Abstract
Objective
To examine the role of liposomes for the encapsulation of drugs and their suitability for chemotherapy of breast cancer.
Results
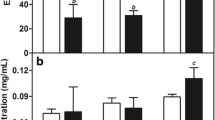
Pegylated liposomal trans-anethole nanoparticles were synthesized through a reverse-phase evaporation technique. Nanoparticles were characterized in terms of mean diameter, size distribution, zeta potential, encapsulation and drug loading efficiency, drug release pattern and cytotoxicity effects. Size and zeta potential of pegylated nanoliposomal drug and blank pegylated nanoliposomal were 257 nm and −28 mV; 35.7 nm and −21 mV, respectively. Encapsulation and drug loading efficiency were 78 ± 2.5 and 2.3 ± 4.1 %, respectively. There was a 57 % release of trans-anethole from pegylated liposomal nanoparticles in 48 h. Compared to free drug, toxicological studies indicated around 9- and 8-fold cytotoxicity effect against MCF-7 and T47D cell lines respectively.
Conclusions
PEG-liposomes provided a high stability and slow release of trans-anethole in two cancer cell lines.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen TM, Cullis PR (2013) Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:36–48
Bangham AD, Standish MM, Watkins JC (1965) Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J Mol Biol 13:238–252
Cho Y, Shi R, Borgens RB, Ivanisevic A (2008) Functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based drug delivery system to rescue acrolein-mediated cell death. Nanomedicine (Lond) 3:507–519
Choo EJ, Rhee YH, Jeong SJ, Lee HJ, Kim HS, Ko HS, Kim JH, Kwon TR, Jung JH, Kim JH, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Kim DK, Chen CY, Kim SH (2011) Anethole exerts antimetatstaic activity via inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase 2/9 and AKT/mitogen-activated kinase/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 34:41–46
Cooper DL, Harirforoosh S (2014) Design and optimization of PLGA-based diclofenac loaded nanoparticles. PLoS One 9:e87326
Drukarch B, Schepens E, Jongenelen CA, Stoof JC, Langeveld CH (1997) Astrocyte-mediated enhancement of neuronal survival is abolished by glutathione deficiency. Brain Res 770:123–130
Haley B, Frenkel E (2008) Nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer treatment. Urol Oncol 26:57–64
Kfoury M, Auezova L, Greige-Gerges H, Ruellan S, Fourmentin S (2014) Cyclodextrin, an efficient tool for trans-anethole encapsulation: chromatographic, spectroscopic, thermal and structural studies. Food Chem 164:454–461
Khazaei M, Montaseri A, Khazaei MR, Khanahmadi M (2011) Study of Foeniculum vulgare effect on folliculogenesis in female mice. Int J Fertil Steril 5:122–127
Malam Y, Loizidou M, Seifalian AM (2009) Liposomes and nanoparticles: nanosized vehicles for drug delivery in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:592–599
Nakase I, Lai H, Singh NP, Sasaki T (2008) Anticancer properties of artemisinin derivatives and their targeted delivery by transferrin conjugation. Int J Pharm 354:28–33
Otsuka H, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K (2012) PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:246–255
Park JW (2002) Liposome-based drug delivery in breast cancer treatment. Breast Cancer Res 4:95–99
Park JW, Hong K, Kirpotin DB, Colbern G, Shalaby R, Baselga J, Shao Y, Nielsen UB, Marks JD, Moore D, Papahadjopoulos D, Benz CC (2002) Anti-HER2 immunoliposomes: enhanced anticancer efficacy due to targeted delivery. Clin Cancer Res 8:1172–1181
Pasut G, Veronese FM (2009) PEG conjugates in clinical development or use as anticancer agents: an overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:1177–1188
Pierga JY, Girre V, Laurence V, Asselain B, Diéras V, Jouve M, Beuzeboc P, Fourquet A, Nos C, Sigal-Zafrani B, Pouillart P, Institut Curie Breast Cancer Study Group (2004) Characteristics and outcome of 1755 operable breast cancers in women over 70 years of age. Breast 13:369–375
Samad A, Sultana Y, Aqil M (2007) Liposomal drug delivery systems: an update review. Curr Drug Deliv 4:297–305
Sharma A, Sharma US (1997) Liposomes in drug delivery: progress and limitations. Intern J Pharmac 154:123–140
Wang X, Yang L, Chen ZG, Shin DM (2008) Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy and imaging. CA Cancer J Clin 58:97–110
Warner E (2011) Clinical practice. Breast-cancer screening. New Engl J Med 365:1025–1032
Yang C, Liu HZ, Fu ZX, Lu WD (2011) Oxaliplatin long-circulating liposomes improved therapeutic index of colorectal carcinoma. BMC Biotechnol 11:21
Yatuv R, Robinson M, Dayan-Tarshish I, Baru M (2010) The use of PEGylated liposomes in the development of drug delivery applications for the treatment of hemophilia. Int J Nanomed 5:581–591
Supporting information
Supplementary Fig. 1—SEM image of pegylated liposomal trans-anethole nanoparticles synthesized by the reverse-phase evaporation technique (×20,000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahbazian, S., Akbarzadeh, A., Torabi, S. et al. Anti-cancer activity of pegylated liposomal trans-anethole on breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and T47D. Biotechnol Lett 37, 1355–1359 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1813-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1813-5