Abstract
Objectives
To modify two main N-glycosylation residues of cellobiohydrolase I from Trichoderma reesei by site-directed mutagenesis for decreasing the extent of glycosylation and exploring possible effects on its properties.
Results
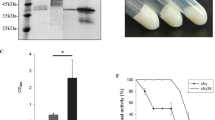
Asparagine 45 and 64 residues were mutated to alanine to make single/double mutants and expressed in P. pastoris. Decreasing N-glycosylation of the recombinant CBH I resulted in an increased affinity of the enzyme for carboxymethylcellulose and also improved the Kcat/Km while the specific activity was decreased. Also, the enzymes were stable up to 80 °C. There was no significant change of the optimum pH and temperature by decrease of glycosylation in the mutated enzymes in comparison to the wild-type at constant incubation time of assay.
Conclusion
Post-translational glycan-modification of CBH I in P. pastoris has different impacts on the properties of the secreted enzymes. Substrate affinity and catalytic efficiency were improved significantly while the activity and high temperature stability were negatively affected.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer H, Teeri TT, Koivula A (2000) Characterization of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase Cel7A secreted from Pichia pastoris using two different promoters. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:486–494
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Godbole S et al (1999) Cloning and expression of Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase I in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Progr 15:828–833
Guedon E, Desvaux M, Petitdemange H (2002) Improvement of cellulolytic properties of Clostridium cellulolyticum by metabolic engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:53–58
Harrison MJ, Nouwens AS, Jardine DR, Zachara NE, Gooley AA, Nevalainen H, Packer NH (1998) Modified glycosylation of cellobiohydrolase I from a high cellulase-producing mutant strain of Trichoderma reesei. Eur J Biochem 256:119–127
Hollenberg CP, Gellissen G (1997) Gene expression in methylotrophic yeasts. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:554–560
Hui JP, White TC, Thibault P (2002) Identification of glycan structure and glycosylation sites in cellobiohydrolase II and endoglucanases I and II from Trichoderma reesei. Glycobiology 12:837–849
Imperiali B, O’Connor SE (1999) Effect of N-linked glycosylation on glycopeptide and glycoprotein structure. Chem Biol 3:643–649
Jeoh T, Michener W, Himmel ME, Decker SR, Adney WS (2008) Implications of cellobiohydrolase glycosylation for use in biomass conversion. Biotechnol Biofuels 1:10
Klarskov K, Piens K, Ståhlberg J, Høj PB, Van Beeumen J, Claeyssens M (1997) Cellobiohydrolase I from Trichoderma reesei: identification of an active-site nucleophile and additional information on sequence including the glycosylation pattern of the core protein. Carbohydr Res 304:143–154
Maras M, Bruyn A, Schraml J, Herdewijn P, Claeyssens M, Fiers W, Contreras R (1997) Structural characterization of N-linked oligosaccharides from cellobiohydrolase I secreted by the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei RUTC 30. Eur J Biochem 245:617–625
Nummi M, Niku-Paavola M, Lappalainen A, Enari T, Raunio V (1983) Cellobiohydrolase from Trichoderma reesei. Biochem J 215:677–683
Palomares LA, Estrada-Moncada S, Ramírez OT (2004) Production of recombinant proteins. Recombinant gene expression. Springer, Berlin, pp 15–51
Qin Y, Wei X, Liu X, Wang T, Qu Y (2008) Purification and characterization of recombinant endoglucanase of Trichoderma reesei expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with higher glycosylation and stability. Protein Expr Purif 58:162–167
Weiner MP, Costa GL, Schoettlin W, Cline J, Mathur E, Bauer JC (1994) Site-directed mutagenesis of double-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 151:119–123
Wu G, Wei L, Liu W, Lin J, Wang L, Qu Y, Zhuang G (2010) Asn64-glycosylation affects Hypocrea jecorina (syn. Trichoderma reesei) cellobiohydrolase Cel7A activity expressed in Pichia pastoris. World J Microb Biotechnol 26:323–328
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the support of Research Council of Shahid Beheshti University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the manuscript content.
Supporting Information
Supplementary Table 1 Primers used in this study for colony PCR and site directed mutagenesis.
Supplementary Fig. 1 CBH I gene sequences from Trichoderma reesei synthesized according to the codon usage of Pichia pastoris.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranaei Siadat, S.O., Mollasalehi, H. & Heydarzadeh, N. Substrate affinity and catalytic efficiency are improved by decreasing glycosylation sites in Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase I expressed in Pichia pastoris . Biotechnol Lett 38, 483–488 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1997-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1997-8