Abstract
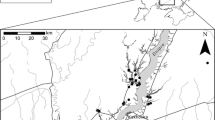
The region of Southern Transylvania in Romania contains large expanses of species-rich grassland and mixed farmland. Within these landscapes, clusters of small, steep-sided slumping hills support mosaics of herbaceous vegetation caused by the heterogeneity in temperature and water supply and maintained by mowing or grazing. These are of conservation interest not only for the high species density, but also the relict steppe-like vegetation types especially found on their south-facing slopes. Usually surrounded by more intensively used mesic grassland, these hills can be considered patches of species-rich grassland vegetation. We therefore surveyed the vascular plants in 10 m2 plots on the south- and north-facing slopes of 50 hills in 12 clusters in order to investigate the influence of their size and isolation on the species richness and composition of the vegetation. We found that larger hills had higher plot-scale species richness, a greater proportion of competitive species and a lower proportion of species of steppe-like vegetation, but only on their south-facing slopes where the conditions are more extreme. Both large and small hills should be considered as important habitats and potential sources of propagules for plant communities in the surrounding areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akeroyd JR, Page N (2011) Conservation of high nature value (HNV) grassland in a farmed landscape in Transylvania, Romania. Contrib Bot 46:57–71
Akeroyd JR, Sutcliffe LME, Popa R, Page N (2013) The LIFE project STIPA: saving Transylvania’s important pastoral agro-ecosystems (Romania). In: Baumbach H, Pfützenreuter S (eds) Steppenlebensräume Eur—Gefährdung, Erhaltungsmassnahmen und Schutz. Thüringer Ministerium für Landwirtschaft, Forsten, Umwelt und Naturschutz, Erfurt, pp 341–350
Barton K (2016) MuMIn: multi-model inference. R package version 1.15.6. http://cran.r-project.org/package=MuMIn. Accessed 22 Mar 2016
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker BM, Walker S (2014) lme4: linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4. R package version 1.1-7. http://cran.r-project.org/package=lme4. Accessed 19 Jan 2016
Becker T (2010) Explaining rarity of the dry grassland perennial Astragalus exscapus. Folia Geobot 45:303–321
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Concepción ED, Díaz M, Baquero RA (2008) Effects of landscape complexity on the ecological effectiveness of agri-environment schemes. Landscape Ecol 23:135–148. doi:10.1007/s10980-007-9150-2
Concepción ED, Díaz M, Kleijn D, Báldi A, Batáry P, Clough Y, Gabriel D, Herzog F, Holzschuh A, Knop E, Marshall EJP, Tscharntke T, Verhulst J (2012) Interactive effects of landscape context constrain the effectiveness of local agri-environmental management. J Appl Ecol 49:695–705. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2012.02131.x
Cremene C, Groza G, Rakosy L, Schileyko AA, Baur A, Erhardt A, Baur B (2005) Alterations of steppe-like grasslands in Eastern Europe: a threat to regional biodiversity hotspots. Conserv Biol 19:1606–1618. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1739.2005.00084.x
Deák B, Tóthmérész B, Valkó O, Sudnik-Wójcikowska B, Moysiyenko II, Bragina TM, Apostolova I, Dembicz I, Bykov NI, Török P (2016) Cultural monuments and nature conservation: a review of the role of kurgans in the conservation and restoration of steppe vegetation. Biodivers Conserv. doi:10.1007/s10531-016-1081-2
Dengler J, Becker T, Ruprecht E, Szabó A, Becker U, Beldean M, Bita-Nicolae C, Dolnik C, Goia I, Peyrat J, Sutcliffe LME, Turtureanu PD, Emin U (2012) Festuco-Brometea communities of the Transylvanian Plateau (Romania)—a preliminary overview on syntaxonomy, ecology, and biodiversity. Tuexenia 32:319–359
Ellenberg H, Weber HE, Düll R, Wirth V, Werner W, Paulißen D (1992) Zeigerwerte von Pflanzen in Mitteleuropa. Scr Geobot 18:1–258
Feurdean A, Marinova E, Nielsen AB, Liakka J, Veres D, Hutchinson SM, Braun M, Timar-Gabro A, Astalos C, Mosburgger V, Hickler T (2015) Origin of the forest steppe and exceptional grassland diversity in Transylvania (central-eastern Europe). J Biogeogr 42:951–963
Gerstner K, Dormann CF, Stein A, Manceur AM, Seppelt R (2014) Effects of land use on plant diversity—a global meta-analysis. J Appl Ecol 51:1690–1700. doi:10.1111/1365-2664.12329
Hahn A, Andres C, Becker T (2013) Vegetation changes in steppe-like grasslands in the “Badraer Lehde-Großer Eller” nature reserve in the Kyffhäuser Mountains (Thuringia) between 1993 and 2015. In: Baumbach H, Pfützenreuter S (eds) Steppenlebensräume Eur—Gefährdung, Erhaltungsmassnahmen und Schutz. Thüringer Ministerium für Landwirtschaft, Forsten, Umwelt und Naturschutz, Erfurt, pp 101–115
Hanski I, Ovaskainen O (2003) Metapopulation theory for fragmented landscapes. Theor Popul Biol 64:119–127. doi:10.1016/S0040-5809(03)00022-4
Helm A, Hanski I, Pärtel M (2006) Slow response of plant species richness to habitat loss and fragmentation. Ecol Lett 9:72–77
Janišová M, Michalcová D, Bacaro G, Ghisla A (2014) Landscape effects on diversity of semi-natural grasslands. Agric Ecosyst Environ 182:47–58. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2013.05.022
Jones A (2007) The challenge of high nature value grasslands conservation in Transylvania (Romania). Transylv Rev Syst Ecol Res 4:73–82
Jones A, Akeroyd JR, Beldean M, Turtureanu PD (2010) Characterization and conservation of xeric grasslands in the Târnava Mare area of Transylvania (Romania). Tuexenia 30:445–456
Kajtoch L, Cieślak E, Varga Z, Paul W, Mazur MA, Sramkó G, Kubisz D (2016) Phylogeographic patterns of steppe species in Eastern Central Europe: a review and the implications for conservation. Biodivers Conserv. doi:10.1007/s10531-016-1065-2
Klotz S, Kühn I, Durka W (2002) BIOLFLOR—Eine Datenbank zu biologisch-ökologischen Merkmalen der Gefäßpflanzen in Deutschland. Schriftenr Vegetationskd 38:1–344
Krauss J, Klein AM, Steffan-Dewenter I, Tscharntke T (2004) Effects of habitat area, isolation, and landscape diversity on plant species richness of calcareous grasslands. Biodivers Conserv 13:1427–1439. doi:10.1023/B:BIOC.0000021323.18165.58
Lindborg R, Helm A, Bommarco R, Heikkinen RK, Kühn I, Pykälä J, Pärtel M (2012) Effect of habitat area and isolation on plant trait distribution in European forests and grasslands. Ecography 35:356–363. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.2011.07286.x
MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1967) The theory of island biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Maloş C (2011) Corelaţii între geologia, procesele geomorfologice şi starea unor specii rare de plante din bazinul transilvaniei. Doctoral Thesis, Babes-Bolyai University, Cluj-Napoca
Matthies D, Bräuer I, Maibom W, Tscharntke T (2004) Population size and the risk of local extinction: empirical evidence from rare plants. Oikos 105:481–488. doi:10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.12800.x
Mikulcak F, Newig J, Milcu AI, Hartel TR, Fischer J (2013) Integrating rural development and biodiversity conservation in Central Romania. Environ Conserv 40:129–137. doi:10.1017/S0376892912000392
Öckinger E, Lindborg R, Sjödin NE, Bommarco R (2012) Landscape matrix modifies richness of plants and insects in grassland fragments. Ecography 35:259–267. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.2011.06870.x
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Wagner HH (2015) vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.2-1. http://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan. Accessed 19 Jan 2016
Pärtel M, Bruun HH, Sammul M (2005) Biodiversity in temperate European grasslands: origin and conservation. Grassl Sci Eur 10:1–14
Quantum GIS Development Team (2013) Quantum GIS geographic information system
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 19 Jan 2016
Reitalu T, Sykes MT, Johansson LJ, Lo M, Hall K, Vandewalle M, Prentice HC (2008) Small-scale plant species richness and evenness in semi-natural grasslands respond differently to habitat fragmentation. J Appl Ecol 142:899–908. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2008.12.020
Reitalu T, Purschke O, Johansson LJ, Hall K, Sykes MT, Prentice HC (2012) Responses of grassland species richness to local and landscape factors depend on spatial scale and habitat specialization. J Veg Sci 23:41–51. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2011.01334.x
Roleček J, Cornej II, Tokarjuk AI (2014) Understanding the extreme species richness of semi-dry grasslands in east-central Europe: a comparative approach. Preslia 86:13–34
Ruprecht E, Szabó A, Enyedi MZ, Dengler J (2009) Steppe-like grasslands in Transylvania (Romania): characterisation and influence of management on species diversity and composition. Tuexenia 29:353–368
Sanda V, Biţă-Nicolae CD, Barabaş N (2003) Flora cormofitelor spontane şi cultivate din România. Bacău, Romania
Sarbu A, Coldea G, Negrean G, Cristea V, Hanganu J, Veen P (2004) Grasslands of Romania. Final report on National Grasslands Inventory 2000–2003. University of Bucharest, Bucharest
Schmucki R, Reimark J, Lindborg R, Cousins SAO (2012) Landscape context and management regime structure plant diversity in grassland communities. J Ecol 100:1164–1173. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2012.01988.x
Schneider E (2013) Steppen und Trockenrasen im Hochland von Siebenbürgen (Rumänien) und ihre Bedeutung für das Natura 2000-Netzwerk. In: Baumbach H, Pfützenreuter S (eds) Steppenlebensräume Eur. Gefährdung, Erhaltungsmaßnahmen und Schutz. Thüringer Ministerium für Landwirtschaft, Forsten, Umwelt und Naturschutz (TMLFUN), Erfurt, pp 177–189
Schneider-Binder E (1996) Reliefbedingte Abfolge von Pflanzengesellschaften an Rutschungshügeln in Südesiebenbürgen (Harbachhochland). Stapfia 45:83–93
Schneider-Binder E (2007) Xerophilous and xero-mesophilous grasslands on slumping hills around the Saxon Villages Apold and Saschiz (Transylvania, Romania). Transylv Rev Syst Ecol Res 4:55–64
Speta E, Rákosy L (2010) Wildpflanzen Siebenbürgens. Plöchl, Freistadt
Sutcliffe LME, Akeroyd JR, Page N, Popa R (2015) Combining approaches to support high nature value Farmland in southern Transylvania, Romania. Hacquetia 14:53–63
Sutcliffe LME, Batáry P, Becker T, Orci KM, Leuschner C (2014) Both local and landscape factors determine plant and Orthoptera diversity in the semi-natural grasslands of Transylvania. Biodivers Conserv, Romania. doi:10.1007/s10531-014-0804-5
Valkó O, Török P, Deák B, Tóthmérész B (2014) Review: prospects and limitations of prescribed burning as a management tool in European grasslands. Basic Appl Ecol 15:26–33. doi:10.1016/j.baae.2013.11.002
Wagner HH, Rico Y, Lehnert H, Boehmer HJ (2012) Process-based long-term evaluation of an ecological network of calcareous grasslands connected by sheep herding. Ecography 36:374–382. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.2012.07463.x
Wilson JB, Peet RK, Dengler J, Pärtel M (2012) Plant species richness: the world records. J Veg Sci 23:796–802. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2012.01400.x
Zulka KP, Abensperg-Traun M, Milasowszky N, Bieringer G, Gereben-Krenn B, Holzinger W, Hölzler G, Rabitsch W, Reischütz A, Querner P, Sauberer N, Schmitzberger I, Willner W, Wrbka T, Zechmeister H (2014) Species richness in dry grassland patches of eastern Austria: a multi-taxon study on the role of local, landscape and habitat quality variables. Agric Ecosyst Environ 182:25–36. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2013.11.016
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jürgen Dengler and two anonymous reviewers for their detailed and constructive comments. We are very grateful to Fundatia ADEPT for financial and logistical support for this study, to Cristi Maloş for providing initial information about the movile, to John Akeroyd for help in the field and with species identification and discussions and Urs Kormann for statistical advice. We would also like to thank Prof. Joachim W. Kadereit for supporting the work of M.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jürgen Dengler.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sutcliffe, L.M.E., Germany, M., Becker, U. et al. How does size and isolation affect patches of steppe-like vegetation on slumping hills in Transylvania, Romania?. Biodivers Conserv 25, 2275–2288 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-016-1108-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-016-1108-8