Abstract
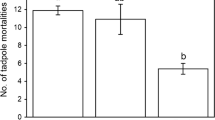
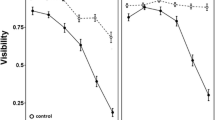
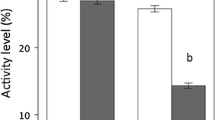
The introduction of non-native predators is thought to have important negative effects on native prey populations. The susceptibility of native prey to non-native or introduced predators may depend on their ability to respond appropriately to the presence of these non-native predators. We conducted a laboratory based behavioral experiment to examine the response of American toad (Bufo americanus) and bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) tadpoles to the presence of cues from the introduced mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis), a potential tadpole predator. Neither the American toad tadpoles nor the bullfrog tadpoles responded behaviorally to the presence of mosquitofish cues. If tadpoles are unable to respond to the presence of mosquitofish cues appropriately, then their ability to avoid predation by mosquitofish may be compromised and this may contribute to the impacts of mosquitofish on some tadpole populations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthington AH (1991) Ecological and genetic impacts of introduced and translocated freshwater fishes in Australia. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48:33–43
Baber MJ, Babbitt KJ (2003) The relative impacts of native and introduced predatory fish on a temporary wetland tadpole assemblage. Oecologia 136:298–295
Baber MJ, Babbitt KJ (2004) Influence of habitat complexity on predator–prey interactions between the fish (Gambusia holbrooki) and tadpoles of Hyla squirella and Gastrophryne carolinensis. Copeia 2004:173–177
Bence JR (1988) Indirect effects and biological control of mosquitoes by mosquitofish. J Appl Ecol 25:505–521
Blanco S, Romo S, Villena M-J (2004) Experimental study on the diet of mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) under different ecological conditions in a shallow lake. Inter Rev Hydrobiol 89:250–262
Burgett AA, Wright CD, Smith GR, Fortune DT, Johnson SL (2007) Impact of ammonium nitrate on wood frog (Rana sylvatica) tadpoles: effects on survivorship and behavior. Herpetol Conserv Biol 2:29–34
Chivers DP, Mirza RS (2001) Importance of predator diet cues in responses of larval wood frogs to fish and invertebrate predators. J Chem Ecol 27:45–51
Clavero M, García-Berthou E (2005) Invasive species are a leading cause of animal extinctions. Trends Ecol Evol 20:110
Courtenay WR Jr, Meffe GK (1989) Small fishes in strange places: a review of introduced poeciliids. In: Meffe GK, Snelson FF Jr (eds) Ecology and evolution of livebearing fishes (Poeciliidae). Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Cox JG, Lima SL (2006) Naiveté and an aquatic-terrestrial dichomtomy in the effects of introduced predators. Trends Ecol Evol 21:674–680
Denoël M, Dzukic G, Kalezic ML (2005) Effects of widespread fish introductions on paedomorphic newts in Europe. Conserv Biol 19:162–170
Eklöv P, Werner EE (2000) Multiple predator effects on size-dependent behavior and mortality of two species of anuran larvae. Oikos 88:250–258
Farley DG (1980) Prey selection by the mosquitofish Gambusia affinis in Fresno County rice fields. Proc Pap Ann Conf California Mosquito Vector Control Assoc 48:51–55
Feminella JW, Hawkins CP (1994) Tailed frog tadpoles differentially alter their feeding behavior in response to non-visual cues from four predators. J N Am Benthol Soc 13:310–320
Gamradt SC, Kats LB (1996) Effect of introduced crayfish and mosquitofish on California newts. Conserv Biol 10:1155–1162
García-Berthou E (1999) Food of introduced mosquitofish: Ontogenetic diet shift and prey selection. J Fish Biol 55:135–147
Goodsell JA, Kats LB (1999) Effect of introduced mosquitofish on Pacific treefrogs and the role of alternative prey. Conserv Biol 13:921–924
Grubb JC (1972) Differential predation by Gambusia affinis on the eggs of seven species of anuran amphibians. Am Midl Nat 88:102–108
Gunzburger MS (2005) Differential predation on tadpoles influences the potential effects of hybridization between Hyla cinerea and Hyla gratiosa. J Herpetol 39:682–687
Gunzburger MS, Travis J (2005) Critical literature review of the evidence for unpalatability of amphibian eggs and larvae. J Herpetol 39:547–571
Gurevitch J, Padilla DK (2004) Are invasive species a major cause of extinctions? Trends Ecol Evol 19:470–474
Hamer AJ, Lane SJ, Mahony MJ (2002a) Management of freshwater wetlands for the endangered green and golden bell frog (Litoria aurea): roles of habitat determinants and space. Biol Conserv 106:413–424
Hamer AJ, Lane SJ, Mahony MJ (2002b) The role of introduced mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) in excluding the native green and golden bell frog (Litoria aurea) from original habitats in south-eastern Australia. Oecologia 132:445–452
Hoare JM, Pledger S, Nelson NJ, Daugherty CH (2007) Avoiding aliens: behavioural plasticity in habitat use enables large, nocturnal geckos to survive Pacific rat invasions. Biol Conserv 136:510–519
Horat P, Semlitsch RD (1994) Effects of predation risk and hunger on the behaviour of two species of tadpoles. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 34:393–401
Howe E, Howe C, Lim R, Burchett M (1997) Impact of the introduced poeciliid Gambusia holbrooki (Girard, 1859) on the growth and reproduction of Pseudomugil signifer (Kner, 1865) in Australia. Mar Freshwater Res 48:425–434
Hurlbert SH, Mulla MS (1981) Impacts of mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) predation on plankton communities. Hydrobiologia 83:125–151
Hurlbert SH, Zedler J, Fairbanks D (1972) Ecosystem alteration by mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) predation. Science 175:639–641
Kats LB, Ferrer RP (2003) Alien predators and amphibian declines: review of two decades of science and the transition to conservation. Div Distrib 9:99–110
Kats LB, Petranka JW, Sih A (1988) Antipredator defenses and the persistence of amphibian larvae with fishes. Ecology 69:1865–1870
Komak S, Crossland MR (2000) An assessment of the introduced mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis holbrooki) as a predator of eggs, hatchlings and tadpoles of native and non-native anurans. Wildl Res 27:185–189
Laurila A (2000) Behavioural responses to predator chemical cues and local variation in antipredator performance in Rana temporaria tadpoles. Oikos 88:159–168
Laurila A, Pakkasmaa S, Merilä J (2006) Population divergence in growth rate and antipredator defences in Rana arvalis. Oecologia 147:585–595
Lawler SP (1989) Behavioural responses to predators and predation risk in four species of larval anurans. Anim Behav 38:1039–1047
Lawler SP, Dritz D, Strange T, Holyoak M (1999) Effects of introduced mosquitofish and bullfrogs on the threatened California red-legged frog. Conserv Biol 13:613–622
Lewis B, Goldingay R (1999) A preliminary assessment of the status of the green and golden bell frog in north-eastern NSW. In: Campbell A (ed) Declines and disappearances of Australian frogs. Environment Australia, Canberra
Lloyd LN, Arthington AH, Milton DA (1986) The mosquitofish—a valuable mosquito-control agent or a pest? In: Kitching RL (ed) The ecology of exotic animals and plants: some Australian case histories. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: Causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol Appl 10:689–710
Mahoney M (1999) Review of the declines and disappearances within the bell frog species group (Litoria aurea species group) in Australia. In: Campbell A (ed) Declines and disappearances of Australian frogs. Environment Australia, Canberra
Mandrillon A-L, Saglio P (2005) Prior exposure to conspecific chemical cues affects predator recognition in larval common toad (Bufo bufo). Arch für Hydrobiol 164:1–12
Margaritora FG, Ferrara O, Vagaggini D (2001) Predatory impact of the mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki Girard) on zooplanktonic populations in a pond at Tenuta di Castelporziano (Rome, central Italy). J Limnol 60:189–193
Marquis O, Saglio P, Neveu A (2004) Effects of predators and conspecific chemical cues on the swimming activity of Rana temporaria and Bufo bufo tadpoles. Arch für Hydrobiol 160:153–170
Meffe GK (1985) Predation and species replacement in American southwestern fishes: a case study. Southwest Nat 30:173–187
Mirza RS, Ferrari MCO, Kiesecker JM, Chivers DP (2006) Responses of American toad tadpoles to predation cues: Behavioural response thresholds, threat-sensitivity and acquired predation recognition. Behaviour 143:877–889
Morgan LA, Buttemer WA (1996) Predation by the non-native fish Gambusia holbrooki on small Litoria aurea and L. dentate tadpoles. Aust Zool 30:143–149
Parris MJ, Reese E, Storfer A (2006) Antipredator behavior of chytridiomycosis-infected northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens) tadpoles. Can J Zool 84:58–65
Petranka JW, Kats LB, Sih A (1987) Predator–prey interactions among fish and larval amphibians: use of chemical cues to detect predatory fish. Anim Behav 35:420–425
Pyke GH, White AW (1996) Habitat requirements for the green and golden bell frog Litoria aurea (Anura: Hylidae). Aust Zool 30:224–232
Pyke GH, White AW (2000) Factors influencing predation on eggs and tadpoles of the endangered Green and Golden Bell Frog Litoria aurea by the introduced Plague Minnow Gambusia holbrooki. Aust Zool 31:496–505
Pyke GH, White AW (2001) A review of the biology of the Greena nd Golden Bell Frog Litoria aurea. Aust Zool 31:563–598
Richardson JML (2001) A comparative study of activity levels in larval anurans and response to the presence of different predators. Behav Ecol 12:51–58
Salo P, Korpimäki E, Banks PB, Nordström M, Dickman CR (2007) Alien predators are more dangerous than native predators to prey populations. Proc R Soc 274B:1237–1243
Schoenherr AA (1981) The role of competition in the replacement of native fishes by introduced species. In: Naiman RJ, Soltz DL (eds) Fishes in North American deserts. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Semlitsch RD, Gavasso S (1992) Behavioural responses of Bufo bufo and Bufo calamita tadpoles to chemical cues of vertebrate and invertebrate predators. Ethol Ecol Evol 4:165–173
Soulé ME (1990) The onslaught of alien species, and other challenges in the coming decade. Conserv Biol 4:233–239
Stauffer RD, Semlitsch RD (1993) Effects of visual, chemical and tactile cues of fish on the behavioural responses of tadpoles. Anim Behav 46:355–364
Vitousek PM, D’Antonio CM, Loope LL, Rejmánek M, Westbrooks R (1996) Biological invasions as global environmental change. Am Sci 84:468–478
Vitousek PM, D’Antonio CM, Loope LL, Rejmánek M, Westbrooks R (1997) Introduced species: a significant component of human-caused global change. N Z J Ecol 21:1–16
Walton WE, Mulla MS (1991) Integrated control of Culex tarsalis larvae using Bacillus sphaericus and Gambusia affinis: Effects on mosquitoes and nontarget organisms in field mesocosms. Bull Soc Vect Ecol 16:203–221
Webb C, Joss J (1997) Does predation by the fish Gambusia holbrooki (Atheriniformes: Poeciliidae) contribute to declining frog populations? Aust Zool 30:316–324
White AW, Pyke GH (1996) Distribution and conservation status of the Green and Golden Bell Frog Litoria aurea in New South Wales. Aust Zool 30:177–189
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Denison University Research Foundation, and the Anderson Endowment of Denison University. This research was conducted under permit of the ODNR, and with approval from the Denison University IACUC (permit # 05-005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, G.R., Boyd, A., Dayer, C.B. et al. Behavioral responses of American toad and bullfrog tadpoles to the presence of cues from the invasive fish, Gambusia affinis . Biol Invasions 10, 743–748 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-007-9166-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-007-9166-1