove of DNA. The cell cycle analysis showed that after the treatment with LHP7 for 30 and 60 min, the proportion of cells in I-phase increased from 8.71 to 12.09 % and from 8.71 to 15.68 %, indicating that LHP7 induced arrest of cells in the I-phase. These results would conduce to elucidate its underlying antibacterial mechanism.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amor KB, Breeuwer P, Verbaarschot P, Rombouts FM, Akkermans ADL, De Vos WM et al (2002) Multiparametric flow cytometry and cell sorting for the assessment of viable, injured, and dead Bifidobacterium cells during bile salt stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(11):5209–5216
Baev D, Li XS, Dong J, Keng P, Edgerton M (2002) Human salivary histatin 5 causes disordered volume regulation and cell cycle arrest in Candida albicans. Infect Immun 70:4777–4784
Boman HG, Agerberth B, Boman A (1993) Mechanisms of action on Escherichia coli of cecropin P1 and PR-39, two antibacterial peptides from pig intestine. Infect Immun 61:2978–2984
Brogden KA (2005) Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol 3:238–250
Cho J, Lee DG (2011) The antimicrobial peptide arenicin-1 promotes generation of reactive oxygen species and induction of apoptosis. BBA-Gen Subjects 1080:1246–1251
Choi H, Lee DG (2012) Antimicrobial peptide pleurocidin synergizes with antibiotics through hydroxyl radical formation and membrane damage, and exerts antibiofilm activity. BBA-Gen Subjects 1820:1831–1838
Dathe M, Wieprecht T (1999) Structural features of helical antimicrobial peptides: their potential to modulate activity on model membranes and biological cells. BBA-Biomembranes 1462(1–2):71–87
Freer E, Pizarro-Cerda J, Weintraub A, Bengoechea JA, Moriyon I, Hultenby K et al (1999) The outer membrane of Brucella ovis shows increased permeability to hydrophobic probes and is more susceptible to cationic peptides than are the outer membranes of mutant rough Brucella abortus strains. Infect Immun 67:6181–6186
Friedrich CL, Moyles D, Beveridge TJ, Hancock REW (2000) Antibacterial action of structurally diverse cationic peptides on Gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(8):2086–2092
Higgins M, Shockman GD, Ryter A (1971) Procaryotic cell division with respect to wall and membranes. Crit Rev Microbiol 1:29–72
Houston ME, Kondejewski LH, Karunaratne DN, Gough M, Fidai S, Hodges RS et al (1998) Influence of preformed α-helix and α-helix induction on the activity of cationic antimicrobial peptides. J Peptide Res 52:81–88
Hsu CH, Chen C, Jou ML, Lee AYL, Lin YC, Yu YP et al (2005) Structural and DNA-binding studies on the bovine antimicrobial peptide, indolicidin: evidence for multiple conformations involved in binding to membranes and DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 33(13):4053–4064
Hwang B, Hwang JS, Lee J, Lee DG (2011) The antimicrobial peptide, psacotheasin induces reactive oxygen species and triggers apoptosis in Candida albicans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 405(2):267–271
Kalfa VC, Jia HP, Kunkle RA, McCray PB Jr, Tack BF, Brogden KA (2001) Congeners of SMAP29 kill ovine pathogens and induce ultrastructural damage in bacterial cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:3256–3261
Keevil CW (2003) Rapid detection of biofilms and adherent pathogens using scanning confocal laser microscopy and episcopic differential interference contrast microscopy. Water Sci Technol 47:105–116
Koo Y, Kim JM, Park IY, Yu BJ, Jang SA, Kim K-S et al (2008) Structure-activity relations of parasin I, a histone H2A-derived antimicrobial peptide. Peptides 29(7):1102–1108
Lee CC, Sun Y, Qian S, Huang HW (2011) Transmembrane pores formed by human antimicrobial peptide LL-37. Biophys J 100:1688–1696
Li LR, Shi YH, Cheserek MJ, Su GF, Le GW (2013) Antibacterial activity and dual mechanisms of peptide analog derived from cell-penetrating peptide against Salmaonella typhimurium and Streptococcus pyogenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1711–1723
Lin GY, Lamb RA (2000) The paramyxovirus simian virus 5 V protein slows progression of the cell cycle. J Virol 74(19):9152–9166
Lorian V, Gemmell CG (1991) Effect of low antibiotic concentrations on bacteria: effects on ultrastructure, virulence, and susceptibility to immunodefenses. In: Lorian V (ed) Antibiotics in laboratory medicine, 3rd edn. The Williams & Wilkins Co, Baltimore, pp 493–555
Mozsolits H, Wirth H-J, Werkmeister J, Aguilar M-I (2001) Analysis of antimicrobial peptide interactions with hybrid bilayer membrane systems using surface plasmon resonance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1512:64–76
Murray AW (1992) Creative blocks: cell-cycle checkpoints and feedback control. Nature 359:599–604
Park CB, Kim HS, Kim SC (1998) Mechanism of action of the antimicrobial peptide buforin II: buforin II kills microorganisms by penetrating the cell membrane and inhibiting cellular functions. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 244:253–257
Park CB, Yi KS, Matsuzaki K, Kim MS, Kim SC (2000) Structure–activity analysis of buforin II, a histone H2A-derived antimicrobial peptide: the proline hinge is responsible for the cell-penetrating ability of buforin II. PNAS 97(15):8245–8250
Pavia KE, Spinella SA, Elmore DE (2012) Novel histone-derived antimicrobial peptides use different antimicrobial mechanisms. BBA-Biomembranes 1818:869–876
Peschel A, Otto M, Jack RW, Kalbacher H, Jung G, Gotz F (1999) Inactivation of the dlt operon in Staphylococcus aureus confers sensitivity to defensins, protegrins, and other antimicrobial peptides. J Biol Chem 274:8405–8410
Powers JPS, Hancock REW (2003) The relationship between peptide structure and antibacterial activity. Peptides 24:1681–1691
Powers JPS, Martin MM, Goosney DL, Hancock REW (2006) The antimicrobial peptide polyphemusin localizes to the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli following treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(4):1522–1524
Pushpanathan M, Gunasekaran P, Rajendhran J (2013) Mechanisms of the antifungal action of marine metagenome-derived peptide, MMGP1, against Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69316
Schneider T, Kruse T, Wimmer R, Wiedemann I, Sass V, Pag U et al (2010) Plectasin, a fungal defensin, targets the bacterial cell wall precursor Lipid II. Science 328:1168–1172
Scott MG, Gold MR, Hancock RE (1999) Interaction of cationic peptides with lipoteichoic acid and gram- positive bacteria. Infect Immun 67:6445–6453
Tanaka T, Knapp D, Nasmyth K (1997) Loading of an MCM protein onto DNA replication origins is regulated by Cdc6p and CDKs. Cell 90(4):649–660
Tian ZG, Dong TT, Teng D, Yang YL, Wang JH (2009a) Design and characterization of novel antimicrobial peptides based on structure parameters by computer-aided method. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1097–1103
Tian ZG, Dong TT, Yang YL, Teng D, Wang JH (2009b) Expression of antimicrobial peptide LH multimers in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:143–149
Torcato IM, Huang YH, Franquelim HG, Gaspar DD, Craik DJ, Castanho MARB et al (2013) The antimicrobial activity of Sub3 is dependent on membrane binding and cell-penetrating ability. ChemBioChem 14(15):2013–2022
Warnes SL, Keevil CW (2011) Mechanism of copper surface toxicity in vancomycin-resistant Enterococci following wet or dry surface contact. Appl Environ Microb 77(17):6049–6059
Wu XZ, Chang WQ, Cheng AX, Sun LM, Lou HX (2010) Plagiochin E, an antifungal active macrocyclic bis (bibenzyl), induced apoptosis in Candida albicans through a metacaspase-dependent apoptotic pathway. BBA-Gen Subjects 1880(4):439–447
Wu MH, Maier E, Benz R, Hancock REW (1999) Mechanism of interaction of different classes of cationic antimicrobial peptides with planar bilayers and with the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochem 38:7235–7242
Xi D, Teng D, Wang XM, Mao RY, Yang YL, Xiang WS et al (2013) Design, expression and characterization of the hybrid antimicrobial peptide LHP7, connected by a flexible linker, against Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. Process Biochem 48(3):453–461
Xiong YQ, Yeaman MR, Bayer AS (1999) In vitro antibacterial activities of platelet microbicidal protein and neutrophil defensin against Staphylococcus aureus are influenced by antibiotics differing in mechanism of action. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1111–1117
Yang YL, Teng D, Zhang J, Tian ZG, Wang JH (2011) Characterization of recombinant plectasin: solubility, antimicrobial activity and factors that affect its activity. Process Biochem 46:1050–1055
Yeaman MR, Bayer AS, Koo SP, Foss W, Sullam PM (1998) Platelet microbicidal proteins and neutrophil defensin disrupt the Staphylococcus aureus cytoplasmic membrane by distinct mechanisms of action. J Clin Invest 101:178–187
Yonezawa A, Kuwahara J, Fujii N, Sugiura Y (1992) Binding of tachyplesin I to DNA revealed by footprinting analysis: significant contribution of secondary structure to DNA binding and implication for biological action. Biochem 31:2998–3004
Zhang J, Yang YL, Teng D, Tian ZG, Wang SR, Wang JH (2011) Expression of plectasin in Pichia pastoris and its characterization as a new antimicrobial peptide against Staphyloccocus and Streptococcus. Protein Expr Purif 78:189–196
Zhu X, Dong N, Wang ZY, Ma Z, Zhang LC, Ma QQ et al (2014) Design of imperfectly amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced cell selectivity. Acta Biomater 10(1):244–257
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge technicians Ms Tong Zhao, Ms Jingnan Liang, Mr Chunli Li and Ms Xiaolan Zhang from the Core Facility at the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) for their technical support with the flow cytometric, TEM, SEM and the CLSM analyses. In addition, all other works of this paper was run in Gene Engineering Laboratory, Feed Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31372346 and No. 31302004), the Project of the National Support Program for Science and Technology in China (No. 2013BAD10B02 and No. 2011BAD26B02), the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest in China (No. 20140410) and the 2013 AMP Direction of National Innovation Program of Agric Sci & Technol in CAAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Di Xi and Xiumin Wang authors are contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, D., Wang, X., Teng, D. et al. Mechanism of action of the tri-hybrid antimicrobial peptide LHP7 from lactoferricin, HP and plectasin on Staphylococcus aureus . Biometals 27, 957–968 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9768-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9768-x