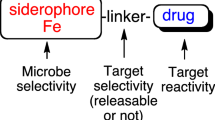
Abstract
Pathogenic microbes rapidly develop resistance to antibiotics. To keep ahead in the “microbial war”, extensive interdisciplinary research is needed. A primary cause of drug resistance is the overuse of antibiotics that can result in alteration of microbial permeability, alteration of drug target binding sites, induction of enzymes that destroy antibiotics (ie., beta-lactamase) and even induction of efflux mechanisms. A combination of chemical syntheses, microbiological and biochemical studies demonstrate that the known critical dependence of iron assimilation by microbes for growth and virulence can be exploited for the development of new approaches to antibiotic therapy. Iron recognition and active transport relies on the biosyntheses and use of microbe-selective iron-chelating compounds called siderophores. Our studies, and those of others, demonstrate that siderophores and analogs can be used for iron transport-mediated drug delivery (“Trojan Horse” antibiotics) and induction of iron limitation/starvation (Development of new agents to block iron assimilation). Recent extensions of the use of siderophores for the development of novel potent and selective anticancer agents are also described.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barclay R, Ratledge C (1983) Iron-binding compounds of Mycobacterium avium, M. intracellulare, M. scrofulaceum, and mycobactin-dependent M. paratuberculosis and M. avium. J Bacteriol 53:1138–1146
Benz G (1984) Albomycine, I. Enzymatische Spaltung der Desferriform der Albomycine. Liebigs Ann Chem 1399–1407. doi:10.1002/jlac.198419840802
Benz G, Schmidt D (1984) Albomycins, 4. Isolation and total synthesis of (N-5-acetyl-N-5-hydroxy-L-Ornithyl). Liebigs Ann Chem 1434–1440. doi:10.1002/jlac.198419840805
Benz G, Schroder T, Kurz J, Wunsche C, Karl W, Steffens G, Pfitzner J, Schmidt D (1982) Konstitution der Desferriform der Albomycine. Angew Chem Suppl 1322–1335
Benz G, Born L, Briedan M, Grosser R, Kurz J, Paulsen H, Sinnwell V, Weber B (1984) Albomycins, II. Absolute Konfiguration der Desferriform der Albomycine. Liebigs Ann Chem 1408–1423. doi:10.1002/jlac.198419840803
Bosne-David S, Bricard L, Ramiandrasoa FDéRoussent A, Kunesh G, Andremont A (1997) Evaluation of growth promotion and inhibition from Mycobactins and nonmycobacterial Siderophores (Desferrioxamine and FR160) in Mycobacterium aurum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:1837–1839
Braun V, Endriß F (2007) Energy-coupled outer membrane transport proteins and regulatory proteins. Biometals 20:219–231. doi:10.1007/s10534-006-9072-5
Braun V, Günthner K, Hantke K, Zimmermann L (1983) Intracellular activation of albomycin in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol 156:308–315
Brochu A, Brochu N, Nicas TI, Parr TR, Minnick AA, Dolence EK, McKee JA, Miller MJ, Lavoie MC, Malouin F (1992) Modes of action and inhibitory activities of new siderophore-b-lactam conjugates that use specific iron uptake pathways for entry into bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36:2166–2175
Brown KA, Ratledge C (1975) The effect of p-aminosalicylate on iron transport and assimilation in Mycobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 385:207–220
Budzikiewicz H (2004) Siderophores of the Pseudomonadaceae sensu stricto (fluorescent and non-Fluorescent Psedomonas spp.). Prog Chem Org Nat Prod 87:81–327
Bullen JJ (1987) In: Bullen DJ, Griffiths E (eds) Iron and infection: molecular, physiological and clinical aspects, Wiley, New York, pp 1–526
Carpenter JGD, Moore JW (1969) Synthesis of an analogue of mycobactin. J Chem Soc 1610–1611
Dhungana S, Miller MJ, Dong L, Ratledge C, Crumbliss AL (2003) Fe(III) chelation properties of an extracellular siderophore exochelin MN. J Am Chem Soc 125:7654–7663. doi:10.1021/ja029578u
Dolence EK, Minnick AA, Miller MJ (1990) N5-acetyl-N5-hydroxy-l-ornithine-derived siderophore-Carbacephlosporin β-Lactam conjugates: iron transport mediated drug delivery. J Med Chem 33:461–464. doi:10.1021/jm00164a001
Dolence EK, Lin C-E, Miller MJ (1991a) Synthesis and siderophore activi ty of albomycin-like peptides derived from N5-acetyl-N5-hydroxy-l-orinithine. J Med Chem 34:956–968. doi:10.1021/jm00107a013
Dolence EK, Minnick AA, Lin C-E, Miller MJ (1991b) Synthesis and siderophore and antibacterial activity of N5-acetyl-N5-hydroxy-l-ornithine-derived Siderophore-β-lactam conjugates: iron-transport-mediated drug delivery. J Med Chem 34:968–978. doi:10.1021/jm00107a014
Dong L, Roosenberg JM, Miller MJ (2002) The total synthesis of deferrisalmycin B. J Am Chem Soc 124:15001–15005. doi:10.1021/ja028386w
Fennell KA, Möllmann U, Miller MJ (2008) Syntheses and biological activity of amamistatin B and analogs. J Org Chem 73:1018–1024. doi:10.1021/jo7020532
Ferguson AD, Hofmann E, Coulton JW (1998) Siderophore-mediated Iron tansport: crystal structure of FhuA with bound lipopolysaccharide. Science 282:2215. doi:10.1126/science.282.5397.2215
Ferguson AD, Chakraborty R, Smith BS, Esser L, van der Helm D, Deisenhofer J (2002) Structural basis of gating by the outer membrane transporter FecA. Science 295:1715–1719. doi:10.1126/science.1067313
Ferreras JA, Ryu JS, Di Lello F, Tan DS, Quadri LEN (2005) Small molecule inhibition of siderophore biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Yersinia pestis. Nat Chem Biol 1:219–232. doi:10.1038/nchembio706
Floyd RA, Lewis CA (1983) Hydroxyl free-radical formation from hydrogen peroxide by ferrous iron nucleotide complexes. Biochemistry 22:2645–2649. doi:10.1021/bi00280a008
Ghosh A, Ghosh M, Niu C, Malouin F, Möllmann U, Miller MJ (1996) Iron transport-mediated drug delivery using mixed-ligand siderophore-β-lactam conjugates. Chem Biol 3:1011–1019. doi:10.1016/S1074-5521(96)90167-2
Graf E, Mahoney JR, Bryant RG, Eaton JW (1984) Iron-catalysed hydroxyl radical formation-stringent requirement for free iron coordination site. J Biol Chem 259:3620–3624
Guerinot ML (1994) Microbial iron transport. Annu Rev Microbiol 48:743. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.003523
Gutteridge JMC, Richmond R, Halliwell B (1979) Inhibition of iron-catalyzed formation of hydroxyl radicals for superoxide and lipid peroxidation by desferrioxamine. Biochem J 184:469–472
Hall RM, Ratledge C (1986) Distribution and application of mycobactins for the characterization of species within the genus Rhodococcus. J Gen Microbiol 132:853–856
Heinisch L, Wittmann S, Stoiber T, Berg A, Ankel-Fuchs D, Möllmann U (2002). J Med Chem 45:3032–3040. doi:10.1021/jm010546b
Hider RC (1984) Structure and bonding, vol 58. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p 25
Horwitz LD (1998) Method of treatment of atherosclerosis and vascular injury by the prevention of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. US Patent 5786326 and Chem Abstr 129:144856p
Horwitz LD, Sherman NA, Kong Y, Pike AW, Gobin J, Fennessey PV, Horwitz MA (1988) Lipophilic siderophores of Mycobacterium tuberculosis prevent cardiac reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5263–5268. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.9.5263
Horwitz LD, Horwitz MA, Gibson BW, Reeve J (1999) Use of exochelins in the preservation of organs for transplant. US Patent 5721209 and Chem Abst 130:47472y
Ikeda Y, Nonaka H, Furrmai T, Onaka H, Igarashi Y (2005) Nocardimicins A, B, C, D, E and F, siderophores with Muscarinic M3 reeptor Inhibiting activity from Nocardia sp. TP-A0674. J Nat Prod 68:1061–1065
Jaynes BH, Dirlam JP, Hecker SJ (1996) Antibacterial agents. In: Bristol JA (ed) Annual reports in medicinal chemistry, vol 31. Academic Press, London, pp 121–130
Katsu K, Kitoh K, Inoue M, Mitsuhashi S (1982) In vitro antibacterial activity of E-0702, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 22:181–185
Kong Y, Lesneefsky EJ, Ye J, Horwitz LD (1994) Prevention of lipid peroxidation does not prevent oxidant-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction. Am J Physiol 267:H2371–H2377
Levy SB (1992) The antibiotic paradox how miracle drugs are destroying the miraclej. Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–296
Macham LP, Ratledge C (1975) A new group of waster-soluble iron-binding compounds from Mycobacteria: the exochelins. J Gen Microbiol 89:379–382
Macham LP, Ratledge C, Nocton JC (1975) Extracellular iron acquisition by Mycobacteria: role of the exochelins and evidence against the participation of mycobactin. Infect Immun 12:1242–1251
Macham LP, Stephenson MC, Ratledge C (1977) Iron transport in Mycobacterium smegmatis: the isolation, purification and function of exochelin MS. J Gen Microbiol 101:41–49
McCready KA, Ratledge C (1977) Mycobactins from Mycobacterium avium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 7:288–289
Mckee JA, Sharma SK, Miller MJ (1991) Iron transport mediated drug delivery systems: synthesis and antibacterial activity of spermidine- and lysine-based siderophore-β-lactam conjugates. Bioconjug Chem 2:281–291
Messenger AJM, Hall RM, Ratledge C (1986) Iron uptake processes in Mycobacterium vaccae R877R, a Mycobacterium lacking mycobactin. J Gen Microbiol 132:845–852
Miethke M, Marahiel MA (2007) Siderophore-based iron acquisition and pathogen control. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 71:413–415
Miller MJ (1989) Syntheses and therapeutic potential of hydroxamic acid based siderophores and analogues. Chem Rev 89:1563–1579
Miller MJ, Malouin F (1993) Microbial iron chelators as drug delivery agents: rational design and synthesis of siderophore-drug conjugates. Acc Chem Res 26:241–249
Miller MJ, Malouin F (1994) Sjiderophore-mediated drug delivery: the design, synthesis, and study of siderophore-antibiotic and antifungal conjugates. In: Bergeron RJ, Brittenham GM (eds) The development of iron chelators for clinical use. CRC, Boca Ratonj, pp 275–306
Miller MJ, Malouin F, Dolence EK, Gasparski CM, Ghosh M, Guzzo PR, Lotz BT, McKee JA, Minnick A, Teng M (1993) Iron transport mediated drug delivery. In: Bently PH, Ponsford R (eds) Recent advances in the chemistry of anti-infective agents, vol 119. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 135–159
Minnick AA, McKee JA, Dolence EK, Miller MJ (1992) Iron transport-mediated antibacterial activity of and development of resistance to hydroxamate and catechol siderophore-carbacephalosporin conjugates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36:840–850
Moody DB, Yung DC, Cheng T-Y, Rosat J-P, Roura-mir C, O’Connor PB, Zajonc DM, Walz A, Miller MJ, Levery SB, Wilson IA, Costello CE, Brenner MB (2004) T cell activation by lipopeptide antigens. Science 303:527–531
Morrison NE (1995) Mycobacterium leprae iron nutrition: bacterrioferritin, mycobactin, Exochelin and inatracellular growth. Int J Lepr 63:86–91
Murakami Y, Kato S, Nakajima M, Matsuoka M, Kawai H, Shin-Ya K, Seto H (1996) Formobactin, a novel free radical scavenging and neuronal cell protecting substance from Nocardia sp. J Antibiot 49:839–845
Neilands JB, Valenta JR (1985) Iron-containing antibiotics. In: Sigel H (ed) Metal ions in biological systems, vol 19. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 313–333
Patel PV, Ratledge C (1973) Isolation of lipid-soluble compounds that bind ferric ions from Nocardia species. Biochem Soc Trans 1:886–888
Paulsen H, Briedan M, Benz G (1987) Branched and chain-extended sugars. synthesis of the deferri form of the oxygen analog of delta-1-albomycin. Liebigs Ann Chem 8:565–575
Payne SM (1988) Iron and virulence in the family Enterobacteriacae. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol 16:81
Quadri LEN (2007) Strategic paradigm shifts in the antimicrobial drug discovery process of the 21st century. Infectious disorders—drug targets 7:230–237
Quadri LEN, Sello J, Keating TA, Weinreb PH, Walsh CT (1998) Identification of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene cluster encoding the biosynthetic enzymes for assembly of the virulence-conferring siderophore mycobactin. Chem Biol 5:631–645
Ratledge C (1971) Transport of iron by mycobactin in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 45:856–862
Ratledge C (1984) Metabolism of iron and other metals by Mycobacteria. Microbiol Ser 15:603–627
Ratledge C (1987) In: Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB (eds) Iron transport in microbes, plants, and animals. VCH Press, Weinheim, FRG, pp 207
Ratledge C (2004) Iron, mycobacteria and tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 84:110–130
Ratledge C, Brown KA (1972) Inhibition of mycobactin formation in Mycobacterium smegmatis by p-aminosalicylate. Am Rev Resp Dis 106:774–776
Ratledge C, Marshall BJ (1972) Iron transport in Mycobacterum smegmatis: the role of mycobactin. Biochim Biophys Acta 279:58–74
Ratledge C, Patel PV (1976) The isolation, properties and taxonomic relevance of lipid-soluble, iron-binding compounds (the nocobactins) from Nocardia. J Gen Microbiol 93:141–152
Ratledge C, Snow GA (1974) Isolation and structure of nocobactin na, a lipid-soluble iron-binding compound from Nocardia asteroids. Biochem J 139:407–413
Ratledge C, Patel PV, Mundy J (1982) Iron transport in Mycobacterium smegmatis: the location of mycobactin by electron microscopy. J Gen Microbiol 128:1559–1565
Rogers HJ (1987) Bacterial iron transport as a target for antibacterial agents. In: Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB (eds) Iron transport in microbes, plants, and animals. VCH Press, Weinheim, pp 223–233
Roosenberg JM, Lin Y-M, Lu Y, Miller MJ (2000) Studies and syntheses of siderophore, microbial iron chelators, and analogs as potential drug delivery agents. Curr Med Chem 7(2):159–197
Sharman GJ, Williams DH, Ewing DF, Ratledge C (1995a) Isolation, purification and structure of exochelin MS, the extracellular siderophore from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Biochem J 305:187–196
Sharman GJ, Williams DH, Ewing DF, Ratledge C (1995b) Determination of the structure of exochelin MN, the extracellular Siderophore from Mycobacterium neoaurum. Chem & Biol 2:553–561
Snow GA (1970) Mycobactins: iron-chelating growth factors from Mycobacteria. Bacteriol Rev 34:99–125
Somu RV, Wilson DJ, Bennett EM, Boshoff H, Celia L, Beck BJ, Barry CEIII, Aldrich CC (2006) Antitubercular nucleosides that inhibit siderophore biosynthesis: SAR of the glycosyl domain. J Med Chem 49:7623–7635
Stephenson MC, Ratledge C (1978) The transport of iron from ferriexochelin by Mycobacterium smegmatis. Biochem Soc Trans 6:423–425
Stephenson MC, Ratledge C (1979) Iron transport in Mycobacterium smegmatis: uptake of iron from ferriexochelin. J Gen Microbiol 110:193–202
Suenaga K, Kokubo S, Shinohara C, Tsuji T, Uemura D (1999) Structures of Amamistatins A and B, novel growth inhibitors of human tumor cell lines from an Actinomycete. Tetrahedron Lett 40:1945–1948
Tsukamoto M, Murooka K, Nakajima S, Abe S, Suzuki H, Hirano K, Kondo H, Kojira K, Suda H (1997) BE-32030 A, B, C, D, and E, new antitumor substances produced by Nocardia sp. A32030. J Antibiot 50:815–821
Vergne AF, Walz AJ, Miller MJ (2000) Iron chelators from Mycobacteria (1954–1999) and potential therapeutic applications. Nat Prod Rep 17:99–116
Vertesy W, Aretz W, Fehlhaber H-W, Kogler H (1995) Salmycin A-D, Antibiotika aus Streptomyces violaceus, DSM 8286, mit Siderophore-Aminoglycosid-Struktur. Helv Chim Acta 78:46–60
Walling C (1975) Fenton’s reagent revisited. Acc Chem Res 8:125–131
Walz AJ, Miller MJ (2007) β-Lactams in synthesis: short syntheses of cobactin analogs. Tetrahedron Lett 48:5103–5105
Watanabe N-A, Nagasu T, Katsu K, Kitoh K (1987) E-0702, a new cephalosporin, is incorporated into Escherichia coli cells via the tonB-dependent iron transport system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31:497–504
Wheeler PR, Ratledge C (1994) Metabolism of M. tuberculosis. In: Bloom BR (ed) Tuberculosis pathogenesis, protection, and control. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, pp 353–385
Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB (1987) (eds) Iron transport in microbes, plants, and animals. VCH Press, Weinheim, FRG, pp 1–533
Zajonc DM, Crispin MDM, Bowden TA, Young DC, Cheng T-Y, Hu J, Costello CE, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Miller MJ, Brenner MB, Moody DB, Wilson IA (2005) Molecular mechanism of lipopeptide presentation by CD1a. Immunity 22:209–219
Zweier JL (1988) Measurement of superoxide-derived free-radicals in the reperfused heart-evidence for a free-radical mechanism of reperfusion injury. Biol Chem 263:1353–1357
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the NIH (AI054193) and the US Army Medical Research & Material Command (DAMD17-03-1-0206). The authors gratefully acknowledge Mrs. Patty Miller for performing MCF-7 and PC-3 cellular assays at Notre Dame. Baojie Wan at the University of Chicago’s Institute for Tuberculosis Research kindly provided M. tuberculosis inhibition data. The excellent technical assistance of Irmgard Heinemann and Uta Wohfield with microbial assays at the HKI is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, M.J., Zhu, H., Xu, Y. et al. Utilization of microbial iron assimilation processes for the development of new antibiotics and inspiration for the design of new anticancer agents. Biometals 22, 61–75 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9185-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9185-0