Abstract
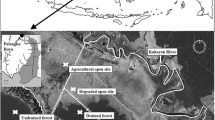
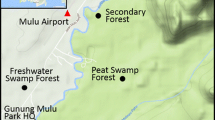
This study compares the organic chemistry of peat beneath one of last remaining pristine tropical peat forests in Southeast Asia with a neighbouring peat dome that has been deforested, but not intentionally drained, in the Belait district of Brunei Darussalam, Borneo. We characterized the solid and dissolved organic matter collected from the two domes, through a combination of methods including elemental analysis, phenolic content and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) investigation of solid peat, as well as optical characterisation (absorbance, fluorescence) of dissolved organic matter (DOM). The peat had a high content of lignin, consistent with its origin from the Shorea albida trees on the domes. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration in the pore water was significantly greater in the deforested site (79.9 ± 5.5 mg l−1) than the pristine site (62.2 ± 2.2 mg l−1). The dissolved organic matter was richer in nitrogen and phenolics in the deforested site. The optical properties (Fluorescence Index) indicated a modification of DOM cycling in the deforested site (enhanced decomposition of the peat and fresh litter). Comparison of the solid peat composition between the two sites also suggests effects of deforestation: sulphur, nitrogen and phenolic contents were higher in the deforested site. Taken together, these observations are consistent with peat enhanced decomposition in the deforested site, even without engineered drainage.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JAR (1983) The tropical peat swamps of Western Malaysia. Ecosyst World 4b:181–199
Anshari GZ, Afifudin M, Nuriman M, Gusmayanti E, Arianie L, Susana R, Nusantara RW, Sugardjito J, Rafiastanto A (2010) Drainage and land use impacts on changes in selected peat properties and peat degradation in West Kalimantan Province, Indonesia. Biogeosciences 7(11):3403–3419
Appel MH (1993) Phenolics in ecological interactions: the importance of oxidation. J Chem Ecol 19(7):1521–1552
Artz RRE, Chapman SJ, Robertson AHJ, Potts JM, Laggoun-Défarge F, Gogo S, Comont L, Disnar J-R, Francez A-J (2008) FTIR spectroscopy can be used as a screening tool for organic matter quality in regenerating cutover peatlands. Soil Biol Biochem 40(2):515–527
Asdak C, Jarvis PG, van Gardingen P, Fraser A (1998) Rainfall interception loss in unlogged and logged forest areas of Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. J Hydrol 206(3–4):237–244
Bala G, Caldeira K, Wickett M, Phillips TJ, Lobell DB, Delire C, Mirin A (2007) Combined climate and carbon-cycle effects of large-scale deforestation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(16):6550–6555
Baum A, Rixen T, Samiaji J (2007) Relevance of peat draining rivers in Central Sumatra for the riverine input of dissolved organic carbon into the ocean. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73(3–4):563–570
Calvert GD, Durig JR, Esterle JS (1991) Controls on the chemical variability of peat types in a domed peat deposit, Baram River Area, Sarawak, Malaysia. Int J Coal Geol 17(2):171–188
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation–emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37(24):5701–5710
Chin YP, Aiken G, Oloughlin E (1994) Molecular-weight, polydispersity and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 28(11):1853–1858
Clymo RS (1984) The limits to peat bog growth. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser 303(1117):605–654
Cocozza C, D’Orazio V, Miano TM, Shotyk W (2003) Characterization of solid and aqueous phases of a peat bog profile using molecular fluorescence spectroscopy, ESR and FT-IR, and comparison with physical properties. Org Geochem 34(1):49–60
Comont L, Laggoun-Défarge F, Disnar J-R (2006) Evolution of organic matter indicators in response to major environmental changes: the case of a formerly cut-over peat bog (Le Russey, Jura Mountains, France). Org Geochem 37(12):1736–1751
Couwenberg J, Dommain R, Joosten H (2010) Greenhouse gas fluxes from tropical peatlands in south-east Asia. Glob Change Biol 16(6):1715–1732
Durig DT, Esterle JS, Dickson TJ, Durig JR (1988) An investigation of the chemical variability of woody peat by FT-IR spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc 42(7):1239–1244
Fellman JB, D’Amore DV, Hood E, Boone RD (2008) Fluorescence characteristics and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in forest and wetland soils from coastal temperate watersheds in Southeast Alaska. Biogeochemistry 88(2):169–184
Freeman C, Ostle NJ, Fenner N, Kang H (2004) A regulatory role for phenol oxidase during decomposition in peatlands. Soil Biol Biochem 36(10):1663–1667
Glatzel S, Kalbitz K, Dalva M, Moore T (2003) Dissolved organic matter properties and their relationship to carbon dioxide efflux from restored peat bogs. Geoderma 113(3–4):397–411
Hergoualc’h Kl, Verchot LV (2011) Stocks and fluxes of carbon associated with land use change in southeast Asian tropical peatlands: a review. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 25:13
Hirano T, Segah H, Harada T, Limin S, June T, Hirata R, Osaki M (2007) Carbon dioxide balance of a tropical peat swamp forest in Kalimantan, Indonesia. Glob Change Biol 13(2):412–425
Hirano T, Jauhiainen J, Inoue T, Takahashi H (2009) Controls on the carbon balance of tropical peatlands. Ecosystems 12(6):873–887
Hoffmann WA, Schroeder W, Jackson RB (2003) Regional feedbacks among fire, climate, and tropical deforestation. J Geophys Res 108:11
Hooijer A (2005) Hydrology of tropical wetland forests: recent research results from Srawak peatswamps. In: Forest, water and people in the humid tropics. UNESCO international hydrology series. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press
Hooijer A, Silvius M, Wosten H, Page S (2006) Assessment of CO2 emissions from drained peatlands in SE Asia. Delft Hydraulics report Q3943. IEA, Delft
Hooijer A, Page S, Canadell JG, Silvius M, Kwadijk J, Wösten H, Jauhiainen J (2010) Current and future CO2 emissions from drained peatlands in southeast Asia. Biogeosciences 7:1505–1514
Ise T, Moorcroft PR (2006) The global-scale temperature and moisture dependencies of soil organic carbon decomposition: an analysis using a mechanistic decomposition model. Biogeochemistry 80(3):217–231
Jauhiainen J, Takahashi H, Heikkinen JEP, Martikainen PJ, Vasander H (2005) Carbon fluxes from a tropical peat swamp forest floor. Glob Change Biol 11(10):1788–1797
Jauhiainen J, Hooijer A, Page SE (2012) Carbon dioxide emissions from an Acacia plantation on peatland in Sumatra, Indonesia. Biogeosciences 9:617–630
Jennings E, Järvinen M, Allott N, Arvola L, Moore K, Naden P, Nic Aonghusa C, Nõges T, Weyhenmeyer GA (2009) Impacts of climate on the flux of dissolved organic carbon from catchments. In: George Glen (ed) The impact of climate change on European lakes. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 199–220
Jones TG, Freeman C, Lloyd A, Mills G (2009) Impacts of elevated atmospheric ozone on peatland below-ground DOC characteristics. Ecol Eng 35(6):971–977
Kalbitz K, Geyer W, Geyer S (1999) Spectroscopic properties of dissolved humic substances, a reflection of land use history in a fen area. Biogeochemistry 47(2):219–238
Kalbitz K, Geyer S, Gehre M (2000) Land use impacts on the isotopic signature (13C, 14C, 15 N) of water-soluble fulvic acids in a German Fen area. Soil Sci 165(9):681–758
Kobayashi S (1999) Initial phase of secondary succession in the exploited peat swamp forest (Shorea albida) at Sungai Damit, Belait in Brunei Darussalam. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on tropical peatlands, pp 205–214. ISTP, Bogor, 22–23 November 1999
Kreutzweiser DP, Hazlett PW, Gunn JM (2008) Logging impacts on the biogeochemistry of boreal forest soils and nutrient export to aquatic systems: a review. Environ Rev 16:157–179
Kuhry P, Vitt DH (1996) Fossil carbon/nitrogen ratios as a measure of peat decomposition. Ecology 77(1):271–275
Laiho R (2006) Decomposition in peatlands: reconciling seemingly contrasting results on the impacts of lowered water levels. Soil Biol Biochem 38(8):2011–2024
Maie N, Parish KJ, Watanabe A, Knicker H, Benner R, Abe T, Kaiser K, Jaffé R (2006) Chemical characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in an oligotrophic subtropical coastal ecosystem. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(17):4491–4506
Malcolm RL (1990) The uniqueness of humic substances in each of soil, stream and marine environments. Anal Chim Acta 232:19–30
Malmer N, Holm E (1984) Variation in the C/N-quotient of peat in relation to decomposition rate and age determination with 210 Pb. Oikos 43(2):171–182
McKnight DM, Boyer EW, Westerhoff PK, Doran PT, Kulbe T, Andersen DT (2001) Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol Oceanogr 46(1):38–48
Miettinen J, Shi C, Liew SC (2011) Deforestation rates in insular Southeast Asia between 2000 and 2010. Glob Change Biol 17(7):2261–2270
Minkkinen K, Byrne KA, Trettin C (2008) Climate impacts of peatland forestry. In: Peatland and climate change. IPS, pp 98–121
Miyamoto E, Matsuda S, Ando H, Kakuda K, Jong F, Watanabe A (2009) Effect of sago palm (Metroxylon Sagu Rottb.) Cultivation on the chemical properties of soil and water in tropical peat soil ecosystem. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 85(2):157–167
Moore TR, Clarkson BR (2007) Dissolved organic carbon in New Zealand peatlands. NZ J Mar Freshwat Res 41(1):137–141
Moore S, Gauci V, Evans CD, Page SE (2011) Fluvial organic carbon losses from a Bornean blackwater river. Biogeosciences 8:901–909
Nieminen M (2004) Export of dissolved organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus following clear-cutting of three norway spruce forest growing on drained peatlands in Southern Finland. Silva Fennica 38:2
Page SE, Siegert F, Rieley JO, Boehm HV, Jaya A, Limin S (2002) The amount of carbon released from peat and forest fires in Indonesia during 1997. Nature 420(6911):61–65. doi:10.1038/nature01131
Page SE, Rieley JO, Banks CJ (2011a) Global and regional importance of the tropical peatland carbon pool. Glob Change Biol 17:798–818. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02279.x
Page SE, Morisson R, Malins C, Hooijer A, Rieley JO, Jauhiainen J (2011b) Review of peat surface greenhouse gas emissions from oil palm plantations in Southeast Asia. ICCT white paper 15. International Council on Clean Transportation, Washington, DC
Porcal P, Koprivnjak J, Molot LA, Dillon PJ (2009) Humic substances—part 7: the biogeochemistry of dissolved organic carbon and its interactions with climate change. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16(6):714–726
Rieley, JO, Wüst RAJ, Jauhiainen J, Page SE, Wösten H, Hooijer A, Siegert J, Limin SH, Vasander H, Stahlhut H (2008) Tropical peatlands: carbon stores, carbon gas emissions and contribution to climate change processes. In: Atarck M (ed) Peatlands and carbon cycle, vol 6. International Peat Society, Quebec, p 224
Rixen T, Antje B, Thomas P, Wolfgang B, Joko S, Christine J (2008) The Siak, a tropical black water river in Central Sumatra on the verge of anoxia. Biogeochemistry 90:129–140. doi:10.1007/s10533-008-9239-y
Singleton VL, Joseph Rossi A (1965) Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic–phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic 16(3):144–158
van der Werf GR, Morton DC, DeFries RS, Olivier JGJ, Kasibhatla PS, Jackson RB, Collatz GJ, Randerson JT (2009) CO2 emissions from forest loss. Nat Geosci 2(11):737–738
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37(20):4702–4708
Williams CJ, Yavitt JB, Wieder RK, Cleavitt NL (1998) Cupric oxide oxidation products of northern peat and peat-forming plants. Can J Bot 76(1):51–62
Worrall F, Burt T (2005) Predicting the future DOC flux from upland peat catchments. J Hydrol 300(1–4):126–139
Yamashita Y, Scinto LJ, Maie N, Jaffé R (2010) Dissolved organic matter characteristics across a subtropical wetland’s landscape: application of optical properties in the assessment of environmental dynamics. Ecosystems 13:1006–1019
Yanai RD, Currie WS, Goodale CL (2003) Soil carbon dynamics after forest harvest: an ecosystem paradigm reconsidered. Ecosystems 6(3):197–212
Yule C, Gomez L (2009) Leaf litter decomposition in a tropical peat swamp forest in peninsular Malaysia. Wetl Ecol Manag 17(3):231–241
Zaccone C, D’Orazio V, Shotyk W, Miano TM (2009) Chemical and spectroscopic investigation of pore water and aqueous extracts of corresponding peat samples throughout a bog core (Jura Mountains, Switzerland). J Soils Sediments 9:443–456
Acknowledgments
This project is funded by the Singapore National Research Foundation (NRF) through the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART) Center for Environmental Sensing and Monitoring (CENSAM). Laure Gandois benefited from a SMART post doctoral fellowship. The authors warmly thank Richard Corlett for facilitating access to analytical facilities at NUS, Amy Chua, Kai Fu Ming, Shaliha Suut and Jang Ak.Eri from the Forestry Department in Brunei for their great help during field work, as well as Scott Fendorf, Guangchao Li and Doug Turner of the EM-I analytical center at Stanford University, and the staff of the Department of Chemistry at NUS for great help in samples analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandois, L., Cobb, A.R., Hei, I.C. et al. Impact of deforestation on solid and dissolved organic matter characteristics of tropical peat forests: implications for carbon release. Biogeochemistry 114, 183–199 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-012-9799-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-012-9799-8