Abstract
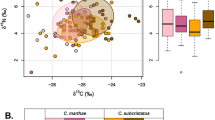
A trophic niche overlap in native and alien turtle species can lead to competitive interactions whereby allochthonous turtles may outcompete autochthonous individuals and eventually affect viability of natural populations. The European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) is an autochthonous species threatened by habitat encroachment and competition with the red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans). The latter is an invasive species introduced in Europe from midwestern United States as a pet and now widespread in the natural habitats of E. orbicularis. The extent of trophic competition between E. orbicularis and T. s. elegans in northern Italy was assessed by nitrogen and carbon stable isotope analysis (δ15N and δ13C). We used blood and claw samples in order to obtain information on diet components over a short- (3–4 months) and long-term (12 months) time frame, respectively. Analysis of claw samples showed a clear separation between the diets of adults of the two species, but suggested a trophic overlap among adult invaders and young autochthonous turtles. Blood samples, on the other hand, revealed a partial overlap between niches, indicating a short-term correspondence in diet composition between species. We found that, for specific life stages and times of the year, there is potential for trophic competition, which may have important consequences for the management and conservation of E. orbicularis in Italy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aresco MJ, James FC (2005) Ecological relationships of turtles in northern Florida lakes: a study of omnivory and the structure of a lake food web. Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Tallahassee
Bearhop S, Adams CE, Waldron S, Fuller RA, MacLeod H (2004) Determining trophic niche width: a novel approach using stable isotope analysis. J Anim Ecol 73:1007–1012
Boecklen WJ, Yarnes CT, Cook BA, James AC (2011) On the use of stable isotopes in trophic ecology. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 42:411–440
Bøhn T, Amundsen PA, Sparrow A (2008) Competitive exclusion after invasion? Biol Invasions 10:359–368
Bulté G, Blouin-Demers G (2008) Northern map turtles (Graptemys geographica) derive energy from the pelagic pathway through predation on zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Freshw Biol 53:497–508
Cadi A, Joly P (2003) Competition for basking places between the endangered European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis galloitalica) and the introduced red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans). Can J Zool 81:1392–1398
Cadi A, Joly P (2004) Impact of the introduction of the red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans) on survival rates of the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis). Biodivers Conserv 13:2511–2518
Carman VG, Botto F, Gaitan E, Albareda D, Campagna C, Mianzan H (2014) A jellyfish diet for the herbivorous green turtle Chelonia mydas in the temperate SW Atlantic. Mar Biol 161:339–349
Caut S, Guirlet E, Angulo E, Das K, Girondot M (2008) Isotope analysis reveals foraging area dichotomy for Atlantic leatherback turtles. PLoS ONE 3:e1845
Chaikoff IL, Entenman C (1946) The lipids of blood, liver, and egg yolk of the turtle. J Biol Chem 166:683–689
Cicek K, Ayaz D (2011) Food composition of the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) in lake Suluklu (Western Anatolia, Turkey). J Freshw Ecol 26:571–578
Crescente A, Sperone E, Paolillo G, Barnabò I, Brunelli E, Tripepi S (2014) Nesting ecology of the exotic Trachemys scripta elegans in an area of Southern Italy (Angitola Lake, Calabria). Amphibia-Reptilia 35:366–370
Dalerum F, Angerbjörn A (2005) Resolving temporal variation in vertebrate diets using naturally occurring stable isotopes. Oecologia 144:647–658
De Niro MJ, Epstein S (1978) Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:495–506
De Niro MJ, Epstein S (1981) Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:341–351
Ethier DM, Kyle CJ, Kyser TK, Nocera JJ (2010) Variability in the growth patterns of the cornified claw sheath among vertebrates: implications for using biogeochemistry to study animal movement. Can J Zool 88:1043–1051
Ferrari V, Lavezzi F (1995) I fontanili e i bodri in provincia di Cremona. Centro di documentazione ambientale, Provincia di Cremona. Primastudio, Cremona
Ficetola GF, De Bernardi F (2006) Is the European “pond” turtle Emys orbicularis strictly aquatic and carnivorous? Amphibia-Reptilia 27:445–447
Fry B (2006) Stable isotope ecology. Springer, Berlin
Gannes LZ, O’Brien DM, Martinez Del Rio C (1997) Stable isotopes in animal ecology: assumptions, caveats, and a call for more laboratory experiments. Ecology 78:1271–1276
Glen AS, Dickman CR (2008) Niche overlap between marsupial and eutherian carnivores: does competition threaten the endangered spotted-tailed quoll? J Appl Ecol 45:700–707
Hobson KA, Clark RG (1992) Assessing avian diets using stable isotopes II: factors influencing diet—tissue fractionation. Condor 94:189–197
Jackson AL, Inger R, Parnell AC, Bearhop S (2011) Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J Anim Ecol 80:595–602
Kalogianni E, Giakoumi S, Andriopoulou A, Chatzinikolaou Y (2014) Prey utilisation and trophic overlap between the non native mosquitofish and a native fish in two Mediterranean rivers. Mediterr Mar Sci 15:287–301
Krawchuk MA, Brooks RJ (1998) Basking behavior as a measure of reproductive cost and energy allocation in the painted turtle, Chrysemys picta. Herpetologica 54:112–121
Lara NRF, Marques TS, Montelo KM, de Ataìdes AG, Verdade LM, Malvasio A, de Camargo PB (2012) A trophic study of the sympatric Amazonian freshwater turtles Podocnemis unifilis and Podocnemis expansa (Testudines, Podocnemidae) using carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analyses. Can J Zool 90:1394–1401
Layman CA, Arrington DA, Montaña CG, Post DM (2007) Can stable isotope ratios provide for community—wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 88:42–48
Layman CA, Araujo MS, Boucek R, Harrison E, Jud ZR, Matich P, Hammerschlag-Peyer CM, Rosenblatt AE, Vaudo JJ, Yeager LA, Post DM, Bearhop S (2012) Applying stable isotopes to examine food-web structure: an overview of analytical tools. Biol Rev 87:545–562
Lebboroni M, Chelazzi G (1991) Activity patterns of Emys orbicularis L. (Chelonia Emydidae) in central Italy. Ethol Ecol Evol 3:257–268
Lefevre K, Brooks RJ (1995) Effects of sex and body size on basking behavior in a Northern population of the painted turtle, Chrysemys picta. Herpetologica 51:217–224
Lowe S, Browne M, Boudjelas S, De Poorter M (2000) 100 of the world’s worst invasive alien species. A selection from the global invasive species database. Invasive Species Specialist Group, Auckland
Magoulick DD, Piercey GL (2016) Trophic overlap between native and invasive stream crayfish. Hydrobiologia 766:237–246
Mancinelli G, Vizzini S, Mazzola A, Maci S, Basset A (2013) Cross-validation of δ15N and FishBase estimates of fish trophic position in a Mediterranean lagoon: the importance of the isotopic baseline. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 135:77–85
Matsuo R, Ochiai K (2009) Dietary overlap among two introduced and one native sympatric carnivore species, the raccoon, the masked palm civet, and the raccoon dog, in Chiba Prefecture, Japan. Mammal Study 34:187–194
McCutchan JH Jr, Lewis WM Jr, McGrath CK, McGrath CC (2003) Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. Oikos 102:378–390
Middelburg JJ (2014) Stable isotopes dissect aquatic food webs from the top to the bottom. Biogeosciences 11:2357–2371
Newsome SD, Martinez del Rio C, Bearhop S, Phillips DL (2007) A niche for isotopic ecology. Front Ecol Environ 5:429–436
Ottonello D, Salvidio S, Rosecchi E (2005) Feeding habits of the European pond terrapin Emys orbicularis in Camargue (Rhone delta, Southern France). Amphibia-Reptilia 26:562–565
Parnell AC, Inger R, Bearhop S, Jackson AL (2010) Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 5:e9672
Pearson SH, Avery HW, Kilham SS, Velinsky DJ, Spotila JR (2013) Stable isotopes of C and N reveal habitat dependent dietary overlap between native and introduced turtles Pseudemys rubriventris and Trachemys scripta. PLoS ONE 8:e62891
Pérez-Santigosa N, Florencio M, Hidalgo-Vila J, Diaz-Paniagua C (2011) Does the exotic invader turtle, Trachemys scripta elegans, compete for food with coexisting native turtles? Amphibia-Reptilia 32:167–175
Pérez-Santigosa N, Hidalgo-Vila J, Diaz-Paniagua C (2013) Comparing activity patterns and aquatic home range areas among exotic and native turtles in Southern Spain. Chelonian Conserv Biol 12:313–319
Peterson BJ, Fry B (1987) Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:293–320
Phillips RB, Winchell CS, Schmidt RH (2007) Dietary overlap of an alien and native carnivore on San Clemente Island, California. J Mammal 88:173–180
Pianka ER (1981) Competition and niche theory. In: May RM (ed) Theoretical ecology: principles and applications. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 167–196
Polo-Cavia N, Lòpez P, Martìn J (2010) Competitive interactions during basking between native and invasive freshwater turtle species. Biol Invasions 12:2141–2152
Polo-Cavia N, Lòpez P, Martìn J (2011) Aggressive interactions during feeding between native and invasive freshwater turtles. Biol Invasions 13:1387–1396
Post DM (2002) Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods and assumptions. Ecology 83:703–718
Post DM, Layman CA, Arrington DA, Takimoto G, Quattrochi J, Montaña CG (2007) Getting to the fat of the matter: models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope analyses. Oecologia 152:179–189
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Reich KJ, Bjorndal KA, Bolten AB (2007) The ‘lost years’ of green turtles: using stable isotopes to study cryptic lifestages. Biol Lett 3:712–714
Rollinat R (1934) La Vie des Reptiles de la France Centrale. Librairie Delagrave, Paris
Sampson SJ, Chick JH, Pegg MA (2009) Diet overlap among two Asian carp and three native fishes in backwater lakes on the Illinois and Mississippi rivers. Biol Invasions 11:483–496
Schwarcz HP (1991) Some theoretical aspects of isotope paleodiet studies. J Archaeol Sci 18:261–275
Seminoff JA, Jones TT, Eguchi T, Jones DR, Dutton PH (2006) Stable isotope discrimination (δ13C and δ15N) between soft tissues of the green sea turtle Chelonia mydas and its diet. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 308:271–278
Seminoff JA, Bjorndal KA, Bolten AB (2007) Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope discrimination and turnover in pond sliders Trachemys scripta: insights for trophic study of freshwater turtles. Copeia 2007:534–542
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (2012) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research. WH Freeman and Co, New York
Tieszen LL, Boutton TW, Tesdahl KG, Slade NA (1983) Fractionation and turnover of stable carbon isotopes in animal tissues: implication for δ13C analysis of diet. Oecologia 57:32–37
Vander Zanden MJ, Casselman JM, Rasmussen JB (1999) Stable isotope evidence for the food web consequences of species invasions in lakes. Nature 401:464–467
Vander Zanden HB, Bjorndal KA, Mustin W, Ponciano JM, Bolten AB (2012) Inherent variation in stable isotope values and discrimination factors in two life stages of green turtle. Physiol Biochem Zool 85:431–441
Vanderklift MA, Ponsard S (2003) Sources of variation in consumer-diet δ15N enrichment: a meta-analysis. Oecologia 136:169–182
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin
Zuffi MAL, Gariboldi A (1995) Sexual dimorphism in Italian populations of the European pond terrapin, Emys orbicularis. In: Llorente GA, Montori A, Santos X, Carretero MA (eds) Scientia Herpetologica. Asociación Herpetológica Española, Barcelona, pp 124–129
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank F. Frizzi for his support during the preparation of the manuscript. We are also grateful to one anonymous reviewer for his/her helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balzani, P., Vizzini, S., Santini, G. et al. Stable isotope analysis of trophic niche in two co-occurring native and invasive terrapins, Emys orbicularis and Trachemys scripta elegans . Biol Invasions 18, 3611–3621 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-016-1251-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-016-1251-x