Abstract
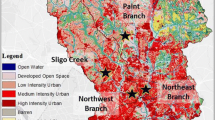
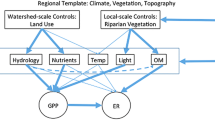
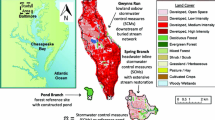
An urban watershed continuum framework hypothesizes that there are coupled changes in (1) carbon and nitrogen cycling, (2) groundwater-surface water interactions, and (3) ecosystem metabolism along broader hydrologic flowpaths. It expands our understanding of urban streams beyond a reach scale. We evaluated this framework by analyzing longitudinal patterns in: C and N concentrations and mass balances, groundwater-surface interactions, and stream metabolism and carbon quality from headwaters to larger order streams. 52 monitoring sites were sampled seasonally and monthly along the Gwynns Falls watershed, which drains 170 km2 of the Baltimore Long-Term Ecological Research site. Regarding our first hypothesis of coupled C and N cycles, there were significant inverse linear relationships between nitrate and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and nitrogen longitudinally (P < 0.05). Regarding our second hypothesis of coupled groundwater-surface water interactions, groundwater seepage and leaky piped infrastructure contributed significant inputs of water and N to stream reaches based on mass balance and chloride/fluoride tracer data. Regarding our third hypothesis of coupled ecosystem metabolism and carbon quality, stream metabolism increased downstream and showed potential to enhance DOC lability (e.g., ~4 times higher mean monthly primary production in urban streams than forest streams). DOC lability also increased with distance downstream and watershed urbanization based on protein and humic-like fractions, with major implications for ecosystem metabolism, biological oxygen demand, and CO2 production and alkalinity. Overall, our results showed significant in-stream retention and release (0–100 %) of watershed C and N loads over the scale of kilometers, seldom considered when evaluating monitoring, management, and restoration effectiveness. Given dynamic transport and retention across evolving spatial scales, there is a strong need to longitudinally and synoptically expand studies of hydrologic and biogeochemical processes beyond a stream reach scale along the urban watershed continuum.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander RB, Smith RA, Schwarz GE (2000) Effect of stream channel size on the delivery of nitrogen to the Gulf of Mexico. Nature 403:758–761
Arango CP, Tank JL, Johnson LT, Hamilton SK (2008) Assimilatory uptake rather than nitrification and denitrification determines nitrogen removal patterns in streams of varying land use. Limnol Oceanogr 53:2558–2572
Battin TJ, Butturini A, Sabater F (1999) Immobilization and metabolism of dissolved organic carbon by natural sediment biofilms in a Mediterranean and temperate stream. Aquat Microb Ecol 19:297–305
Battin TJ, Kaplan LA, Findlay S, Hopkinson CS, Marti E, Packman AI, Newbold JD, Sabater F (2008) Biophysical controls on organic carbon fluxes in fluvial networks. Nat Geosci 1:95–100
Bernot MJ, Dodds WK (2005) Nitrogen retention, removal, and saturation in lotic ecosystems. Ecosystems 8:442–453
Bhaskar AS, Welty C (2012) Water balances along an urban-to-rural gradient of Metropolitan Baltimore, 2001–2009. Environ Eng Geosci 18:37–50
Bronk D, Ward B (2005) Inorganic and organic nitrogen cycling in the Southern California Bight. Deep Sea Res Part I 52:2285–2300
Bronk D, See J, Bradley P, Killberg L (2007) DON as a source of bioavailable nitrogen for phytoplankton. Biogeosciences 4:283–296
Brookshire ENJ, Valett HM, Thomas SA, Webster JR (2005) Coupled cycling of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon in a forest stream. Ecology 86:2487–2496
Burns DA (1998) Retention of NO3− in an upland stream environment: a mass balance approach. Biogeochemistry 40:73–96
Claessens L, Tague CL, Groffman PM, Melack JM (2009) Longitudinal assessment of the effect of concentration on stream N uptake rates in an urbanizing watershed. Biogeochemistry 98:63–74. doi:10.1007/s10533-009-9376-y
Coble PG (1996) Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation emission matrix spectroscopy. Mar Chem 51:325–346
Cole JJ, Caraco NF (2001) Carbon in catchments: connecting terrestrial carbon losses with aquatic metabolism. Mar Freshw Res 52:101–110
Cole JJ, Prairie YT, Caraco NF, McDowell WH, Tranvik LJ, Striegl RG, Duarte CM, Kortelainen P, Downing JA, Middelburg JJ, Melack J (2007) Plumbing the global carbon cycle: integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 10:171–184
del Giorgio PA, Pace ML (2008) Relative independence of dissolved organic carbon transport and processing in a large temperate river: the Hudson River as both pipe and reactor. Limnol Oceanogr 53:185–197
Divers MT, Elliott EM, Bain DJ (2013) Constraining nitrogen inputs to urban streams from leaking sewers using inverse modeling: implications for dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) retention in urban environments. Environ Sci Technol 47:1816–1823
Duan SW, Kaushal SS (2013) Warming increases carbon-nutrient fluxes from sediments in streams across land use. Biogeosciences 10:1–15
Duff JH, Tesoriero AJ, Richardson WB, Strauss EA, Munn MD (2008) Whole-stream response to nitrate loading in three streams draining agricultural landscapes. J Environ Qual 37:1133–1144. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0187
Fellows CS, Valett HM, Dahm CN, Mulholland PJ, Thomas SA (2006) Coupling nutrient uptake and energy flow in headwater streams. Ecosystems 9:788–804
Galloway JN, Aber JD, Erisman JW, Seitzinger SP, Howarth RW, Cowling EB, Cosby BJ (2003) The nitrogen cascade. Bioscience 53:341–356
Gregory SV, Swanson FJ, McKee WA, Cummins KW (1991) An ecosystem perspective of riparian zones. Bioscience 41:540–551
Grimm NB, Sheibley RW, Crenshaw CL, Dahm CN, Roach WJ, Zeglin LH (2005) N retention and transformation in urban streams. J N Am Benthol Soc 24:626–642
Grimm NB, Faeth SH, Golubiewski NE, Redman CL, Wu JG, Bai XM, Briggs JM (2008) Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 319:756–760
Groffman PM, Law NL, Belt KT, Band LE, Fisher GT (2004) Nitrogen fluxes and retention in urban watershed ecosystems. Ecosystems 7:393–403. doi:10.1007/s10021-003-0039-x
Groffman PM, Dorsey AM, Mayer PM (2005) N processing within geomorphic structures in urban streams. J N Am Benthol Soc 24:613–625
Harmel R, Cooper R, Slade R, Haney RL, Arnold JG (2006) Cumulative uncertainty in measured streamflow and water quality data for small watersheds. Trans-Am Soc Agric Eng 49:689–701
Holtgrieve GW, Schindler DE, Branch TA, A’Mar ZT (2010) Simultaneous quantification of aquatic ecosystem metabolism and reaeration using a Bayesian statistical model of oxygen dynamics. Limnol Oceanogr 55:1047–1063
Howarth RW, Fruci JR, Sherman D (1991) Inputs of sediment and carbon to an estuarine ecosystem—influence of land-use. Ecol Appl 1:27–39
Hudson N, Baker A, Ward D, Reynlds DM, Brunsdon C, Carliell-Marquet C, Browning S (2008) Can fluorescence spectrometry be used as a surrogate for the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) test in water quality assessment? An example from South West England. Sci Total Environ 391:149–158
Johnson LT, Tank JL, Arango CP (2009) The effect of land use on dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen uptake in streams. Freshw Biol 54:2335–2350
Junk WJ (1999) The flood pulse concept of large rivers: learning from the tropics. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 115:261–280
Kalscheur KN, Penskar RR, Daley AD, Pechauer SM, Kelly JJ, Peterson CG, Gray KA (2012) Effects of anthropogenic inputs on the organic quality of urbanized streams. Water Res 46:2515–2524
Kaplan LA, Newbold JD, Van Horn DJ, Dow CL, Aufdenkampe AK, Jackson JK (2006) Organic matter transport in New York City drinking-water-supply watersheds. J N Am Benthol Soc 25:912–927
Kaplan LA, Wiegner TN, Newbold JD, Ostrom PH, Gandhi H (2008) Untangling the complex issue of dissolved organic carbon uptake: a stable isotope approach. Freshw Biol 53:855–864
Kaushal SS, Belt KT (2012) The urban watershed continuum: evolving spatial and temporal dimensions. Urban Ecosyst. doi:10.1007/s11252-012-0226-7
Kaushal SS, Binford MW (1999) Relationship between C:N ratios of lake sediments, organic matter sources, and historical deforestation in Lake Pleasant, Massachusetts, USA. J Paleolimnol 22:439–442
Kaushal SS, Lewis WM (2003) Patterns in the chemical fractionation of organic nitrogen in Rocky Mountain streams. Ecosystems 6:483–492. doi:10.1007/s10021-003-0175-3
Kaushal SS, Lewis WM (2005) Fate and transport of organic nitrogen in minimally disturbed montane streams of Colorado, USA. Biogeochemistry 74:303–321. doi:10.1007/s10533-004-4723-5
Kaushal SS, Groffman PM, Likens GE, Belt KT, Stack WP, Kelly VR, Band LE, Fisher GT (2005) Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:13517–13520. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506414102
Kaushal SS, Lewis WM Jr, McCutchan JH Jr (2006) Land use change and nitrogen enrichment of a rocky mountain watershed. Ecol Appl 16:299–312
Kaushal SS, Groffman PM, Band LE, Shields CA, Morgan RP, Palmer MA, Belt KT, Swan CM, Findlay SEG, Fisher GT (2008a) Interaction between urbanization and climate variability amplifies watershed nitrate export in Maryland. Environ Sci Technol 42:5872–5878. doi:10.1021/es800264f
Kaushal SS, Groffman PM, Mayer PM, Stritz E, Gold AJ (2008b) Effects of stream restoration on denitrification in an urbanizing watershed. Ecol Appl 18:789–804
Kaushal SS, Likens GE, Jaworski NA, Pace ML, Sides AM, Seekell D, Belt KT, Secor DH, Wingate RL (2010) Rising stream and river temperatures in the United States. Front Ecol Environ 8:461–466. doi:10.1890/090037
Kaushal SS, Groffman PM, Band LE, Elliott EM, Shields CA, Kendall C (2011) Tracking nonpoint source nitrogen pollution in human-impacted watersheds. Environ Sci Technol 45:8225–8232. doi:10.1021/es200779e
Kaushal SS, Likens GE, Utz R, Pace ML, Grese M, Yepsen M (2013) Increased river alkalinization in the Eastern US. Environ Sci Technol 47(18):10302–10311. doi:10.1021/es401046s
Kaushal SS, Mayer PM, Vidon PM, Smith RM, Pennino MJ, Duan SW, Newcomer TA, Welty C, Belt KT (2014) Land use and climate variability amplify carbon, nutrient, and contaminant pulses: a review with management implications. J Am Water Resour Assoc 43(1):41–59
Kemp WM, Boynton WR, Adoli JE, Boesch DF, Boicourt WC, Brush GS, Cornwell JC, Fisher TR, Gilbert PM, Hagy JD, Harding LW, Houde EJ, Kimmel DC, Miller WD, Newell RIE, Roman MR, Smith EM, Stevenson JC (2005) Eutrophication of Chesapeake Bay: historical trends and ecological interactions. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 303:1–29
Klocker CA, Kaushal SS, Groffman PM, Mayer PM, Morgan RP (2009) Nitrogen uptake and denitrification in restored and unrestored streams in urban Maryland, USA. Aquat Sci 71:411–424. doi:10.1007/s00027-009-0118-y
Mallin MA, McIver MR, Ensign SH, Cahoon LB (2004) Photosynthetic and heterotrophic impacts of nutrient loading to blackwater streams. Ecol Appl 14:823–838
Mallin MA, Johnson VL, Ensign SH, MacPherson TA (2006) Factors contributing to hypoxia in rivers, lakes, and streams. Limnol Oceanogr 51:690–701
Mayer PM, Groffman PM, Striz EA, Kaushal SS (2010) Nitrogen dynamics at the groundwater-surface water interface of a degraded urban stream. J Environ Qual 39:810–823. doi:10.2134/jeq2009.0012
Mulholland PJ, Marzolf ER, Webster JR, Hart DR, Hendricks SP (1997) Evidence that hyporheic zones increase heterotrophic metabolism and phosphorus uptake in forest streams. Limnol Oceanogr 42:443–451
Mulholland PJ, Helton AM, Poole GC, Hall RO, Hamilton SK, Peterson BL, Tank JL, Ashkenas LR, Cooper LW, Dahm CN, Dodds WK, Findlay SEG, Gregory SV, Grimm NB, Johnson SL, McDowell WH, Meyer JL, Valett HM, Webster JR, Arango CP, Beaulieu JL, Bernot MB, Burgin AJ, Crenshaw CL, Johnson LT, Niederlehner BR, O’Brien JM, Potter JD, Sheibley RW, Sobota DJ, Thomas SM (2008) Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 452:202–205. doi:10.1038/nature06686
Newcomer TA, Kaushal SS, Mayer PM, Shields AR, Canuel EA, Groffman PM, Gold AJ (2012) Influence of natural and novel organic carbon sources on denitrification in forest, degraded urban, and restored streams. Ecol Monogr 82:449–466
Newcomer TA, Kaushal SS, Mayer PM, Grese M Effects of stormwater management and stream restoration on watershed nitrogen retention. Biogeochemistry (In Review)
Paul MJ, Meyer JL (2001) Streams in the urban landscape. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:333–365
Pennino MJ, Kaushal SS, Beaulieu JJ, Mayer PM, Arango CP (2014) Effects of urban stream burial on nitrogen uptake and ecosystem metabolism: implications for watershed nitrogen and carbon fluxes. doi:10.1007/s10533-014-9958-1
Peterson BJ, Wollheim WM, Mulholland PJ, Webster JR, Meyer JL, Tank JL, Martí E, Bowden WB, Valett HM, Hershey AE, McDowell WH, Dodds WK, Hamilton SK, Gregory SV, Morrall DD (2001) Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 292:86–90
Petrone KC, Richards JS, Grierson PF (2009) Bioavailability and composition of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in a near coastal catchment of south-western Australia. Biogeochemistry 92:27–40. doi:10.1007/s10533-008-9238-z
Pribyl AL, Mccutchan JH, Lewis WM, Saunders JF III (2005) Whole-system estimation of denitrification in a plains river: a comparison of two methods. Biogeochemistry 73:439–455. doi:10.1007/s10533-004-0565-4
Raymond PA, Oh NH, Turner RE, Broussard W (2008) Anthropogenically enhanced fluxes of water and carbon from the Mississippi River. Nature 451:449–452
Roberts BJ, Mulholland PJ (2007) In-stream biotic control on nutrient biogeochemistry in a forested stream, West Fork of Walker Branch. J Geophys Res 112:G04002
Ryan RJ, Welty C, Larson PC (2010) Variation in surface water-groundwater exchange with land use in an urban stream. J Hydrol 392:1–11
Sauer VB, Meyer R (1992) Determination of error in individual discharge measurements. US Geological Survey Norcross, GA Open-File Report pp 92–144
Scott D, Harvey J, Alexander R, Schwarz G (2007) Dominance of organic nitrogen from headwater streams to large rivers across the conterminous United States. Global Biogeochem Cycles 21:GB1003
Seitzinger SP, Sanders RW (1997a) Contribution of dissolved organic nitrogen from rivers to estuarine eutrophication. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 159:1–12
Seitzinger SP, Sanders RW (1997b) Contribution of dissolved organic nitrogen from rivers to estuarine eutrophication. Marine Ecol-Progress Ser 159:1–12
Seitzinger SP, Sanders RW, Styles R (2002a) Bioavailability of DON from natural and anthropogenic sources to estuarine plankton. Limnol Oceanogr 47:353–366
Seitzinger SP, Styles RV, Boyer EW, Alexander RB, Billen G, Howarth RW, Mayer B, Van Breemen N (2002b) Nitrogen retention in rivers: model development and application to watersheds in the northeastern USA. Biogeochemistry 57:199–237
Shields CA, Band LE, Law N, Groffman PM, Kaushal SS, Savvas K, Fisher GT, Belt KT (2008) Streamflow distribution of non point source nitrogen export from urban-rural catchments in the Chesapeake Bay watershed. Water Resour Res 44:W09416. doi:10.1029/2007WR006360
Sickman JO, Zanoli MJ, Mann HL (2007) Effects of urbanization on organic carbon loads in the Sacramento River, California. Water Resour Res 43:W11422. doi:10.1029/2007WR005954
Sivirichi GM, Kaushal SS, Mayer PM, Welty C, Belt KT, Newcomer TA, Newcomb KD, Grese MM (2011) Longitudinal variability in streamwater chemistry and carbon and nitrogen fluxes in restored and degraded urban stream networks. J Environ Monit 13:288–303. doi:10.1039/c0em00055h
Sjodin AL, Lewis WM, Saunders JF III (1997) Denitrification as a component of the nitrogen budget for a large plains river. Biogeochemistry 39:327–342
Smith TE, Laursen AE, Deacon JR (2008) Nitrogen attenuation in the Connecticut River, northeastern USA; a comparison of mass balance and N2 production modeling approaches. Biogeochemistry 87:311–323. doi:10.1007/s10533-008-9186-7
Sobota DJ, Johnson SL, Gregory SV, Ashkenas LR (2012) A stable isotope tracer study of the influences of adjacent land use and riparian condition on fates of nitrate in streams. Ecosystems 15:1–17
Stanley EH, Powers SM, Lottig NR, Buffam I, Crawford JT (2012) Contemporary changes in dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in human-dominated rivers: is there a role for DOC management? Freshw Biol 57:26–42
Stepanauskas R, Jørgensen NOG, Eigaard OR, Žvikas A, Tranvik LJ, Leonardson L (2002) Summer inputs of riverine nutrients to the Baltic Sea: bioavailability and eutrophication relevance. Ecol Monogr 72:579–597
Stewart RJ, Wollheim WM, Gooseff MN, Briggs MA, Jacobs JM, Peterson BJ, Hopkinson CS (2011) Separation of river network-scale nitrogen removal among the main channel and two transient storage compartments. Water Resour Res 47:1. doi:10.1029/2010WR009896
Stolpe B, Guo LD, Shiller AM, Hassellov M (2010) Size and composition of colloidal organic matter and trace elements in the Mississippi River, Pearl River and the northern Gulf of Mexico, as characterized by flow field-flow fractionation. Mar Chem 118:119–128
Triska FJ, Duff JH, Sheibley RW, Jackman AP, Avanzino RJ (2007) Retention-transport through four hydrologically connected zones in a headwater catchment of the upper Mississippi River. J Am Water Resour Assoc 43:60–71
Vannote RL, Minshall GW, Cummins KW, Sedell JR, Cushing CE (1980) River continuum concept. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:130–137
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW, Likens GE, Matson PA, Schindler DW, Schlesinger WH, Tilman DG (1997) Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecol Appl 7:737–750
Walsh CJ, Roy AH, Feminella JW, Cottingham PD, Groffman PM, Morgan RP (2005) The urban stream syndrome: current knowledge and the search for a cure. J N Am Benthol Soc 24:706–723
Wiegner TN, Seitzinger SP (2004) Seasonal bioavailability of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen from pristine and polluted freshwater wetlands. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1703–1712
Wiegner TN, Seitzinger SP, Glibert PM, Bronk DA (2006) Bioavailability of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon from nine rivers in the eastern United States. Aquat Microb Ecol 43:277–287
Wollheim WM, Peterson BJ, Thomas SM, Hopkinson CS, Vörösmarty CJ (2008) Dynamics of N removal over annual time periods in a suburban river network. J Geophys Res 113:G03038
Acknowledgments
Peter Groffman, Melissa Grese, and Walter Boynton provided helpful comments on earlier drafts of this manuscript. Charley Driscoll and 3 anonymous reviewers also provided helpful comments and suggestions. This research was supported by NSF DBI 0640300, NSF CBET 1058502, NASA NNX11AM28G, Baltimore Ecosystem Study LTER project (NSF DEB-0423476 and DEB-1027188), Maryland Sea Grant Award SA7528085-U, Maryland Sea Grant Award NA05OAR4171042, Maryland Sea Grant Award R/WS-2, and EPA Chesapeake Bay Program. USGS, Baltimore City, and Baltimore County provided logistical support. We thank James McCutchan, Michael Wilberg, Elizabeth Price, Keaton Norquist and Ryan Woodland for helpful discussions. Dan Dillon, Carlos Lozano, Matthew Newcomb, Sarah Ghorpade and Jon Bearr assisted with field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: C. T. Driscoll.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushal, S.S., Delaney-Newcomb, K., Findlay, S.E.G. et al. Longitudinal patterns in carbon and nitrogen fluxes and stream metabolism along an urban watershed continuum. Biogeochemistry 121, 23–44 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-014-9979-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-014-9979-9