Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of parthenolide on apoptosis and autophagy and to study the role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cervical cancer.
Results
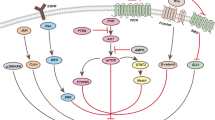
Parthenolide inhibits HeLa cell viability in a dose dependent-manner and was confirmed by MTT assay. Parthenolide (6 µM) induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis and autophagy by activation of caspase-3, upregulation of Bax, Beclin-1, ATG5, ATG3 and down-regulation of Bcl-2 and mTOR. Parthenolide also inhibits PI3K and Akt expression through activation of PTEN expression. Moreover, parthenolide induces generation of reactive oxygen species that leads to the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential.
Conclusion
Parthenolide induces apoptosis and autophagy-mediated growth inhibition in HeLa cells by suppressing the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and mitochondrial membrane depolarization and ROS generation. Parthenolide may be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of cervical cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arico S, Petiot A, Bauvy C, Dubbelhuis PF, Meijer AJ, Codogno P, Ogier-Deni E (2001) The tumor suppressor PTEN positively regulates macroautophagy by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J Biol Chem 276:35243–35246
D’Anneo A, Carlisi D, Lauricella M, Emanuele S, Di Fiore R, Vento R, Tesoriere G (2013a) Parthenolide induces caspase-independent and AIF-mediated cell death in human osteosarcoma and melanoma cells. J Cell Physiol 228:952–967
D’Anneo A, Carlisi D, Lauricella M, Puleio R, Martinez R, Di Bella S, Di Marco P, Emanuele S, Di Fiore R, Guercio A, Vento R, Tesoriere G (2013b) Parthenolide generates reactive oxygen species and autophagy in MDA-MB231 cells. A soluble parthenolide analogue inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in a xenograft model of breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 4:e891
Di Cristofano A, Pesce B, Cordon-Cardo C, Pandolfi PP (1998) Pten is essential for embryonic development and tumour suppression. Nat Genet 19:348–355
Dong M, Zhou JP, Zhang H, Guo KJ, Tian YL, Dong YT (2005) Clinicopathological significance of Bcl-2 and Bax protein expression in human pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 11:2744–2747
Ellenson LH, Wu TC (2004) Focus on endometrial and cervical cancer. Cancer Cell 5:533–538
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127:2893–2917
Janku F, McConkey DJ, Hong DS, Kurzrock R (2011) Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:528–539
Karlidag T, Cobanoglu B, Keles E, Alpay HC, Ozercan I, Kaygusuz I, Yalcin S, Sakallioglu O (2007) Expression of Bax, p53, and p27/kip in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma with or without cervical nodal metastasis. Am J Otolaryngol 28:31–36
Kepp O, Galluzzi L, Lipinski M, Yuan J, Kroemer G (2011) Cell death assays for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:221–237
Kim JH, Liu L, Lee SO, Kim YT, You KR, Kim DG (2005) Susceptibility of cholangiocarcinoma cells to parthenolide-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 65:6312–6320
Kim IH, Kim SW, Kim SH, Lee SO, Lee ST, Kim DG, Lee MJ, Park WH (2012) Parthenolide-induced apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells and anti-fibrotic effects in an in vivo rat model. Exp Mol Med 44:448–456
Knight DW (1995) Feverfew: chemistry and biological activity. Nat Prod Rep 12:271–276
Kwok BH, Koh B, Ndubuisi MI, Elofsson M, Crews CM (2001) The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide from the medical herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits Ikappa B kinase. Chem Biol 8:759–766
Liu JW, Cai MX, Xin Y, Wu QS, Ma J, Yang P, Xie HY, Huang DS (2010) Parthenolide induces proliferation inhibition and apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:108
Mathema VB, Koh YS, Thakuri BC, Sillanpaa M (2012) Parthenolide, a sesquiterpene lactone, expresses multiple anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities. Inflammation 35:560–565
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y (2011) The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:107–132
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ (2004) Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 306:990–995
Suen DF, Norris KL, Youle RK (2008) Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev 22:1577–1590
Sun Y, St Clair DK, Xu Y, Crooks PA, St Clair WH (2010) A NADPH oxidase- dependent redox signaling pathway mediates the selective radio sensitization effect of parthenolide in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 70:2880–2890
Sun Y, Zou M, Hu C, Qin Y, Song X, Lu N, Guo Q (2013) Wogonoside induces autophagy in MDA-MB-231 cells by regulating MAPK-mTOR pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 51:53–60
Wang W, Adachi M, Zhang R, Zhou J, Zhu D (2009) A novel combination therapy with arsenic trioxide and parthenolide against pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas 38:114–123
Won YK, Ong CN, Shi X, Shen HM (2004) Chemopreventive activity of parthenolide against UVB-induced skin cancer and its mechanisms. Carcinogenesis 25:1449–1458
Zhang S, Ong CN, Shen HM (2004) Critical roles of intracellular thiols and calcium in parthenolide-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett 208:143–153
Zhao X, Liu X, Su L (2014) Parthenolide induces apoptosis via TNFRSF10B and PMAIP1 pathways in human lung cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 33:3
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Bharathidasan University for providing financial assistance to Mr. Jeyamohan Sridharan through University Research Fellowship (URF). We also thank DST-FIST programme for the instrument facility. The authors are grateful to Dr. Sathees C Ragavan, Indian Institute of Science, Karnataka and Prof. G. Sudhandiran, University of Madras, Tamil Nadu, India for providing the antibodies.
Supporting Information
Supplementary Table 1—Quantitative real-time PCR primers used in this study.
Supplementary Fig. 1—Chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation in HeLa cells.
Supplementary Fig. 2—Determination of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm).
Supplementary Fig. 3—Parthenolide induced ROS generation in HeLa cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeyamohan, S., Moorthy, R.K., Kannan, M.K. et al. Parthenolide induces apoptosis and autophagy through the suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cervical cancer. Biotechnol Lett 38, 1251–1260 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2102-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2102-7